| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The elements in groups (vertical columns) of the periodic table exhibit similar chemical behavior. This similarity occurs because the members of a group have the same number and distribution of electrons in their valence shells. However, there are also other patterns in chemical properties on the periodic table. For example, as we move down a group, the metallic character of the atoms increases. Oxygen, at the top of group 16 (6A), is a colorless gas; in the middle of the group, selenium is a semiconducting solid; and, toward the bottom, polonium is a silver-grey solid that conducts electricity.
As we go across a period from left to right, we add a proton to the nucleus and an electron to the valence shell with each successive element. As we go down the elements in a group, the number of electrons in the valence shell remains constant, but the principal quantum number increases by one each time. An understanding of the electronic structure of the elements allows us to examine some of the properties that govern their chemical behavior. These properties vary periodically as the electronic structure of the elements changes. They are (1) size (radius) of atoms and ions, (2) ionization energies, and (3) electron affinities.
Explore visualizations of the periodic trends discussed in this section (and many more trends). With just a few clicks, you can create three-dimensional versions of the periodic table showing atomic size or graphs of ionization energies from all measured elements.
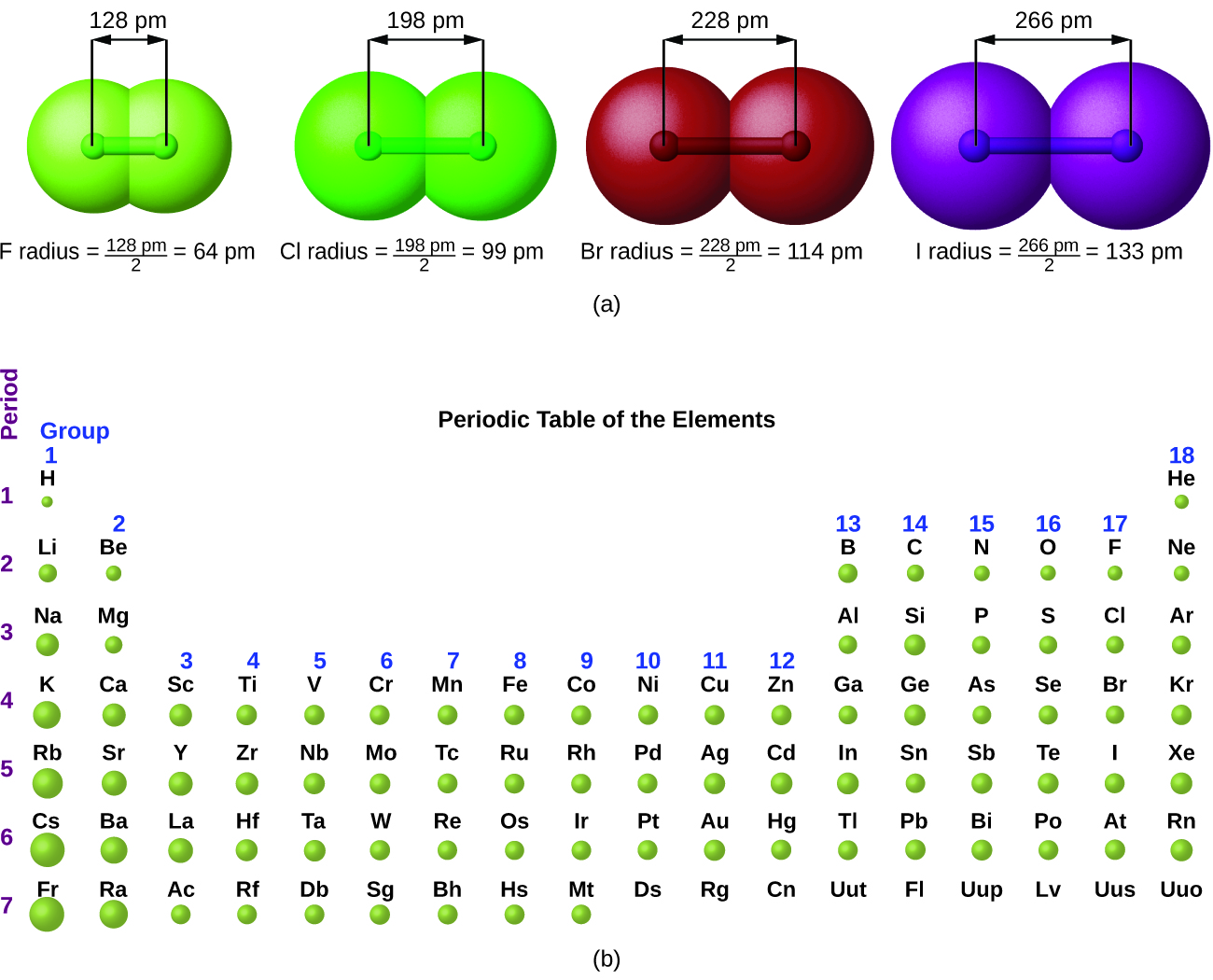
The quantum mechanical picture makes it difficult to establish a definite size of an atom. However, there are several practical ways to define the radius of atoms and, thus, to determine their relative sizes that give roughly similar values. We will use the covalent radius ( [link] ), which is defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms when they are joined by a covalent bond (this measurement is possible because atoms within molecules still retain much of their atomic identity). We know that as we scan down a group, the principal quantum number, n , increases by one for each element. Thus, the electrons are being added to a region of space that is increasingly distant from the nucleus. Consequently, the size of the atom (and its covalent radius) must increase as we increase the distance of the outermost electrons from the nucleus. This trend is illustrated for the covalent radii of the halogens in [link] and [link] . The trends for the entire periodic table can be seen in [link] .
| Covalent Radii of the Halogen Group Elements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Atom | Covalent radius (pm) | Nuclear charge |
| F | 64 | +9 |
| Cl | 99 | +17 |
| Br | 114 | +35 |
| I | 133 | +53 |
| At | 148 | +85 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?