| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
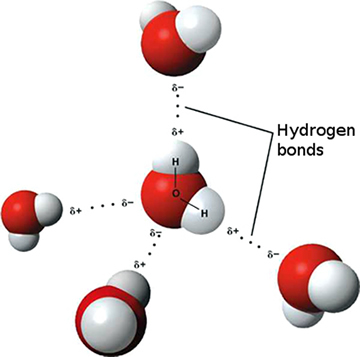
Compared to other molecules of similar molecular weight, water (H 2 O) has unique physical properties including high values for melting and boiling point, surface tension (water’s cohesion, or “stickiness”), and capacity to dissolve soluble minerals, i.e., act as a solvent . These properties are related to its asymmetrical structure and polar nature , which means it is electrically neutral overall but it has a net positive charge on the side with the two hydrogen atoms and a net negative charge on the oxygen side (see Figure Structure of Water, Polar Charge of Water, and Hydrogen Bonds between Water Molecules ). This separation of the electrical charge within a water molecule results in hydrogen bonds with other water molecules, mineral surfaces (hydrogen bonding produces the water films on minerals in the unsaturated zone of the subsurface), and dissolved ions (atoms with a negative or positive charge). Many minerals and pollutants dissolve readily in water because water forms hydration shells (spheres of loosely coordinated, oriented water molecules) around ions.
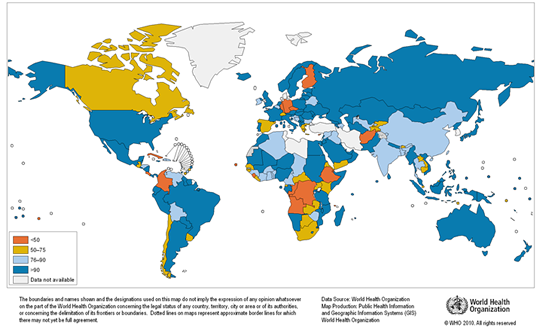
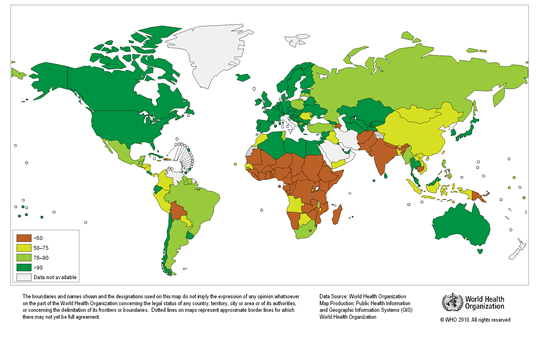
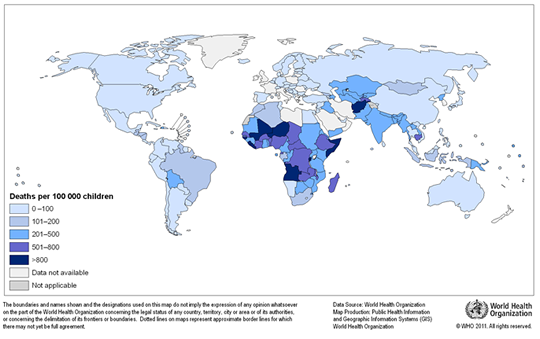
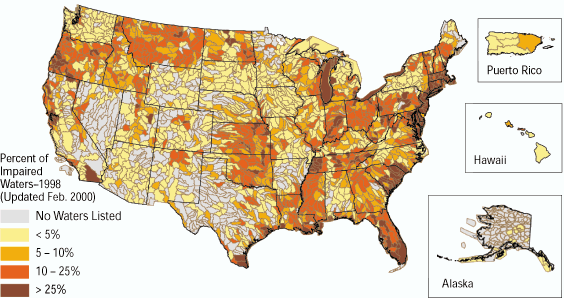
Any natural water contains dissolved chemicals; some of these are important human nutrients, while others can be harmful to human health. The abundance of a water pollutant is commonly given in very small concentration units such as parts per million (ppm) or even parts per billion (ppb). An arsenic concentration of 1 ppm means 1 part of arsenic per million parts of water. This is equivalent to one drop of arsenic in 50 liters of water. To give you a different perspective on appreciating small concentration units, converting 1 ppm to length units is 1 cm (0.4 in) in 10 km (6 miles) and converting 1 ppm to time units is 30 seconds in a year. Total dissolved solids (TDS) represent the total amount of dissolved material in water. Average TDS (salinity) values for rainwater, river water, and seawater are about 4 ppm, 120 ppm, and 35,000 ppm. As discussed in Module Climate Processes; External and Internal Controls , the most important processes that affect the salinity of natural waters are evaporation, which distills nearly pure water and leaves the dissolved ions in the original water, and chemical weathering, which involves mineral dissolution that adds dissolved ions to water. Fresh water is commonly defined as containing less than either 1,000 or 500 ppm TDS, but the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends that drinking water not exceed 500 ppm TDS or else it will have an unpleasant salty taste.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?