| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A photon is a quantum of EM radiation. Its energy is given by and is related to the frequency and wavelength of the radiation by
where is the energy of a single photon and is the speed of light. When working with small systems, energy in eV is often useful. Note that Planck’s constant in these units is
Since many wavelengths are stated in nanometers (nm), it is also useful to know that
These will make many calculations a little easier.
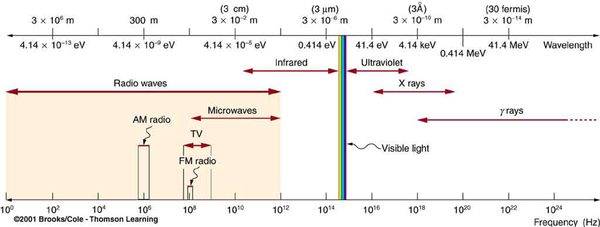
All EM radiation is composed of photons. [link] shows various divisions of the EM spectrum plotted against wavelength, frequency, and photon energy. Previously in this book, photon characteristics were alluded to in the discussion of some of the characteristics of UV, x rays, and rays, the first of which start with frequencies just above violet in the visible spectrum. It was noted that these types of EM radiation have characteristics much different than visible light. We can now see that such properties arise because photon energy is larger at high frequencies.
| Rotational energies of molecules | eV |
| Vibrational energies of molecules | 0.1 eV |
| Energy between outer electron shells in atoms | 1 eV |
| Binding energy of a weakly bound molecule | 1 eV |
| Energy of red light | 2 eV |
| Binding energy of a tightly bound molecule | 10 eV |
| Energy to ionize atom or molecule | 10 to 1000 eV |
Photons act as individual quanta and interact with individual electrons, atoms, molecules, and so on. The energy a photon carries is, thus, crucial to the effects it has. [link] lists representative submicroscopic energies in eV. When we compare photon energies from the EM spectrum in [link] with energies in the table, we can see how effects vary with the type of EM radiation.
Gamma rays , a form of nuclear and cosmic EM radiation, can have the highest frequencies and, hence, the highest photon energies in the EM spectrum. For example, a -ray photon with has an energy This is sufficient energy to ionize thousands of atoms and molecules, since only 10 to 1000 eV are needed per ionization. In fact, rays are one type of ionizing radiation , as are x rays and UV, because they produce ionization in materials that absorb them. Because so much ionization can be produced, a single -ray photon can cause significant damage to biological tissue, killing cells or damaging their ability to properly reproduce. When cell reproduction is disrupted, the result can be cancer, one of the known effects of exposure to ionizing radiation. Since cancer cells are rapidly reproducing, they are exceptionally sensitive to the disruption produced by ionizing radiation. This means that ionizing radiation has positive uses in cancer treatment as well as risks in producing cancer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Basic physics for medical imaging' conversation and receive update notifications?