| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
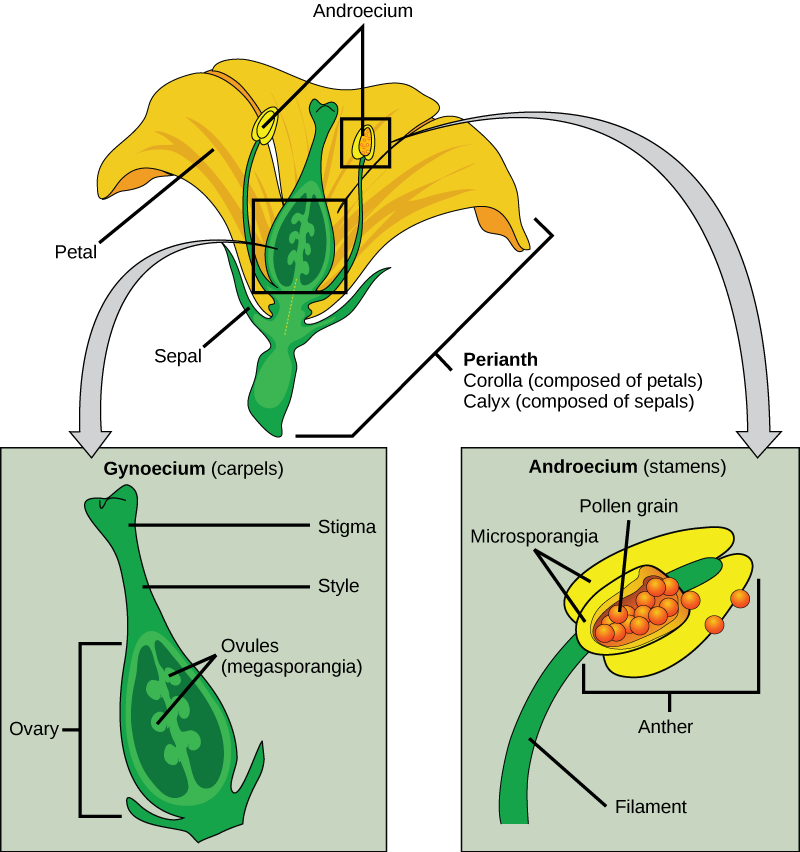
If the anther is missing, what type of reproductive structure will the flower be unable to produce? What term is used to describe an incomplete flower lacking the androecium? What term describes an incomplete flower lacking a gynoecium?
If all four whorls (the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium) are present, the flower is described as complete. If any of the four parts is missing, the flower is known as incomplete. Flowers that contain both an androecium and a gynoecium are called perfect, androgynous or hermaphrodites. There are two types of incomplete flowers: staminate flowers contain only an androecium, and carpellate flowers have only a gynoecium ( [link] ).
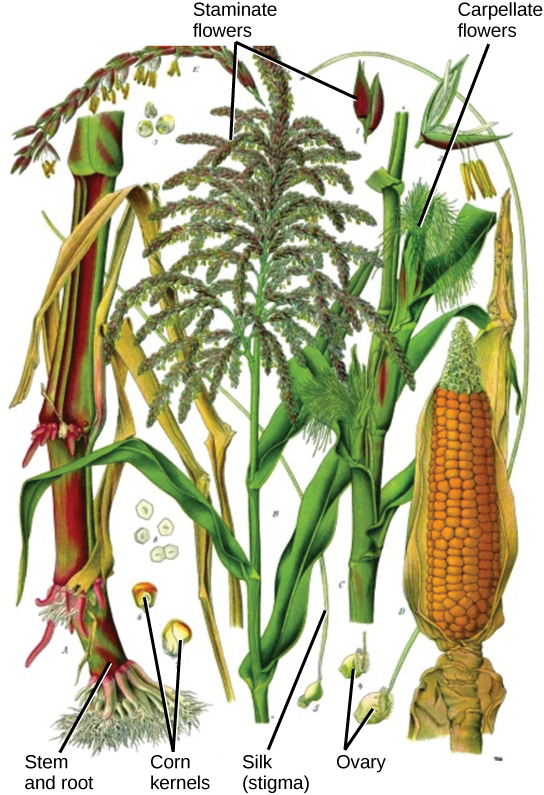
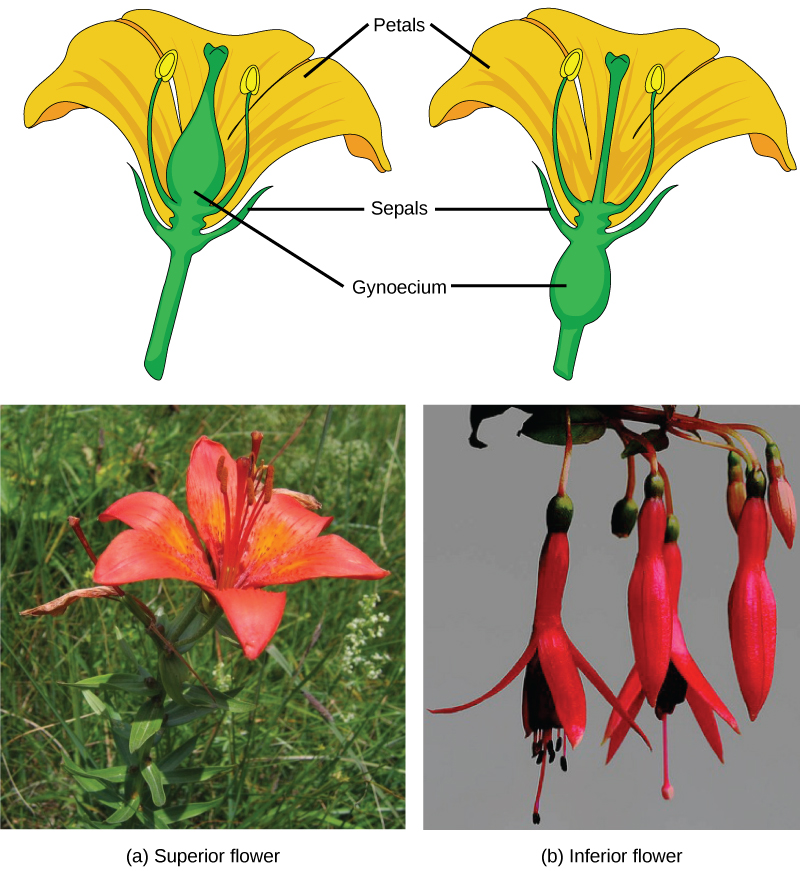
If both male and female flowers are borne on the same plant, the species is called monoecious (meaning “one home”): examples are corn and pea. Species with male and female flowers borne on separate plants are termed dioecious, or “two homes,” examples of which are C. papaya and Cannabis . The ovary, which may contain one or multiple ovules, may be placed above other flower parts, which is referred to as superior; or, it may be placed below the other flower parts, referred to as inferior ( [link] ).
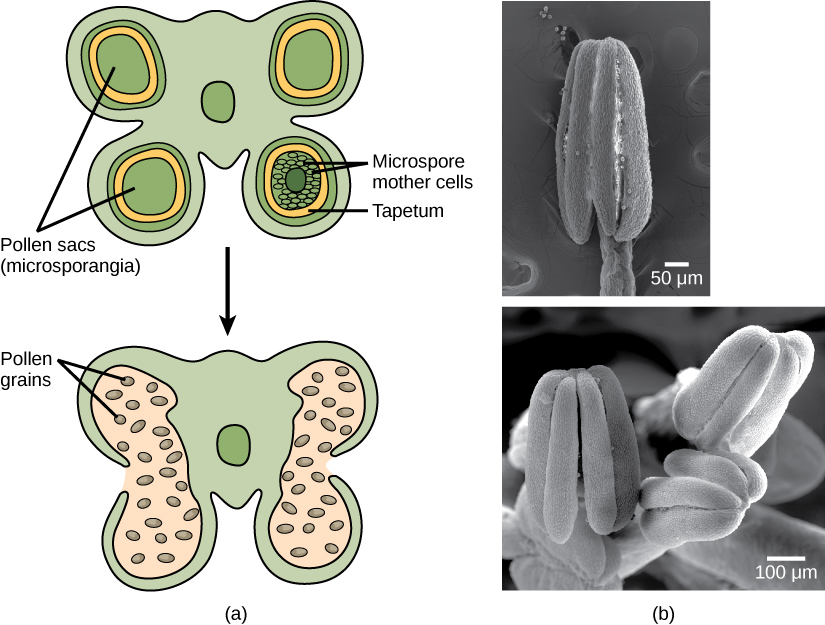
The male gametophyte develops and reaches maturity in an immature anther. In a plant’s male reproductive organs, development of pollen takes place in a structure known as the microsporangium ( [link] ). The microsporangia, which are usually bi-lobed, are pollen sacs in which the microspores develop into pollen grains. These are found in the anther, which is at the end of the stamen—the long filament that supports the anther.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology ii' conversation and receive update notifications?