| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Functions of the form are known as exponential functions. The general shape of a graph of a function of this form is shown in [link] .
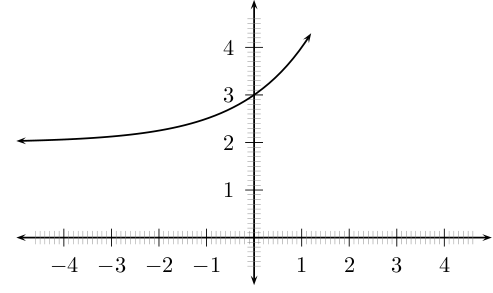
You should have found that the value of affects whether the graph curves upwards ( ) or curves downwards ( ).
You should have also found that the value of affects the position of the -intercept.
These different properties are summarised in [link] .
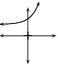 |
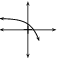 | |
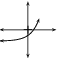 |
 |
For , the function is defined for all real values of . Therefore, the domain is .
The range of is dependent on the sign of .
If then:
Therefore, if , then the range is .
If then:
Therefore, if , then the range is .
For example, the domain of is . For the range,
Therefore the range is .
For functions of the form, , the intercepts with the and axis is calculated by setting for the -intercept and by setting for the -intercept.
The -intercept is calculated as follows:
For example, the -intercept of is given by setting to get:
The -intercepts are calculated by setting as follows:
Which only has a real solution if either or . Otherwise, the graph of the function of form does not have any -intercepts.
For example, the -intercept of is given by setting to get:
which has no real solution. Therefore, the graph of does not have any -intercepts.
There is one asymptote for functions of the form . The asymptote can be determined by examining the range.
We saw that the function was undefined at . Therefore the asymptote is .
For example, the domain of is because is defined for all . We also see that is undefined at . Therefore the range is .
From this we deduce that the asymptote is at .
In order to sketch graphs of functions of the form, , we need to calculate determine four characteristics:
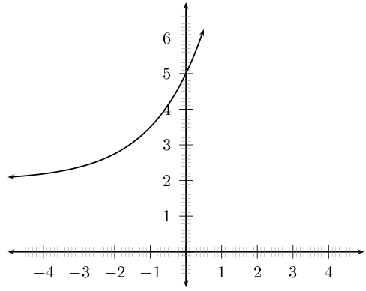
For example, sketch the graph of . Mark the intercepts.
We have determined the domain to be and the range to be .
The -intercept is and there are no -intercepts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 maths [ncs]' conversation and receive update notifications?