| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If the same 1.00 J of ionizing energy were absorbed in her 2.00-kg forearm alone, then the dose to the forearm would be
and the unaffected tissue would have a zero rad dose. While calculating radiation doses, you divide the energy absorbed by the mass of affected tissue. You must specify the affected region, such as the whole body or forearm in addition to giving the numerical dose in rads. The SI unit for radiation dose is the gray (Gy) , which is defined to be
However, the rad is still commonly used. Although the energy per kilogram in 1 rad is small, it has significant effects since the energy causes ionization. The energy needed for a single ionization is a few eV, or less than . Thus, 0.01 J of ionizing energy can create a huge number of ion pairs and have an effect at the cellular level.
The effects of ionizing radiation may be directly proportional to the dose in rads, but they also depend on the type of radiation and the type of tissue. That is, for a given dose in rads, the effects depend on whether the radiation is x-ray, or some other type of ionizing radiation. In the earlier discussion of the range of ionizing radiation, it was noted that energy is deposited in a series of ionizations and not in a single interaction. Each ion pair or ionization requires a certain amount of energy, so that the number of ion pairs is directly proportional to the amount of the deposited ionizing energy. But, if the range of the radiation is small, as it is for s, then the ionization and the damage created is more concentrated and harder for the organism to repair, as seen in [link] . Concentrated damage is more difficult for biological organisms to repair than damage that is spread out, so short-range particles have greater biological effects. The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) or quality factor (QF) is given in [link] for several types of ionizing radiation—the effect of the radiation is directly proportional to the RBE. A dose unit more closely related to effects in biological tissue is called the roentgen equivalent man or rem and is defined to be the dose in rads multiplied by the relative biological effectiveness.
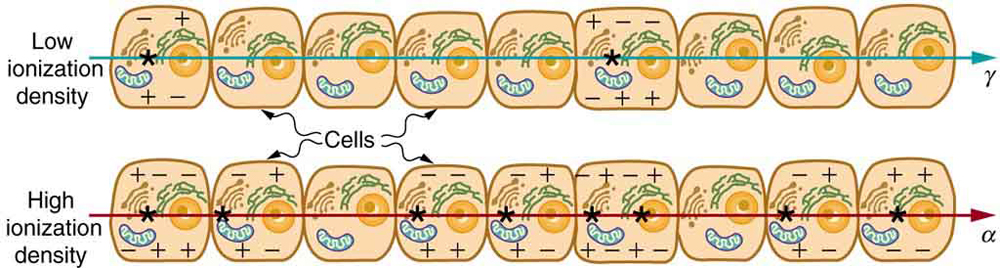
So, if a person had a whole-body dose of 2.00 rad of radiation, the dose in rem would be . If the person had a whole-body dose of 2.00 rad of radiation, then the dose in rem would be . The s would have 20 times the effect on the person than the s for the same deposited energy. The SI equivalent of the rem is the sievert (Sv), defined to be , so that

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Basic physics for medical imaging' conversation and receive update notifications?