| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
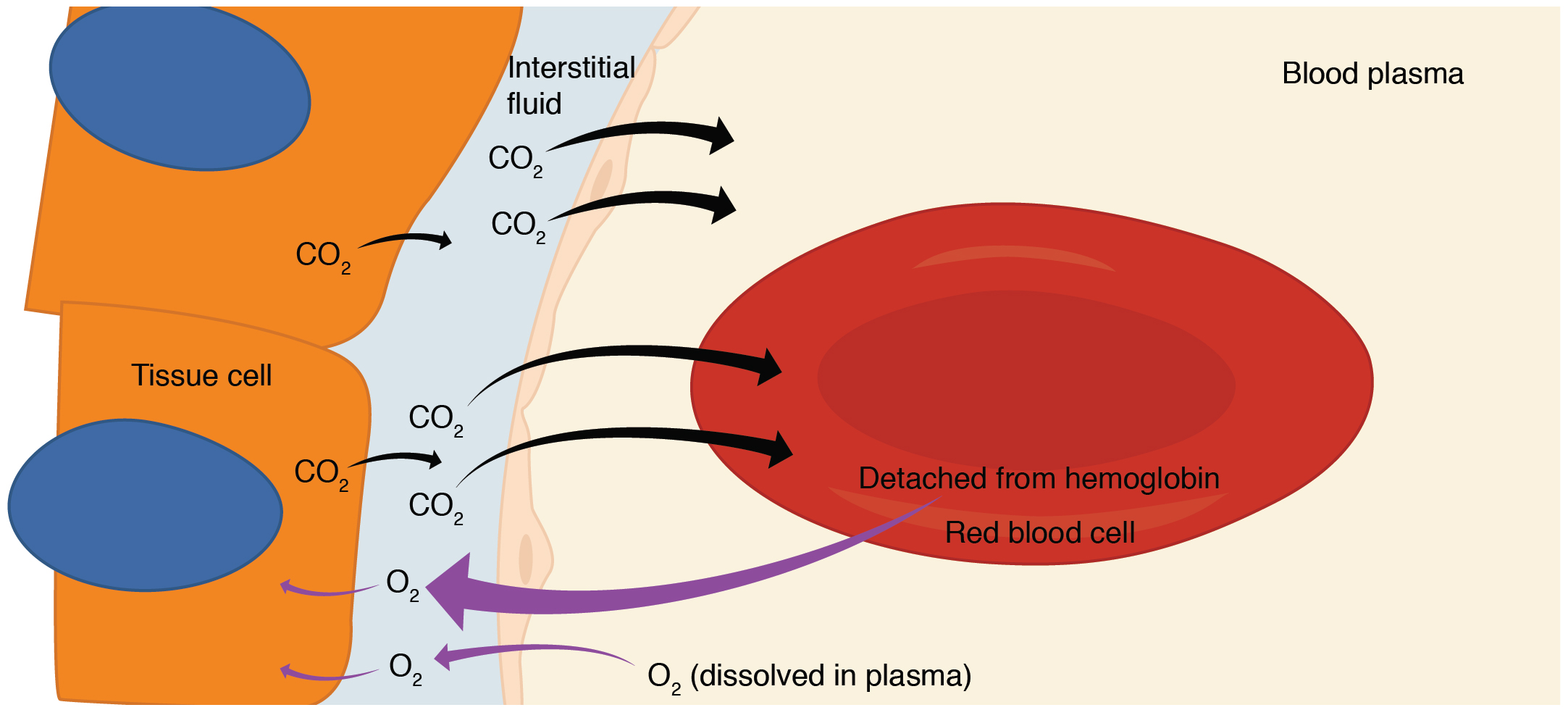
Internal respiration is gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues ( [link] ). Similar to external respiration, internal respiration also occurs as simple diffusion due to a partial pressure gradient. However, the partial pressure gradients are opposite of those present at the respiratory membrane. The partial pressure of oxygen in tissues is low, about 40 mm Hg, because oxygen is continuously used for cellular respiration. In contrast, the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood is about 100 mm Hg. This creates a pressure gradient that causes oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin, diffuse out of the blood, cross the interstitial space, and enter the tissue. Hemoglobin that has little oxygen bound to it loses much of its brightness, so that blood returning to the heart is more burgundy in color.
Considering that cellular respiration continuously produces carbon dioxide, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is lower in the blood than it is in the tissue, causing carbon dioxide to diffuse out of the tissue, cross the interstitial fluid, and enter the blood. It is then carried back to the lungs either bound to hemoglobin, dissolved in plasma, or in a converted form. By the time blood returns to the heart, the partial pressure of oxygen has returned to about 40 mm Hg, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide has returned to about 45 mm Hg. The blood is then pumped back to the lungs to be oxygenated once again during external respiration.
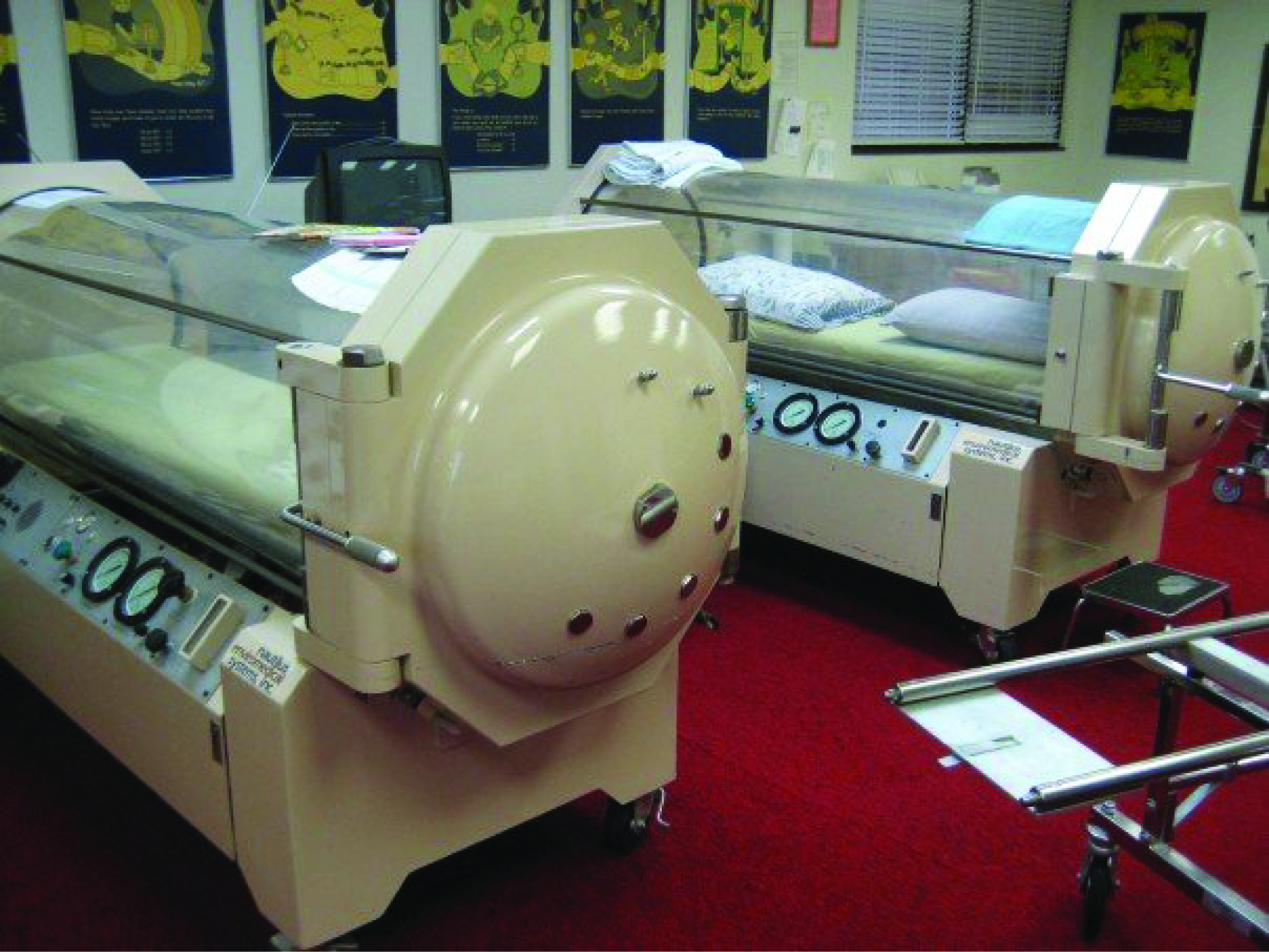

Hyperbaric chamber treatment is based on the behavior of gases. As you recall, gases move from a region of higher partial pressure to a region of lower partial pressure. In a hyperbaric chamber, the atmospheric pressure is increased, causing a greater amount of oxygen than normal to diffuse into the bloodstream of the patient. Hyperbaric chamber therapy is used to treat a variety of medical problems, such as wound and graft healing, anaerobic bacterial infections, and carbon monoxide poisoning. Exposure to and poisoning by carbon monoxide is difficult to reverse, because hemoglobin’s affinity for carbon monoxide is much stronger than its affinity for oxygen, causing carbon monoxide to replace oxygen in the blood. Hyperbaric chamber therapy can treat carbon monoxide poisoning, because the increased atmospheric pressure causes more oxygen to diffuse into the bloodstream. At this increased pressure and increased concentration of oxygen, carbon monoxide is displaced from hemoglobin. Another example is the treatment of anaerobic bacterial infections, which are created by bacteria that cannot or prefer not to live in the presence of oxygen. An increase in blood and tissue levels of oxygen helps to kill the anaerobic bacteria that are responsible for the infection, as oxygen is toxic to anaerobic bacteria. For wounds and grafts, the chamber stimulates the healing process by increasing energy production needed for repair. Increasing oxygen transport allows cells to ramp up cellular respiration and thus ATP production, the energy needed to build new structures.
The behavior of gases can be explained by the principles of Dalton’s law and Henry’s law, both of which describe aspects of gas exchange. Dalton’s law states that each specific gas in a mixture of gases exerts force (its partial pressure) independently of the other gases in the mixture. Henry’s law states that the amount of a specific gas that dissolves in a liquid is a function of its partial pressure. The greater the partial pressure of a gas, the more of that gas will dissolve in a liquid, as the gas moves toward equilibrium. Gas molecules move down a pressure gradient; in other words, gas moves from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure. The partial pressure of oxygen is high in the alveoli and low in the blood of the pulmonary capillaries. As a result, oxygen diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the alveoli into the blood. In contrast, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is high in the pulmonary capillaries and low in the alveoli. Therefore, carbon dioxide diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the blood into the alveoli. The amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide that diffuses across the respiratory membrane is similar.
Ventilation is the process that moves air into and out of the alveoli, and perfusion affects the flow of blood in the capillaries. Both are important in gas exchange, as ventilation must be sufficient to create a high partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli. If ventilation is insufficient and the partial pressure of oxygen drops in the alveolar air, the capillary is constricted and blood flow is redirected to alveoli with sufficient ventilation. External respiration refers to gas exchange that occurs in the alveoli, whereas internal respiration refers to gas exchange that occurs in the tissue. Both are driven by partial pressure differences.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?