| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Gases exert pressure, which is force per unit area. The pressure of a gas may be expressed in the SI unit of pascal or kilopascal, as well as in many other units including torr, atmosphere, and bar. Atmospheric pressure is measured using a barometer; other gas pressures can be measured using one of several types of manometers.
Why are sharp knives more effective than dull knives (Hint: think about the definition of pressure)?
The cutting edge of a knife that has been sharpened has a smaller surface area than a dull knife. Since pressure is force per unit area, a sharp knife will exert a higher pressure with the same amount of force and cut through material more effectively.
Why do some small bridges have weight limits that depend on how many wheels or axles the crossing vehicle has?
Why should you roll or belly-crawl rather than walk across a thinly-frozen pond?
Lying down distributes your weight over a larger surface area, exerting less pressure on the ice compared to standing up. If you exert less pressure, you are less likely to break through thin ice.
A typical barometric pressure in Redding, California, is about 750 mm Hg. Calculate this pressure in atm and kPa.
A typical barometric pressure in Denver, Colorado, is 615 mm Hg. What is this pressure in atmospheres and kilopascals?
0.809 atm; 82.0 kPa
A typical barometric pressure in Kansas City is 740 torr. What is this pressure in atmospheres, in millimeters of mercury, and in kilopascals?
Canadian tire pressure gauges are marked in units of kilopascals. What reading on such a gauge corresponds to 32 psi?
2.2 10 2 kPa
During the Viking landings on Mars, the atmospheric pressure was determined to be on the average about 6.50 millibars (1 bar = 0.987 atm). What is that pressure in torr and kPa?
The pressure of the atmosphere on the surface of the planet Venus is about 88.8 atm. Compare that pressure in psi to the normal pressure on earth at sea level in psi.
Earth: 14.7 lb in –2 ; Venus: 13.1 10 3 lb in −2
A medical laboratory catalog describes the pressure in a cylinder of a gas as 14.82 MPa. What is the pressure of this gas in atmospheres and torr?
Consider this scenario and answer the following questions: On a mid-August day in the northeastern United States, the following information appeared in the local newspaper: atmospheric pressure at sea level 29.97 in., 1013.9 mbar.
(a) What was the pressure in kPa?
(b) The pressure near the seacoast in the northeastern United States is usually reported near 30.0 in. Hg. During a hurricane, the pressure may fall to near 28.0 in. Hg. Calculate the drop in pressure in torr.
(a) 101.5 kPa; (b) 51 torr drop
Why is it necessary to use a nonvolatile liquid in a barometer or manometer?
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured at sea level with a closed-end manometer. The liquid in the manometer is mercury. Determine the pressure of the gas in:
(a) torr
(b) Pa
(c) bar
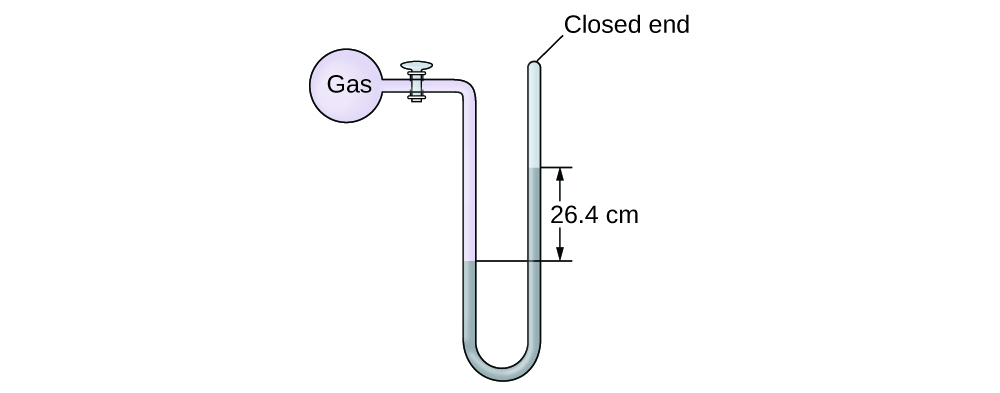
(a) 264 torr; (b) 35,200 Pa; (c) 0.352 bar
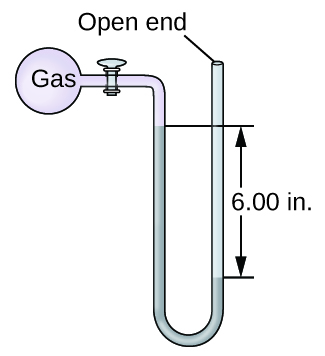
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured with an open-end manometer, partially shown to the right. The liquid in the manometer is mercury. Assuming atmospheric pressure is 29.92 in. Hg, determine the pressure of the gas in:
(a) torr
(b) Pa
(c) bar
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured at sea level with an open-end mercury manometer. Assuming atmospheric pressure is 760.0 mm Hg, determine the pressure of the gas in:
(a) mm Hg
(b) atm
(c) kPa
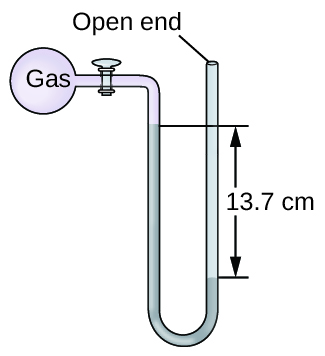
(a) 623 mm Hg; (b) 0.820 atm; (c) 83.1 kPa
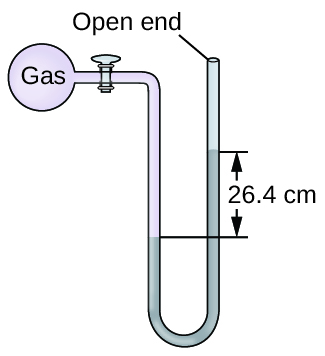
The pressure of a sample of gas is measured at sea level with an open-end mercury manometer. Assuming atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg, determine the pressure of the gas in:
(a) mm Hg
(b) atm
(c) kPa
How would the use of a volatile liquid affect the measurement of a gas using open-ended manometers vs. closed-end manometers?
With a closed-end manometer, no change would be observed, since the vaporized liquid would contribute equal, opposing pressures in both arms of the manometer tube. However, with an open-ended manometer, a higher pressure reading of the gas would be obtained than expected, since P gas = P atm + P vol liquid .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?