| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
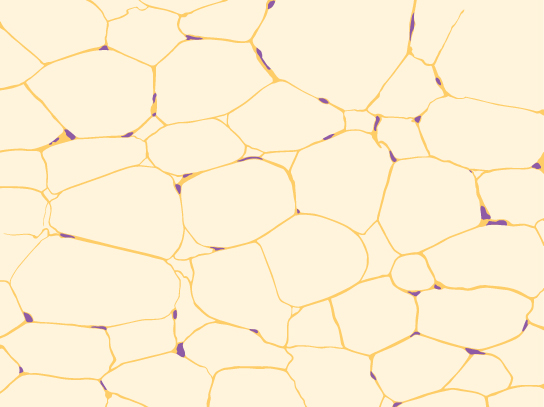
Adipose tissue, or fat tissue, is considered a connective tissue even though it does not have fibroblasts or a real matrix, and only has a few fibers. Adipose tissue is made up of cells called adipocytes (descendants of fibroblasts) that collect and store fat in the form of triglycerides. Adipose tissues serve as energy stores, and additionally serve as insulation to help maintain body temperatures, allowing animals to be endothermic. They also function as cushions to prevent damage to body organs. Under a microscope, adipose tissue cells appear empty due to the extraction of fat during the processing of the material for viewing, as seen in [link] . The thin lines in the image are the cell membranes, and the nuclei are the small, black dots at the edges of the cells.
Blood is considered a connective tissue because it has a fluid matrix (plasma) and is derived from the germ layer known as mesoderm. . The living cell types are red blood cells (RBC), also called erythrocytes, and white blood cells (WBC), also called leukocytes ( [link] ).
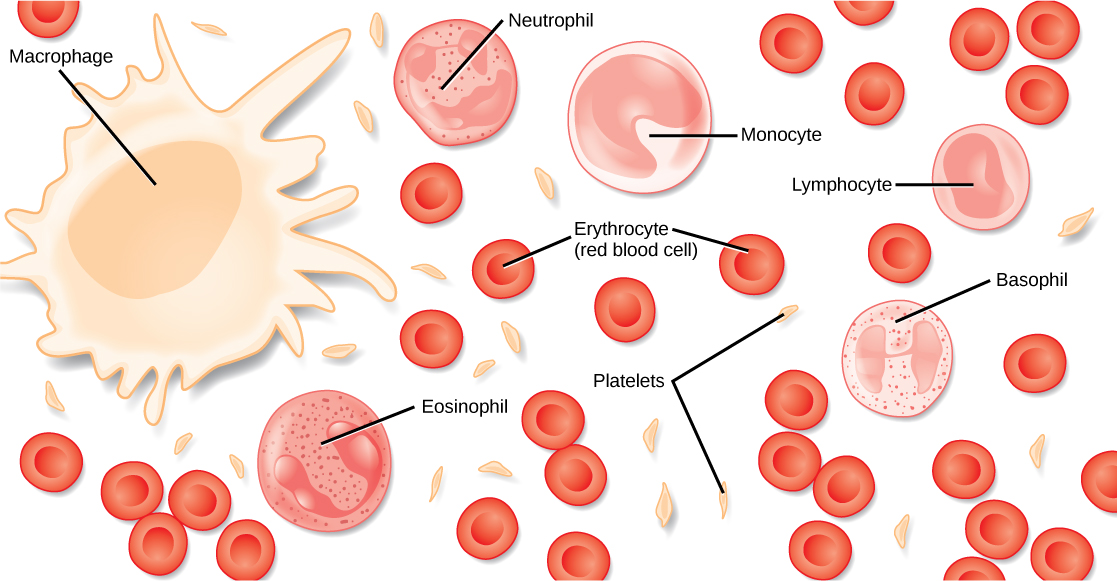
The cell found in greatest abundance in blood is the erythrocyte, or red blood cell ("erythro" = red). The principal function of an erythrocyte is to carry and deliver oxygen to the tissues. There are millions of erythrocytes in every milliliter of your blood. Mammalian erythrocytes lose their nuclei and mitochondria when they mature and are released from the bone marrow where they are generated. Fish, amphibian, and avian red blood cells maintain their nuclei and mitochondria throughout the cell’s life.
Leukocytes, or white blood cells ("leuko" = white), are the other main cellular component of blood. There are 5,000-10,000 leukocytes in every milliliter of your blood. These include cells called lymphocytes, as well as neutrophils, monocytes, and others. Lymphocytes function primarily in the immune response to foreign antigens or material, which you will learn in more detail later in this unit. Neutrophils are phagocytic (they engulf other cells or objects and digest them) cells, and they participate in one of the early lines of defense against microbial invaders or fungal invaders. Another leukocyte that is found in the peripheral blood is the monocyte. Monocytes give rise to phagocytic macrophages that clean up dead and damaged cells in the body, whether they are foreign or from the host animal. Two additional leukocytes in the blood are eosinophils and basophils—both help to facilitate the inflammatory response.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?