| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The elementary parts of all tissues are formed of cells in an analogous, though very diversified manner, so that it may be asserted, that there is one universal principle of development for the elementary parts of organisms, however different, and that this principle is the formation of cells.Theodor Schwann, in Microscopic Researches into the Accordance in the Structure and Growth of Animals and Plants , 1839
Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, and organs make organ systems. The tissues of multicellular, complex animals are four primary types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Recall that tissues are groups of similar cells carrying out a specific related functions. Many different tissues combine to form an organ —like the skin or kidney—that have specialized functions within the body. Organs are organized into organ systems to perform functions; examples include the circulatory system, which consists of the heart and blood vessels, and the digestive system, consisting of several organs, including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas. Organ systems come together to create an entire organism.
Epithelial tissues cover the outside of organs and structures in the body and line the lumens of organs in a single layer or multiple layers of cells. The types of epithelia are classified by the shapes of cells present and the number of layers of cells. Epithelia composed of a single layer of cells is called simple epithelia ; epithelial tissue composed of multiple layers is called stratified epithelia . [link] summarizes the different types of epithelial tissues.
| Different Types of Epithelial Tissues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cell shape | Description | Location |
| squamous | flat, irregular round shape | simple: lung alveoli, capillaries stratified: skin, mouth, vagina |
| cuboidal | cube shaped, central nucleus | glands, renal tubules |
| columnar | tall, narrow, nucleus toward base tall, narrow, nucleus along cell | simple: digestive tract pseudostratified: respiratory tract |
| transitional | round, simple but appear stratified | urinary bladder |
Squamous epithelial cells are generally round, flat, and have a small, centrally located nucleus. The cell outline is slightly irregular, and cells fit together to form a covering or lining. When the cells are arranged in a single layer (simple epithelia), they facilitate diffusion in tissues, such as the areas of gas exchange in the lungs and the exchange of nutrients and waste at blood capillaries.
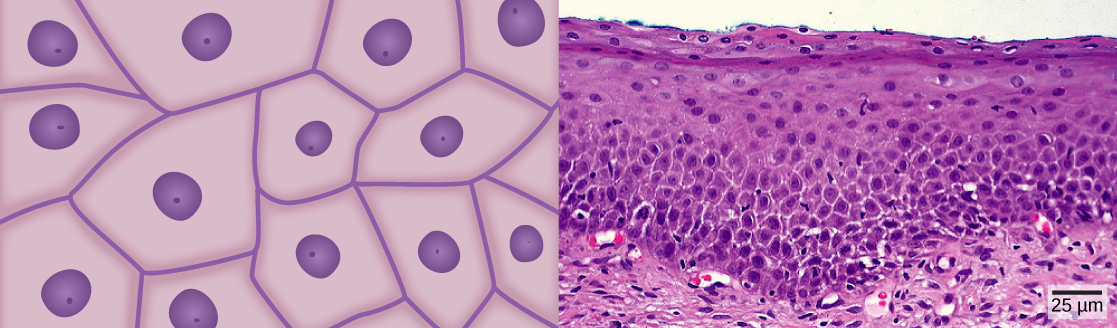
[link] a illustrates a layer of squamous cells with their membranes joined together to form an epithelium. Image [link] b illustrates squamous epithelial cells arranged in stratified layers, where protection is needed on the body from outside abrasion and damage. This is called a stratified squamous epithelium and occurs in the skin and in tissues lining the mouth and vagina.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?