| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
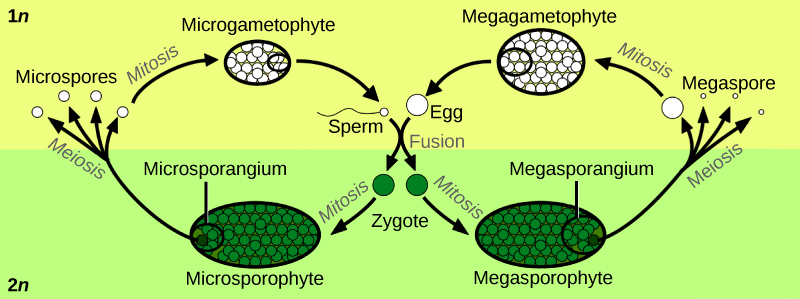
Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. The haploid gametophyte produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. Fusion of the male and females gametes forms the diploid zygote, which develops into the sporophyte . After reaching maturity, the diploid sporophyte produces spores by meiosis, which in turn divide by mitosis to produce the haploid gametophyte. The new gametophyte produces gametes, and the cycle continues. This is the alternation of generations, and is typical of plant reproduction ( [link] ).
The life cycle of higher plants is dominated by the sporophyte stage, with the gametophyte borne on the sporophyte. In ferns, the gametophyte is free-living and very distinct in structure from the diploid sporophyte. In bryophytes, such as mosses, the haploid gametophyte is more developed than the sporophyte.
During the vegetative phase of growth, plants increase in size and produce a shoot system and a root system. As they enter the reproductive phase, some of the branches start to bear flowers. Many flowers are borne singly, whereas some are borne in clusters. The flower is borne on a stalk known as a receptacle. Flower shape, color, and size are unique to each species, and are often used by taxonomists to classify plants.
The lifecycle of angiosperms follows the alternation of generations explained previously. The haploid gametophyte alternates with the diploid sporophyte during the sexual reproduction process of angiosperms. Flowers contain the plant’s reproductive structures.
A typical flower has four main parts—or whorls—known as the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium ( [link] ). The outermost whorl of the flower has green, leafy structures known as sepals. The sepals, collectively called the calyx, help to protect the unopened bud. The second whorl is comprised of petals—usually, brightly colored—collectively called the corolla. The number of sepals and petals varies depending on whether the plant is a monocot or dicot. In monocots, petals usually number three or multiples of three; in dicots, the number of petals is four or five, or multiples of four and five. Together, the calyx and corolla are known as the perianth . The third whorl contains the male reproductive structures and is known as the androecium. The androecium has stamens with anthers that contain the microsporangia. The innermost group of structures in the flower is the gynoecium , or the female reproductive component(s). The carpel is the individual unit of the gynoecium and has a stigma, style, and ovary. A flower may have one or multiple carpels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology ii' conversation and receive update notifications?