| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Between material particles gravitational force act. Between charged particles electro-magnetic force come into picture. The acceleration of charged particles give rise to electromagnetic radiation. In radio-active decay weak forces act. In the nucleus the strong force come into play among the nuclear particles. As seen from the Table(1.27), presently there is a great asymmetry among the four forces. But at the time of Big Bang up to 10 -43 seconds the four forces were of equal magnitude as shown in Figure(1.73). All four forces have gauge symmetry mediated by gauge particles. This gauge symmetry comes from theory of Quantum Electrodynamics also known as Relativistic Quantum Field Theory. James Clarke Maxwell established that electric force and magnetic force are aspects of the same electromagnetic force. Salem – Weinberg showed that electromagnetic force and weak force are synthesized in Grand Unified Field Theory (GUT). Weak forces have hidden symmetry.
According to Particle Physics, hadrons ( baryons and mesons) participate in strong interactions and experience strong force and leptons (electrons and neutrinos) interact weakly. The hadrons are composed of quarks. The triplet of quarks are baryons namelyNeutron, Proton, Lambda and Sigma and doublet of quarks are Mesons(pion and kaon).
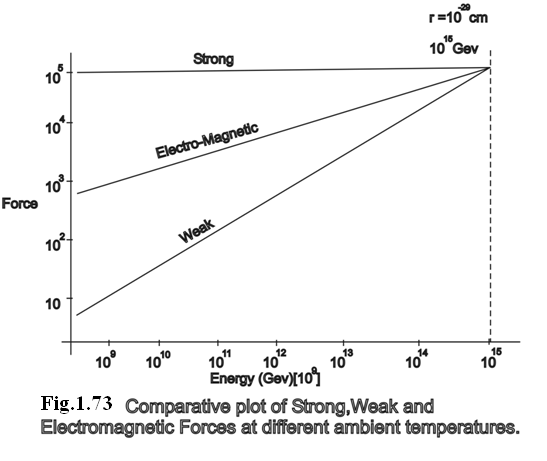
Fig.(1.73). Comparative plot of Strong, Weak and Electromagnetic Forces at different ambient temperatures.
At 10 -43 seconds after the Big Bang, the radius of the Universe was 10 -33 cm and the density was 10 93 gm/cm 3 . At this density matter was in the form of fundamental particles that is in the form of leptons and quarks. In Table(1.28), the charge and the rest mass are enumerated for the fundamental particles. As seen from Table(1.28), quarks have fractional charge but in observable Universe we always find an integer number of electron charge. This clearly shows that quarks never find independent existence . Pairs of Quarks are always confined to the nuclear particles or messenger particles to give (±) unit electron charge or zero charge. Triplets of quarks create Baryons such as n and p with (±)1e charge or zero charge but always with ½ or 3/2 spin . We have been able to achieve more than unity Tera eV. at Brookhaven National Laboratory and observed free quarks They exist as liquid with very little viscosity and not like gas particles.
Table 1.28. Comparaive study of Leptons and Quarks. Two groups and three generations of particles.
| Lepton | symbol | Rest mass(MeV/c 2 ) | Charge | Quarks | Symbol | Rest mass(MeV/c 2 ) | Charge(q) |
| Neutrino | ν e | ? | 0 | Up | u | 310 | 2/3 |
| Electron | e | 0.511 | -1 | Down | d | 310 | -1/3 |
| Mu-neutrino | ν μ | 0 | 0 | Charm | c | 1,500 | 2/3 |
| Muon | μ | 106.6 | -1 | Strange | s | 505 | -1/3 |
| Tau neutrino | ν τ | 164 | 0 | Top | t | >22,500 | 2/3 |
| Tau lepton | τ | 1777 | -1 | Bottom | b | 5,000 | -1/3 |
* All particles have their anti-matter counter part.
Indirect proofs have been obtained for 3 families of particles. In 1992 , CERN, Geneva, and SLAC, Stanford, have conclusively proved that there are only 3 families of particles.
Theory says that if there are N generations of particles then Z 0 ( intermediate vector boson mediating weak forces) have N modes of decay and will have N lifetimes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization' conversation and receive update notifications?