| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Discussion for (e)
Note, coincidentally, that the total power dissipated by the resistors is also 7.20 W, the same as the power put out by the source. That is,
Power is energy per unit time (watts), and so conservation of energy requires the power output of the source to be equal to the total power dissipated by the resistors.
[link] shows resistors in parallel , wired to a voltage source. Resistors are in parallel when each resistor is connected directly to the voltage source by connecting wires having negligible resistance. Each resistor thus has the full voltage of the source applied to it.
Each resistor draws the same current it would if it alone were connected to the voltage source (provided the voltage source is not overloaded). For example, an automobile’s headlights, radio, and so on, are wired in parallel, so that they utilize the full voltage of the source and can operate completely independently. The same is true in your house, or any building. (See [link] (b).)
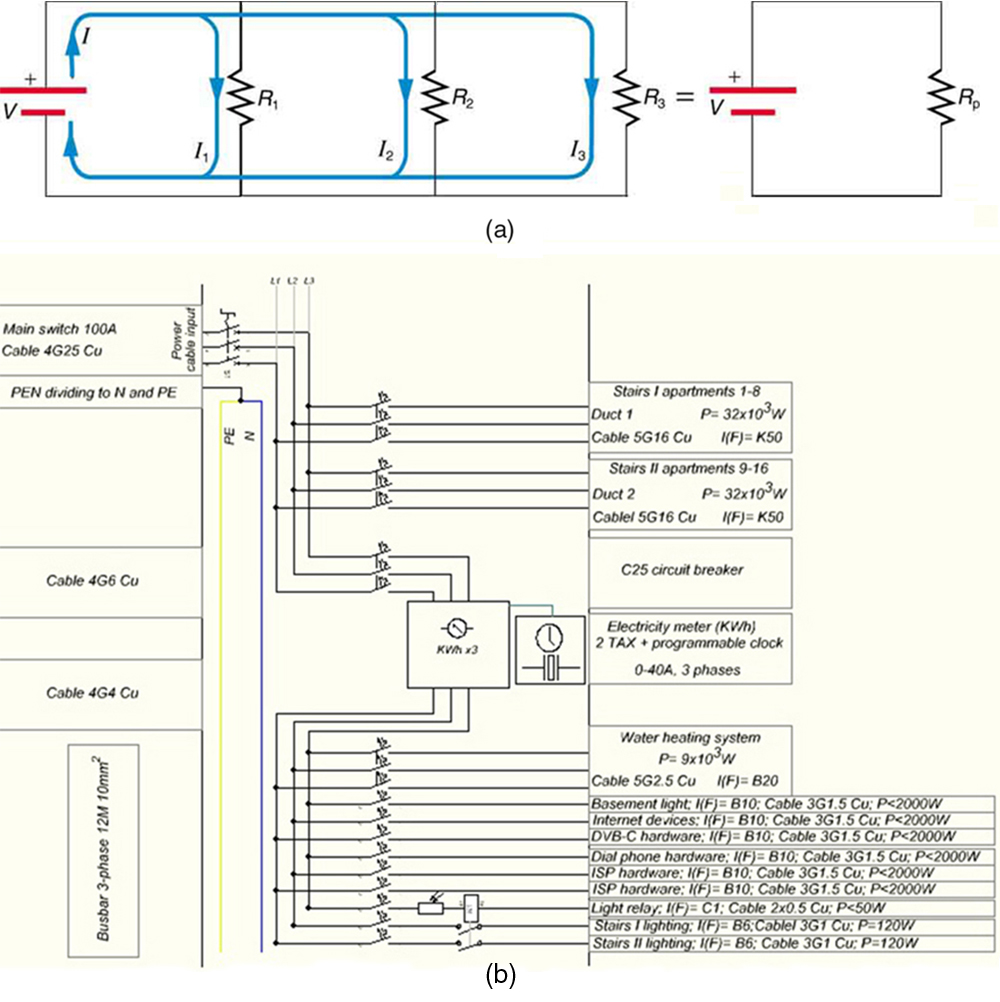
To find an expression for the equivalent parallel resistance , let us consider the currents that flow and how they are related to resistance. Since each resistor in the circuit has the full voltage, the currents flowing through the individual resistors are , , and . Conservation of charge implies that the total current produced by the source is the sum of these currents:
Substituting the expressions for the individual currents gives
Note that Ohm’s law for the equivalent single resistance gives
The terms inside the parentheses in the last two equations must be equal. Generalizing to any number of resistors, the total resistance of a parallel connection is related to the individual resistances by
This relationship results in a total resistance that is less than the smallest of the individual resistances. (This is seen in the next example.) When resistors are connected in parallel, more current flows from the source than would flow for any of them individually, and so the total resistance is lower.
Let the voltage output of the battery and resistances in the parallel connection in [link] be the same as the previously considered series connection: , , , and . (a) What is the total resistance? (b) Find the total current. (c) Calculate the currents in each resistor, and show these add to equal the total current output of the source. (d) Calculate the power dissipated by each resistor. (e) Find the power output of the source, and show that it equals the total power dissipated by the resistors.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory physics - for kpu phys 1100 (2015 edition)' conversation and receive update notifications?