| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Flow rate is defined to be the volume of fluid passing by some location through an area during a period of time, as seen in [link] . In symbols, this can be written as
where is the volume and is the elapsed time.
The SI unit for flow rate is , but a number of other units for are in common use. For example, the heart of a resting adult pumps blood at a rate of 5.00 liters per minute (L/min). Note that a liter (L) is 1/1000 of a cubic meter or 1000 cubic centimeters ( or ). In this text we shall use whatever metric units are most convenient for a given situation.
How many cubic meters of blood does the heart pump in a 75-year lifetime, assuming the average flow rate is 5.00 L/min?
Strategy
Time and flow rate are given, and so the volume can be calculated from the definition of flow rate.
Solution
Solving for volume gives
Substituting known values yields
Discussion
This amount is about 200,000 tons of blood. For comparison, this value is equivalent to about 200 times the volume of water contained in a 6-lane 50-m lap pool.
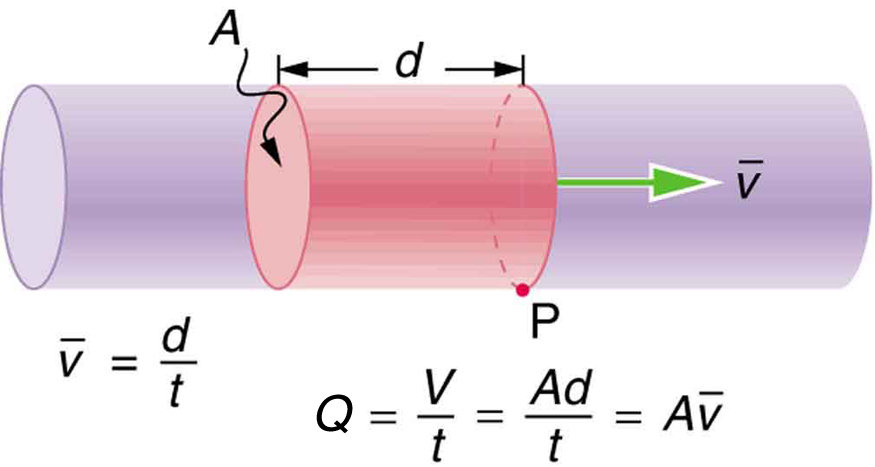
Flow rate and velocity are related, but quite different, physical quantities. To make the distinction clear, think about the flow rate of a river. The greater the velocity of the water, the greater the flow rate of the river. But flow rate also depends on the size of the river. A rapid mountain stream carries far less water than the Amazon River in Brazil, for example. The precise relationship between flow rate and velocity is
where is the cross-sectional area and is the average velocity. This equation seems logical enough. The relationship tells us that flow rate is directly proportional to both the magnitude of the average velocity (hereafter referred to as the speed) and the size of a river, pipe, or other conduit. The larger the conduit, the greater its cross-sectional area. [link] illustrates how this relationship is obtained. The shaded cylinder has a volume
which flows past the point in a time . Dividing both sides of this relationship by gives
We note that and the average speed is . Thus the equation becomes .
[link] shows an incompressible fluid flowing along a pipe of decreasing radius. Because the fluid is incompressible, the same amount of fluid must flow past any point in the tube in a given time to ensure continuity of flow. In this case, because the cross-sectional area of the pipe decreases, the velocity must necessarily increase. This logic can be extended to say that the flow rate must be the same at all points along the pipe. In particular, for points 1 and 2,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?