| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
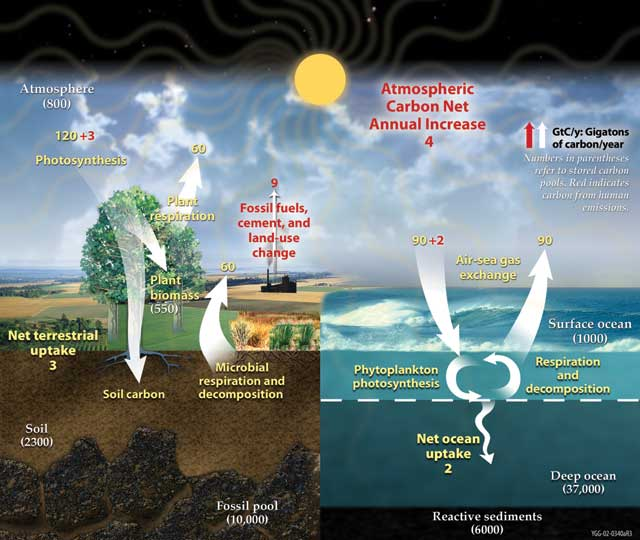
The global carbon cycle contributes substantially to the provisioning ecosystem services upon which humans depend. We harvest approximately 25% of the total plant biomass that is produced each year on the land surface to supply food, fuel wood and fiber from croplands, pastures and forests. In addition, the global carbon cycle plays a key role in regulating ecosystem services because it significantly influences climate via its effects on atmospheric CO 2 concentrations. Atmospheric CO 2 concentration increased from 280 parts per million (ppm) to 390 ppm between the start of industrial revolution in the late eighteenth century and 2010. This reflected a new flux in the global carbon cycle — anthropogenic CO2 emissions — where humans release CO 2 into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels and changing land use. Fossil fuel burning takes carbon from coal, gas, and oil reserves, where it would be otherwise stored on very long time scales, and introduces it into the active carbon cycle. Land use change releases carbon from soil and plant biomass pools into the atmosphere, particularly through the process of deforestation for wood extraction or conversion of land to agriculture. In 2009, the additional flux of carbon into the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources was estimated to be 9 GtC—a significant disturbance to the natural carbon cycle that had been in balance for several thousand years previously. Slightly more than half of this anthropogenic CO 2 is currently being absorbed by greater photosynthesis by plants on land and at sea (5 GtC). However, that means 4 GtC is being added to the atmospheric pool each year and, while total emissions are increasing, the proportion absorbed by photosynthesis and stored on land and in the oceans is declining ( Le Quere et al., 2009 ). Rising atmospheric CO 2 concentrations in the twentieth century caused increases in temperature and started to alter other aspects of the global environment. Global environmental change has already caused a measurable decrease in the global harvest of certain crops. The scale and range of impacts from global environmental change of natural and agricultural ecosystems is projected to increase over the twenty-first century, and will pose a major challenge to human well-being.
The vast majority of water on Earth is saline (salty) and stored in the oceans. Meanwhile, most of the world's fresh water is in the form of ice, snow, and groundwater. This means a significant fraction of the water pool is largely isolated from the water cycle. The major long-term stores of fresh water include ice sheets in Antarctica and Greenland, as well as groundwater pools that were filled during wetter periods of past geological history. In contrast, the water stored in rivers, lakes, and ocean surface is relatively rapidly cycled as it evaporates into the atmosphere and then falls back to the surface as precipitation. The atmospheric pool of water turns over most rapidly because it is small compared to the other pools (e.g.<15% of the freshwater lake pool). Evaporation is the process whereby water is converted from a liquid into a vapor as a result of absorbing energy (usually from solar radiation). Evaporation from vegetated land is referred to as evapotranspiration because it includes water transpired by plants, i.e. water taken up from the soil by roots, transported to leaves and evaporated from leaf surfaces into the atmosphere via stomatal pores. Precipitation is the conversion of atmospheric water from vapor into liquid (rain) or solid forms (snow, hail) that then fall to Earth's surface. Some water from precipitation moves over the land surface by surface runoff and streamflow , while other water from precipitation infiltrates the soil and moves below the surface as groundwater discharge . Water vapor in the atmosphere is commonly moved away from the source of evaporation by wind and the movement of air masses. Consequently, most water falling as precipitation comes from a source of evaporation that is located upwind. Nonetheless, local sources of evaporation can contribute as much as 25-33% of water in precipitation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?