| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Solving this for the Hall emf yields
where is the Hall effect voltage across a conductor of width through which charges move at a speed .
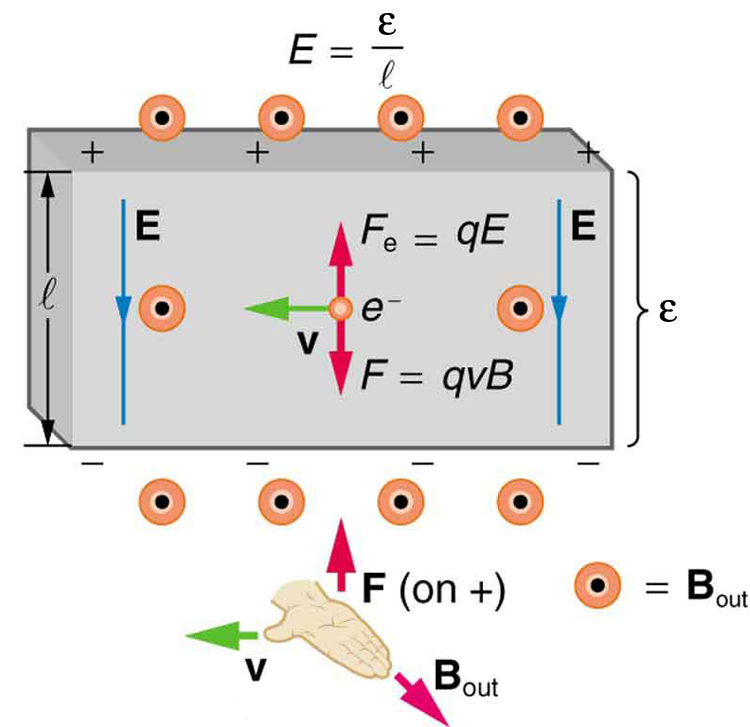
One of the most common uses of the Hall effect is in the measurement of magnetic field strength . Such devices, called Hall probes , can be made very small, allowing fine position mapping. Hall probes can also be made very accurate, usually accomplished by careful calibration. Another application of the Hall effect is to measure fluid flow in any fluid that has free charges (most do). (See [link] .) A magnetic field applied perpendicular to the flow direction produces a Hall emf as shown. Note that the sign of depends not on the sign of the charges, but only on the directions of and . The magnitude of the Hall emf is , where is the pipe diameter, so that the average velocity can be determined from providing the other factors are known.
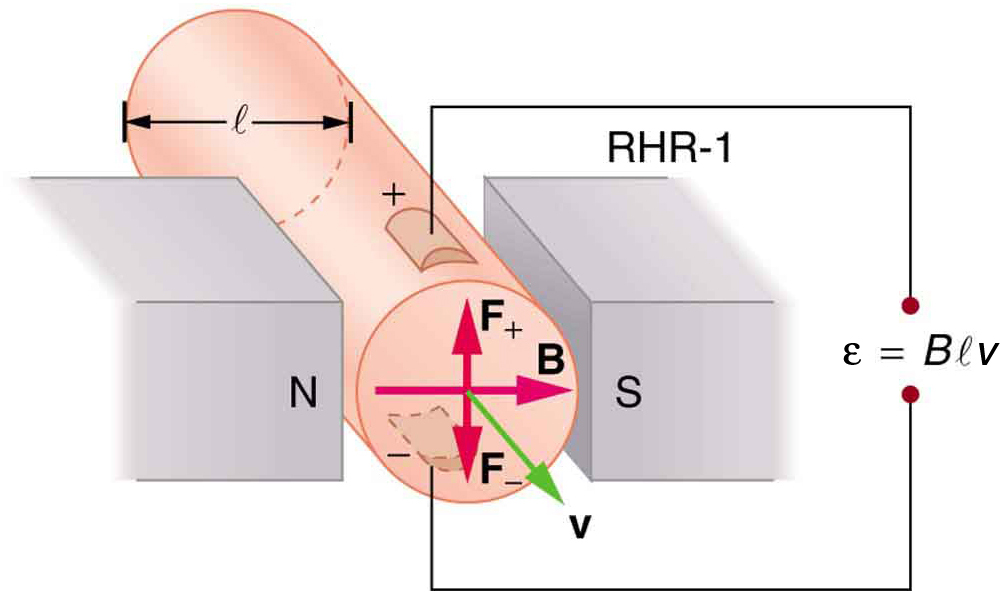
A Hall effect flow probe is placed on an artery, applying a 0.100-T magnetic field across it, in a setup similar to that in [link] . What is the Hall emf, given the vessel’s inside diameter is 4.00 mm and the average blood velocity is 20.0 cm/s?
Strategy
Because , , and are mutually perpendicular, the equation can be used to find .
Solution
Entering the given values for , , and gives
Discussion
This is the average voltage output. Instantaneous voltage varies with pulsating blood flow. The voltage is small in this type of measurement. is particularly difficult to measure, because there are voltages associated with heart action (ECG voltages) that are on the order of millivolts. In practice, this difficulty is overcome by applying an AC magnetic field, so that the Hall emf is AC with the same frequency. An amplifier can be very selective in picking out only the appropriate frequency, eliminating signals and noise at other frequencies.
Discuss how the Hall effect could be used to obtain information on free charge density in a conductor. (Hint: Consider how drift velocity and current are related.)
A large water main is 2.50 m in diameter and the average water velocity is 6.00 m/s. Find the Hall voltage produced if the pipe runs perpendicular to the Earth’s field.
What Hall voltage is produced by a 0.200-T field applied across a 2.60-cm-diameter aorta when blood velocity is 60.0 cm/s?
(a) What is the speed of a supersonic aircraft with a 17.0-m wingspan, if it experiences a 1.60-V Hall voltage between its wing tips when in level flight over the north magnetic pole, where the Earth’s field strength is (b) Explain why very little current flows as a result of this Hall voltage.
(a) 1.18 × 10 3 m/s
(b) Once established, the Hall emf pushes charges one direction and the magnetic force acts in the opposite direction resulting in no net force on the charges. Therefore, no current flows in the direction of the Hall emf. This is the same as in a current-carrying conductor—current does not flow in the direction of the Hall emf.
A nonmechanical water meter could utilize the Hall effect by applying a magnetic field across a metal pipe and measuring the Hall voltage produced. What is the average fluid velocity in a 3.00-cm-diameter pipe, if a 0.500-T field across it creates a 60.0-mV Hall voltage?
Calculate the Hall voltage induced on a patient’s heart while being scanned by an MRI unit. Approximate the conducting path on the heart wall by a wire 7.50 cm long that moves at 10.0 cm/s perpendicular to a 1.50-T magnetic field.
11.3 mV
A Hall probe calibrated to read when placed in a 2.00-T field is placed in a 0.150-T field. What is its output voltage?
Using information in [link] , what would the Hall voltage be if a 2.00-T field is applied across a 10-gauge copper wire (2.588 mm in diameter) carrying a 20.0-A current?
Show that the Hall voltage across wires made of the same material, carrying identical currents, and subjected to the same magnetic field is inversely proportional to their diameters. (Hint: Consider how drift velocity depends on wire diameter.)
A patient with a pacemaker is mistakenly being scanned for an MRI image. A 10.0-cm-long section of pacemaker wire moves at a speed of 10.0 cm/s perpendicular to the MRI unit’s magnetic field and a 20.0-mV Hall voltage is induced. What is the magnetic field strength?
2.00 T

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Basic physics for medical imaging' conversation and receive update notifications?