| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chemical digestion in the small intestine relies on the activities of three accessory digestive organs: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder ( [link] ). The digestive role of the liver is to produce bile and export it to the duodenum. The gallbladder primarily stores, concentrates, and releases bile. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions, and delivers it to the duodenum.
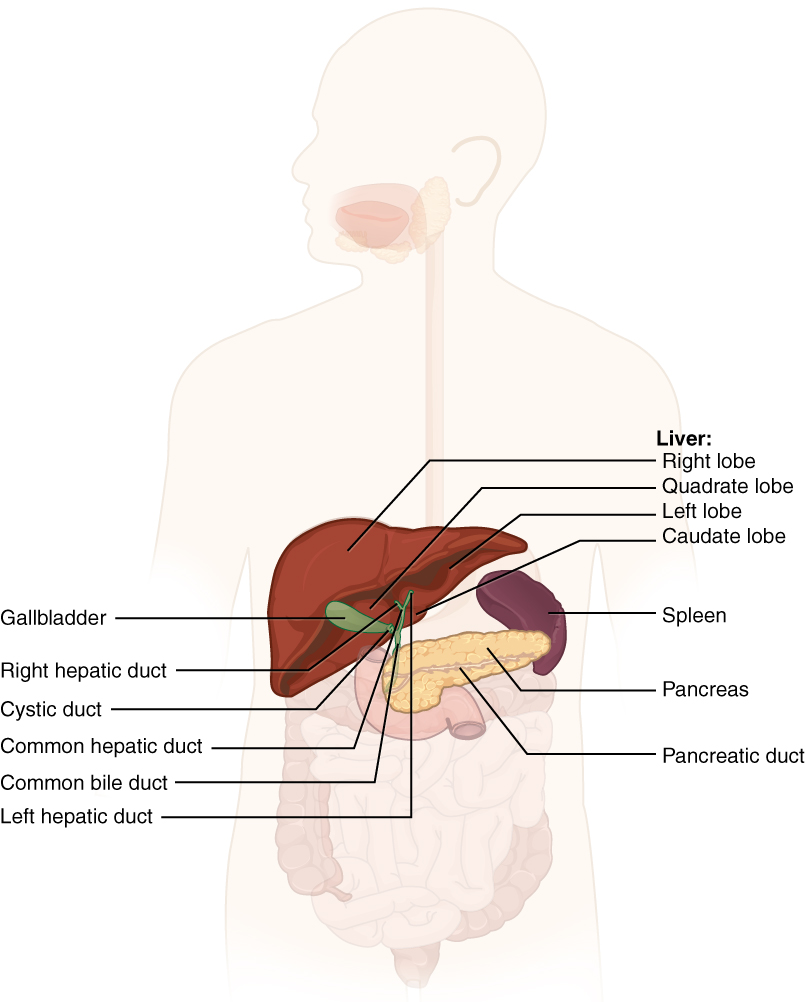
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing about three pounds in an adult. It is also one of the most important organs. In addition to being an accessory digestive organ, it plays a number of roles in metabolism and regulation. The liver lies inferior to the diaphragm in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity and receives protection from the surrounding ribs.
The liver is divided into two primary lobes: a large right lobe and a much smaller left lobe. In the right lobe, some anatomists also identify an inferior quadrate lobe and a posterior caudate lobe, which are defined by internal features. The liver is connected to the abdominal wall and diaphragm by five peritoneal folds referred to as ligaments. These are the falciform ligament, the coronary ligament, two lateral ligaments, and the ligamentum teres hepatis. The falciform ligament and ligamentum teres hepatis are actually remnants of the umbilical vein, and separate the right and left lobes anteriorly. The lesser omentum tethers the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach.
The porta hepatis (“gate to the liver”) is where the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein enter the liver. These two vessels, along with the common hepatic duct, run behind the lateral border of the lesser omentum on the way to their destinations. As shown in [link] , the hepatic artery delivers oxygenated blood from the heart to the liver. The hepatic portal vein delivers partially deoxygenated blood containing nutrients absorbed from the small intestine and actually supplies more oxygen to the liver than do the much smaller hepatic arteries. In addition to nutrients, drugs and toxins are also absorbed. After processing the bloodborne nutrients and toxins, the liver releases nutrients needed by other cells back into the blood, which drains into the central vein and then through the hepatic vein to the inferior vena cava. With this hepatic portal circulation, all blood from the alimentary canal passes through the liver. This largely explains why the liver is the most common site for the metastasis of cancers that originate in the alimentary canal.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: energy, maintenance and environmental exchange' conversation and receive update notifications?