| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When atoms join to form molecules, they are held together by chemical bonds . The type of bond, and the strength of the bond, depends on the atoms that are involved. Thesebonds are called intramolecular forces because they are bonding forces inside a molecule ('intra' means 'within' or 'inside'). Sometimes we simply call theseintramolecular forces chemical bonds.
The force between the atoms of a molecule, which holds them together.
Examples of the types of chemical bonds that can exist between atoms inside a molecule are shown below. These will be looked at in moredetail in Grade 11.
Intermolecular forces are those bonds that hold molecules together. A glass of water for example, contains many molecules of water. These molecules are held together byintermolecular forces. The strength of the intermolecular forces is important because they affect properties such as melting point and boiling point . For example, the stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the melting pointand boiling point for that substance. The strength of the intermolecular forces increases as the size of the molecule increases.
A force between molecules, which holds them together.
The following diagram may help you to understand the difference between intramolecular forces and intermolecular forces.
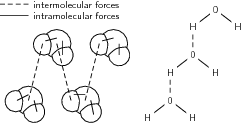
It should be clearer now that there are two types of forces that hold matter together. In the case of water, there are intramolecularforces that hold the two hydrogen atoms to the oxygen atom in each molecule of water (these are the solid lines in the above diagram). There are also intermolecular forces between each of these water molecules . These intermolecular forces join the hydrogen atom from one molecule to the oxygenatom of another molecule (these are the dashed lines in the above figure). As mentioned earlier, these forces are veryimportant because they affect many of the properties of matter such as boiling point, melting point and a number of other properties. Before we go on to look at some of these examples, it is importantthat we first take a look at the Kinetic Theory of Matter .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?