| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Do time intervals depend on who observes them? Intuitively, we expect the time for a process, such as the elapsed time for a foot race, to be the same for all observers. Our experience has been that disagreements over elapsed time have to do with the accuracy of measuring time. When we carefully consider just how time is measured, however, we will find that elapsed time depends on the relative motion of an observer with respect to the process being measured.
Consider how we measure elapsed time. If we use a stopwatch, for example, how do we know when to start and stop the watch? One method is to use the arrival of light from the event, such as observing a light turning green to start a drag race. The timing will be more accurate if some sort of electronic detection is used, avoiding human reaction times and other complications.
Now suppose we use this method to measure the time interval between two flashes of light produced by flash lamps. (See [link] .) Two flash lamps with observer A midway between them are on a rail car that moves to the right relative to observer B. Observer B arranges for the light flashes to be emitted just as A passes B, so that both A and B are equidistant from the lamps when the light is emitted. Observer B measures the time interval between the arrival of the light flashes. According to postulate 2, the speed of light is not affected by the motion of the lamps relative to B. Therefore, light travels equal distances to him at equal speeds. Thus observer B measures the flashes to be simultaneous.
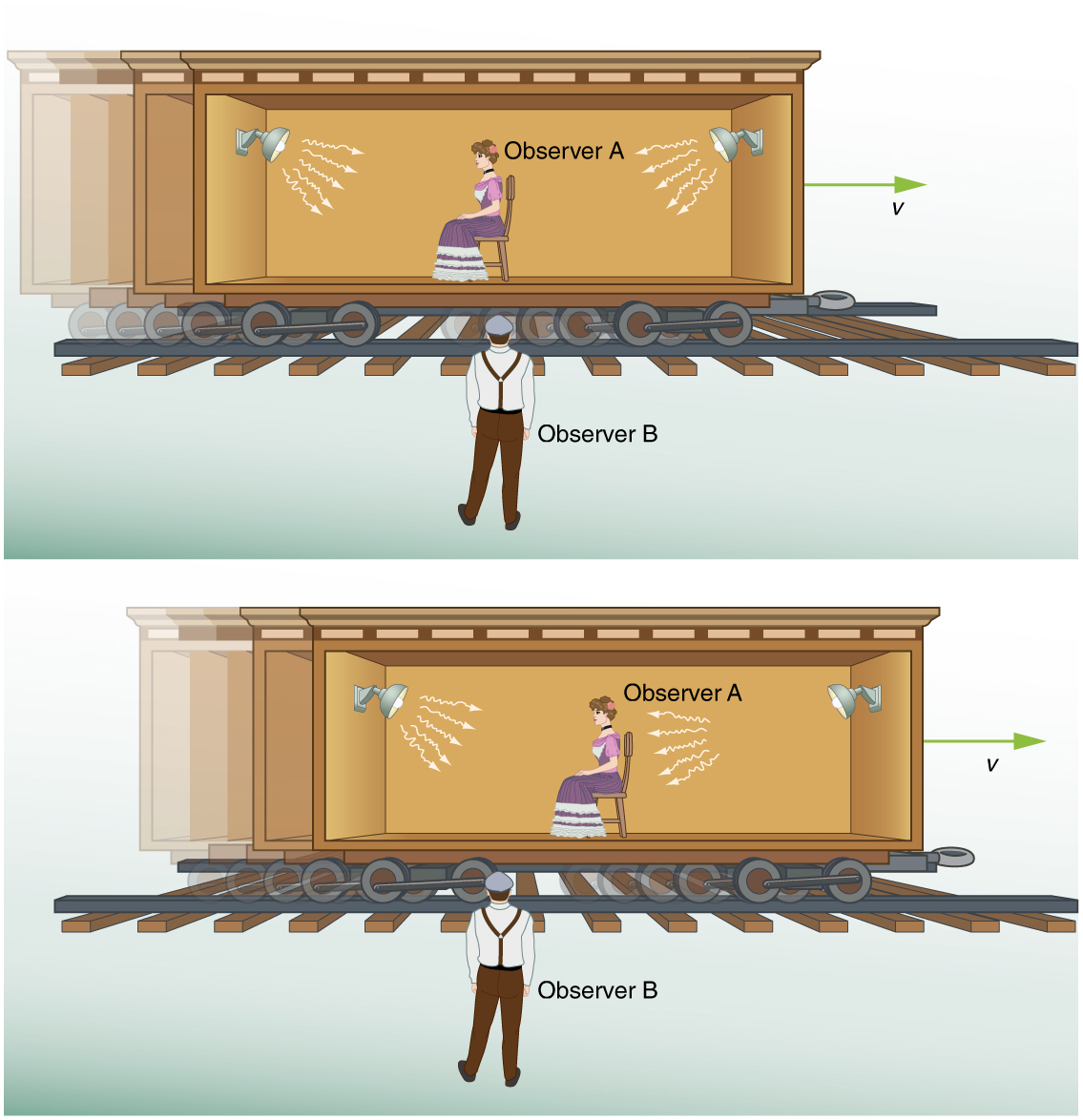
Now consider what observer B sees happen to observer A. Observer B perceives light from the right reaching observer A before light from the left, because she has moved towards that flash lamp, lessening the distance the light must travel and reducing the time it takes to get to her. Light travels at speed relative to both observers, but observer B remains equidistant between the points where the flashes were emitted, while A gets closer to the emission point on the right. From observer B’s point of view, then, there is a time interval between the arrival of the flashes to observer A. From observer B’s point of view, then, there is a time interval between the arrival of the flashes to observer A. In observer A's frame of reference, the flashes occur at different times. Observer B measures the flashes to arrive simultaneously relative to him but not relative to A.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 101' conversation and receive update notifications?