| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
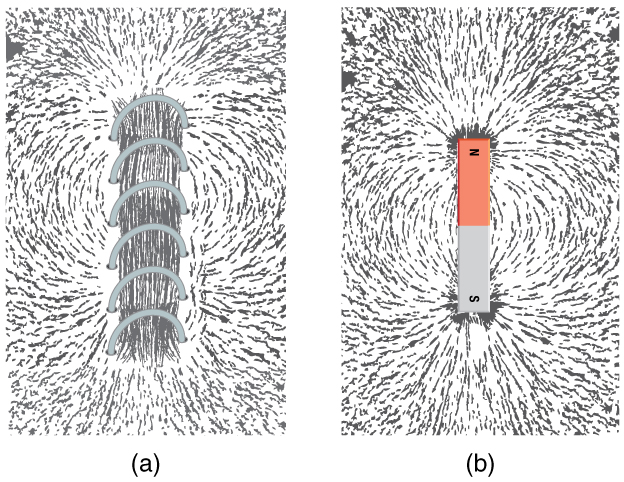
[link] shows that the response of iron filings to a current-carrying coil and to a permanent bar magnet. The patterns are similar. In fact, electromagnets and ferromagnets have the same basic characteristics—for example, they have north and south poles that cannot be separated and for which like poles repel and unlike poles attract.
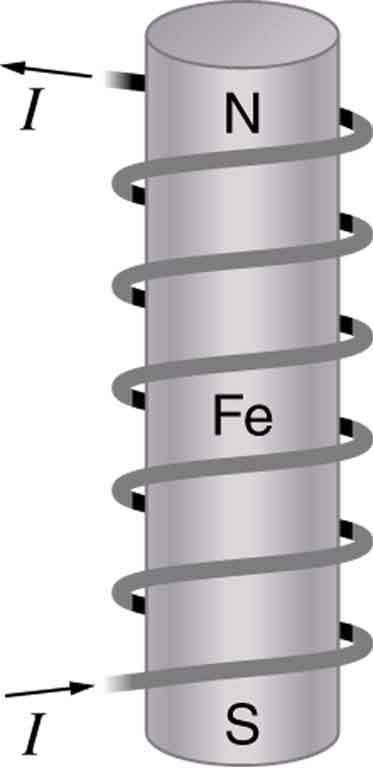
Combining a ferromagnet with an electromagnet can produce particularly strong magnetic effects. (See [link] .) Whenever strong magnetic effects are needed, such as lifting scrap metal, or in particle accelerators, electromagnets are enhanced by ferromagnetic materials. Limits to how strong the magnets can be made are imposed by coil resistance (it will overheat and melt at sufficiently high current), and so superconducting magnets may be employed. These are still limited, because superconducting properties are destroyed by too great a magnetic field.
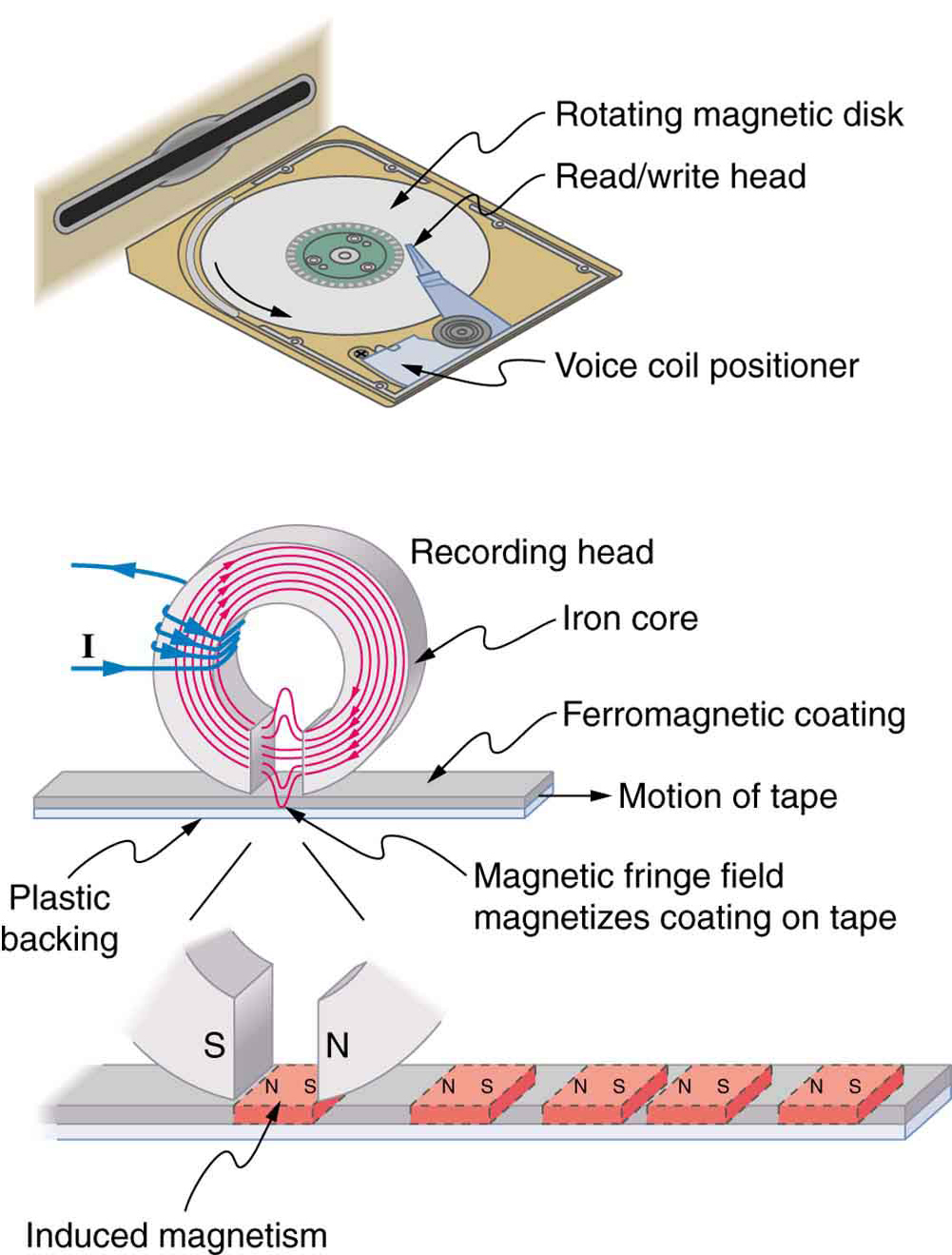
[link] shows a few uses of combinations of electromagnets and ferromagnets. Ferromagnetic materials can act as memory devices, because the orientation of the magnetic fields of small domains can be reversed or erased. Magnetic information storage on videotapes and computer hard drives are among the most common applications. This property is vital in our digital world.
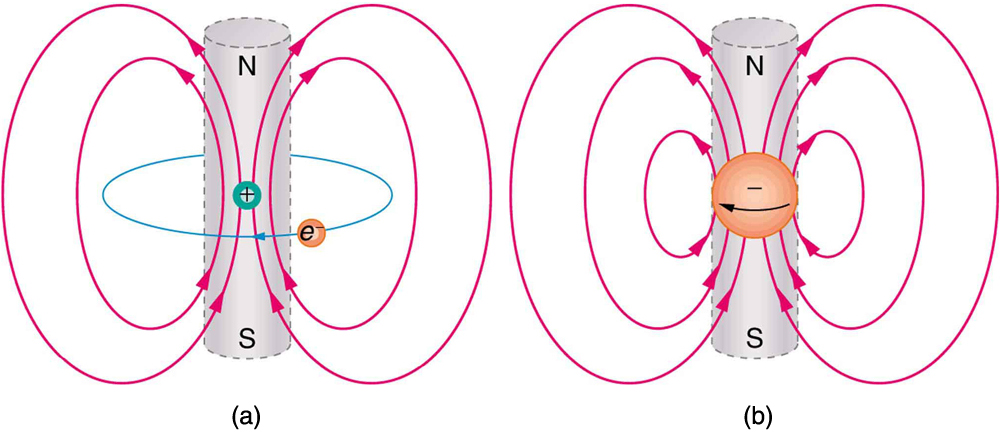
An electromagnet creates magnetism with an electric current. In later sections we explore this more quantitatively, finding the strength and direction of magnetic fields created by various currents. But what about ferromagnets? [link] shows models of how electric currents create magnetism at the submicroscopic level. (Note that we cannot directly observe the paths of individual electrons about atoms, and so a model or visual image, consistent with all direct observations, is made. We can directly observe the electron’s orbital angular momentum, its spin momentum, and subsequent magnetic moments, all of which are explained with electric-current-creating subatomic magnetism.) Currents, including those associated with other submicroscopic particles like protons, allow us to explain ferromagnetism and all other magnetic effects. Ferromagnetism, for example, results from an internal cooperative alignment of electron spins, possible in some materials but not in others.
Crucial to the statement that electric current is the source of all magnetism is the fact that it is impossible to separate north and south magnetic poles. (This is far different from the case of positive and negative charges, which are easily separated.) A current loop always produces a magnetic dipole—that is, a magnetic field that acts like a north pole and south pole pair. Since isolated north and south magnetic poles, called magnetic monopoles , are not observed, currents are used to explain all magnetic effects. If magnetic monopoles did exist, then we would have to modify this underlying connection that all magnetism is due to electrical current. There is no known reason that magnetic monopoles should not exist—they are simply never observed—and so searches at the subnuclear level continue. If they do not exist, we would like to find out why not. If they do exist, we would like to see evidence of them.
Electric current is the source of all magnetism.
Explore the interactions between a compass and bar magnet. Discover how you can use a battery and wire to make a magnet! Can you make it a stronger magnet? Can you make the magnetic field reverse?


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?