| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like the upper limb, the lower limb is divided into three regions. The thigh is that portion of the lower limb located between the hip joint and knee joint. The leg is specifically the region between the knee joint and the ankle joint. Distal to the ankle is the foot . The lower limb contains 30 bones. These are the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges (see [link] ). The femur is the single bone of the thigh. The patella is the kneecap and articulates with the distal femur. The tibia is the larger, weight-bearing bone located on the medial side of the leg, and the fibula is the thin bone of the lateral leg. The bones of the foot are divided into three groups. The posterior portion of the foot is formed by a group of seven bones, each of which is known as a tarsal bone , whereas the mid-foot contains five elongated bones, each of which is a metatarsal bone . The toes contain 14 small bones, each of which is a phalanx bone of the foot .
The femur, or thigh bone, is the single bone of the thigh region ( [link] ). It is the longest and strongest bone of the body, and accounts for approximately one-quarter of a person’s total height. The rounded, proximal end is the head of the femur , which articulates with the acetabulum of the hip bone to form the hip joint . The fovea capitis is a minor indentation on the medial side of the femoral head that serves as the site of attachment for the ligament of the head of the femur . This ligament spans the femur and acetabulum, but is weak and provides little support for the hip joint. It does, however, carry an important artery that supplies the head of the femur.
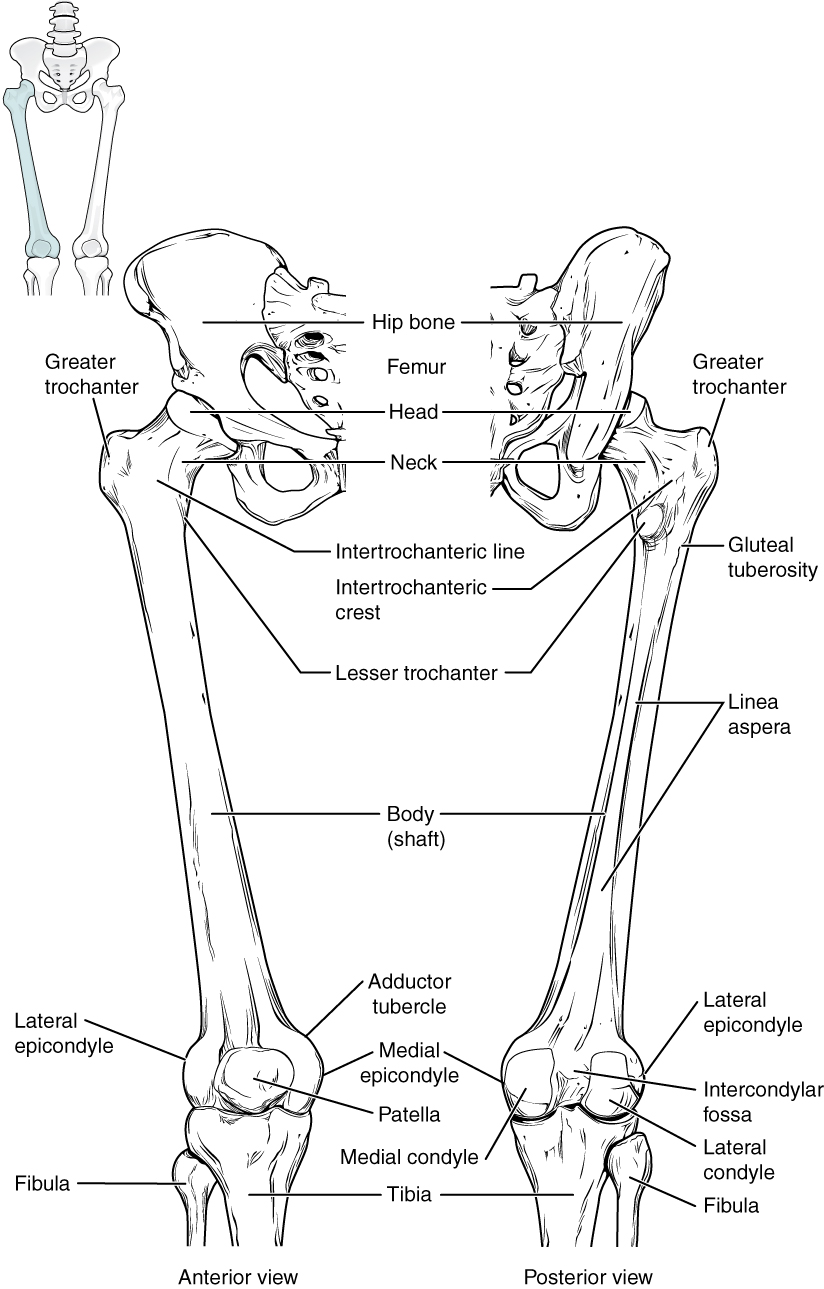
The narrowed region below the head is the neck of the femur . This is a common area for fractures of the femur. The greater trochanter is the large, upward, bony projection located above the base of the neck. Multiple muscles that act across the hip joint attach to the greater trochanter, which, because of its projection from the femur, gives additional leverage to these muscles. The greater trochanter can be felt just under the skin on the lateral side of your upper thigh. The lesser trochanter is a small, bony prominence that lies on the medial aspect of the femur, just below the neck. A single, powerful muscle attaches to the lesser trochanter. Running between the greater and lesser trochanters on the anterior side of the femur is the roughened intertrochanteric line . The trochanters are also connected on the posterior side of the femur by the larger intertrochanteric crest .
The elongated shaft of the femur has a slight anterior bowing or curvature. At its proximal end, the posterior shaft has the gluteal tuberosity , a roughened area extending inferiorly from the greater trochanter. More inferiorly, the gluteal tuberosity becomes continuous with the linea aspera (“rough line”). This is the roughened ridge that passes distally along the posterior side of the mid-femur. Multiple muscles of the hip and thigh regions make long, thin attachments to the femur along the linea aspera.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?