| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A confidence interval for a population mean with a known standard deviation is based on the conclusion of the Central Limit Theorem that the sampling distribution of the sample means follow an approximately normal distribution.
Consider the standardizing formula for the sampling distribution developed in the discussion of the Central Limit Theorem:
Notice that µ is substituted for because we know that the expected value of is µ from the Central Limit theorem and is replaced with , also from the Central Limit Theorem.
In this formula we know , and n, the sample size. What we do not know is μ or Z 1 . We can solve for either one of these in terms of the other. Solving for μ in terms of Z 1 gives:
Remembering that the Central Limit Theorem tells us that the distribution of the 's, the sampling distribution for means, is normal, and that the normal distribution is symmetrical, we can rearrange terms thus:
This is the formula for a confidence interval for the mean of a population.
Notice that Z α has been substituted for Z 1 in this equation. This is where a choice must be made by the statistician. Z α is the number of standard deviations lies from the mean with a certain probability. If we chose Z α = 1.96 we are asking for the 95% confidence interval because we are setting the probability that the true mean lies within the range at 0.95. If we set Z α at 1.64 we are asking for the 90% confidence interval because we have set the probability at 0.90. These numbers can be verified by consulting the Standard Normal table. Divide either 0.95 or 0.90 in half and find that probability inside the body of the table. Then read on the top and left margins the number of standard deviations it takes to get this level of probability.
In reality, we can set whatever level of confidence we desire simply by changing the Z α value in the formula. It is the analyst's choice. Common convention in Economics and most social sciences sets confidence intervals at either 90, 95, or 99 percent levels. Levels less than 90% are considered of little value. The level of confidence of a particular interval estimate is called by (1-α).
A good way to see the development of a confidence interval is to graphically depict the solution to a problem requesting a confidence interval. This is presented in [link] for the example in the introduction concerning the number of downloads from iTunes. That case was for a 95% confidence interval, but other levels of confidence could have just as easily been chosen depending on the need of the analyst. However, the level of confidence MUST be pre-set and not subject to revision as a result of the calculations.
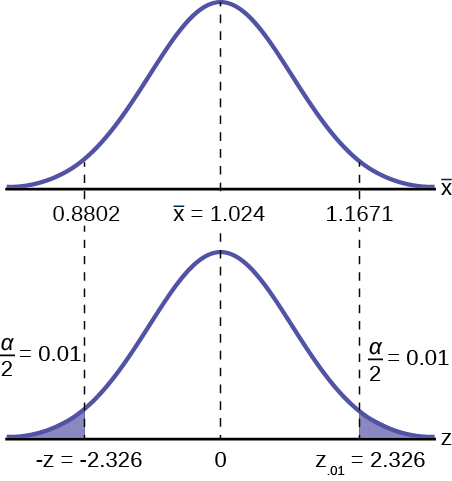
For this example, let's say we know that the actual population mean number of iTunes downloads is 2.1. The true population mean falls within the range of the 95% confidence interval. There is absolutely nothing to guarantee that this will happen. Further, if the true mean falls outside of the interval we will never know it. We must always remember that we will never ever know the true mean. Statistics simply allows us, with a given level of probability (confidence), to say that the true mean is within the range calculated. This is what was called in the introduction, the "level of ignorance admitted".

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory statistics' conversation and receive update notifications?