| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[T] Find the probability that a fair coin is flipped a multiple of three times before coming up heads.
[T] Find the probability that a fair coin will come up heads for the second time after an even number of flips.
[T] Find a series that expresses the probability that a fair coin will come up heads for the second time on a multiple of three flips.
[T] The expected number of times that a fair coin will come up heads is defined as the sum over of times the probability that the coin will come up heads exactly times in a row, or Compute the expected number of consecutive times that a fair coin will come up heads.
as can be shown using summation by parts
[T] A person deposits at the beginning of each quarter into a bank account that earns annual interest compounded quarterly (four times a year).
[T] Suppose that the amount of a drug in a patient’s system diminishes by a multiplicative factor each hour. Suppose that a new dose is administered every hours. Find an expression that gives the amount in the patient’s system after hours for each in terms of the dosage and the ratio ( Hint: Write where and sum over values from the different doses administered.)
The part of the first dose after hours is the part of the second dose is and, in general, the part remaining of the dose is so
[T] A certain drug is effective for an average patient only if there is at least mg per kg in the patient’s system, while it is safe only if there is at most mg per kg in an average patient’s system. Suppose that the amount in a patient’s system diminishes by a multiplicative factor of each hour after a dose is administered. Find the maximum interval of hours between doses, and corresponding dose range (in mg/kg) for this that will enable use of the drug to be both safe and effective in the long term.
Suppose that is a sequence of numbers. Explain why the sequence of partial sums of is increasing.
[T] Suppose that is a sequence of positive numbers and the sequence of partial sums of is bounded above. Explain why converges. Does the conclusion remain true if we remove the hypothesis
[T] Suppose that and that, for given numbers and one defines and Does converge? If so, to what? ( Hint: First argue that for all and is increasing.)
Since and since If for some n , then there is a smallest n . For this n , so a contradiction. Thus and for all n , so is increasing and bounded by Let If then but we can find n such that which implies that contradicting that is increasing to Thus
[T] A version of von Bertalanffy growth can be used to estimate the age of an individual in a homogeneous species from its length if the annual increase in year satisfies with as the length at year as a limiting length, and as a relative growth constant. If and numerically estimate the smallest value of such that Note that Find the corresponding when
[T] Suppose that is a convergent series of positive terms. Explain why
Let and Then eventually becomes arbitrarily close to which means that becomes arbitrarily small as
[T] Find the length of the dashed zig-zag path in the following figure.
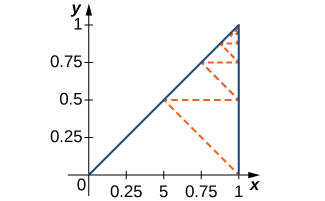
[T] Find the total length of the dashed path in the following figure.
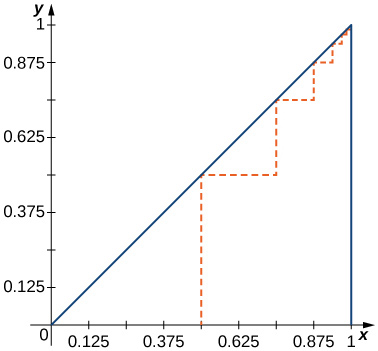
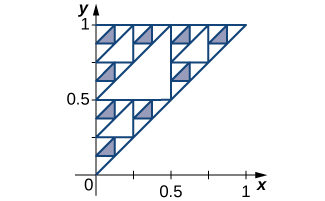
[T] The
Sierpinski triangle is obtained from a triangle by deleting the middle fourth as indicated in the first step, by deleting the middle fourths of the remaining three congruent triangles in the second step, and in general deleting the middle fourths of the remaining triangles in each successive step. Assuming that the original triangle is shown in the figure, find the areas of the remaining parts of the original triangle after
steps and find the total length of all of the boundary triangles after
steps.
[T] The Sierpinski gasket is obtained by dividing the unit square into nine equal sub-squares, removing the middle square, then doing the same at each stage to the remaining sub-squares. The figure shows the remaining set after four iterations. Compute the total area removed after stages, and compute the length the total perimeter of the remaining set after stages.
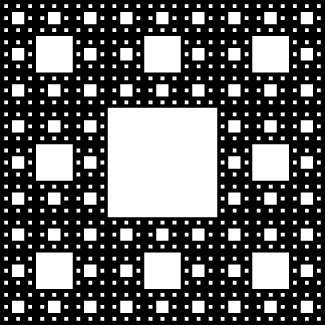
At stage one a square of area is removed, at stage one removes squares of area at stage three one removes squares of area and so on. The total removed area after stages is
as The total perimeter is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?