| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

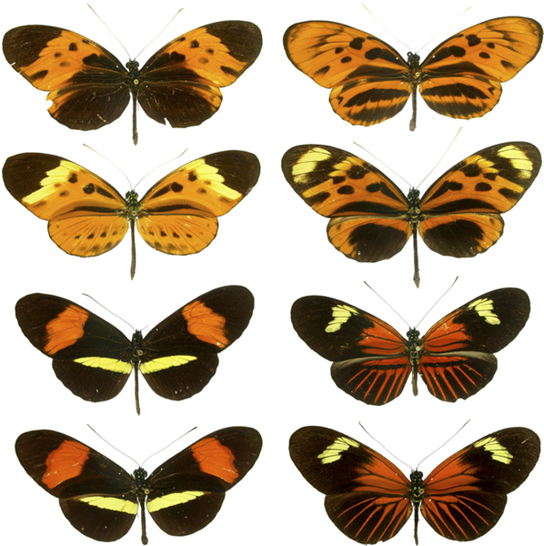
In other cases of mimicry, multiple species share the same warning coloration, but all of them actually have defenses. The commonness of the signal improves the compliance of all the potential predators. [link] shows a variety of foul-tasting butterflies with similar coloration.

Go to this website to view stunning examples of mimicry.
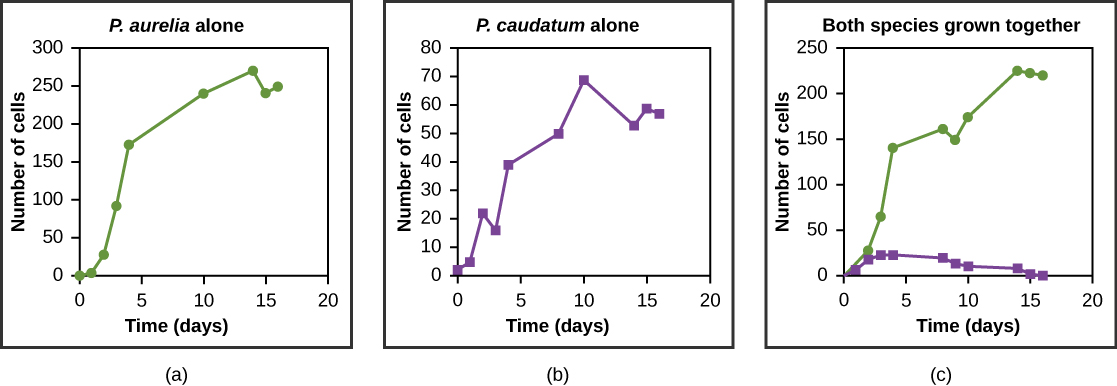
Resources are often limited within a habitat and multiple species may compete to obtain them. Ecologists have come to understand that all species have an ecological niche. A niche is the unique set of resources used by a species, which includes its interactions with other species. The competitive exclusion principle states that two species cannot occupy the same niche in a habitat: in other words, different species cannot coexist in a community if they are competing for all the same resources. This principle works because if there is an overlap in resource use and therefore competition between two species, then traits that lessen reliance on the shared resource will be selected for leading to evolution that reduces the overlap. If either species is unable to evolve to reduce competition, then the species that most efficiently exploits the resource will drive the other species to extinction. An experimental example of this principle is shown in [link] with two protozoan species: Paramecium aurelia and Paramecium caudatum . When grown individually in the laboratory, they both thrive. But when they are placed together in the same test tube (habitat), P. aurelia outcompetes P. caudatum for food, leading to the latter’s eventual extinction.
Symbiotic relationships are close, long-term interactions between individuals of different species. Symbioses may be commensal, in which one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited; mutualistic, in which both species benefit; or parasitic, in which the interaction harms one species and benefits the other.
A commensal relationship occurs when one species benefits from a close prolonged interaction, while the other neither benefits nor is harmed. Birds nesting in trees provide an example of a commensal relationship ( [link] ). The tree is not harmed by the presence of the nest among its branches. The nests are light and produce little strain on the structural integrity of the branch, and most of the leaves, which the tree uses to get energy by photosynthesis, are above the nest so they are unaffected. The bird, on the other hand, benefits greatly. If the bird had to nest in the open, its eggs and young would be vulnerable to predators. Many potential commensal relationships are difficult to identify because it is difficult to prove that one partner does not derive some benefit from the presence of the other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wbrown dacc life science' conversation and receive update notifications?