| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The medulla is the region known as the myelencephalon in the embryonic brain. The initial portion of the name, “myel,” refers to the significant white matter found in this region—especially on its exterior, which is continuous with the white matter of the spinal cord. The tegmentum of the midbrain and pons continues into the medulla because this gray matter is responsible for processing cranial nerve information. A diffuse region of gray matter throughout the brain stem, known as the reticular formation , is related to sleep and wakefulness, such as general brain activity and attention.
The cerebellum , as the name suggests, is the “little brain.” It is covered in gyri and sulci like the cerebrum, and looks like a miniature version of that part of the brain ( [link] ). The cerebellum is largely responsible for comparing information from the cerebrum with sensory feedback from the periphery through the spinal cord. It accounts for approximately 10 percent of the mass of the brain.
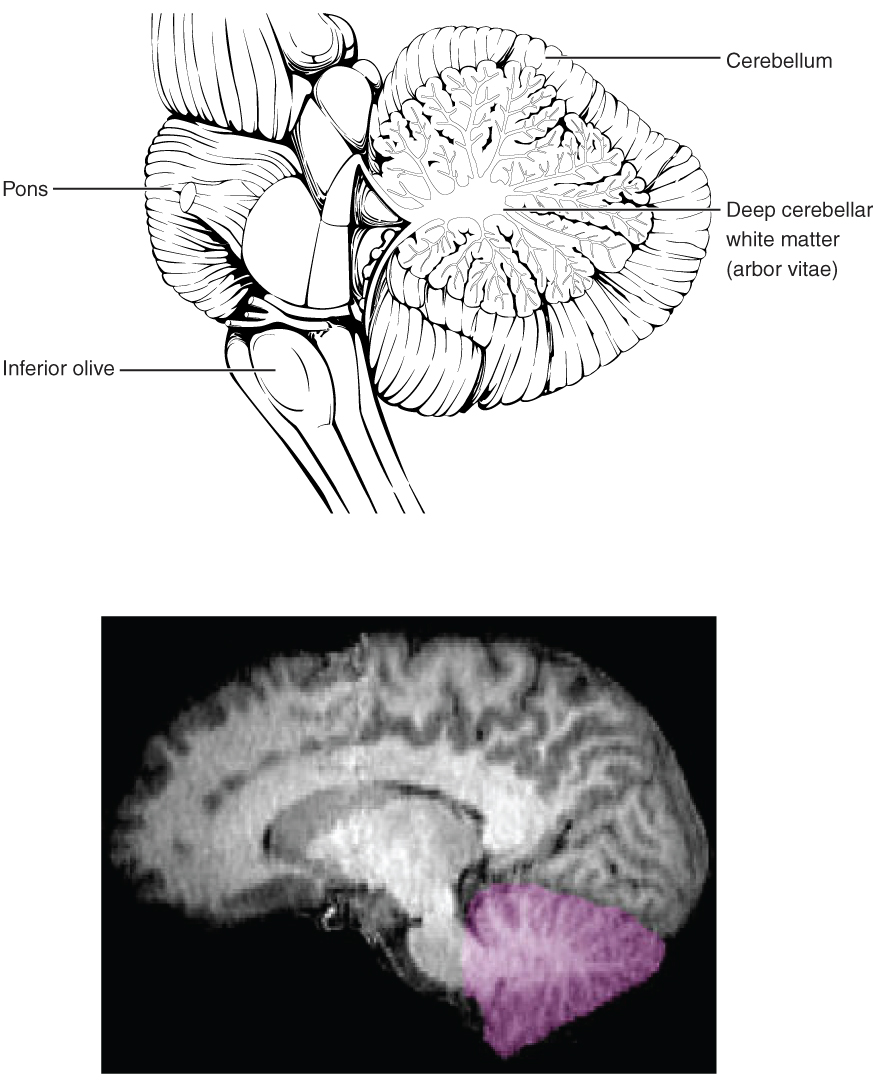
Descending fibers from the cerebrum have branches that connect to neurons in the pons. Those neurons project into the cerebellum, providing a copy of motor commands sent to the spinal cord. Sensory information from the periphery, which enters through spinal or cranial nerves, is copied to a nucleus in the medulla known as the inferior olive . Fibers from this nucleus enter the cerebellum and are compared with the descending commands from the cerebrum. If the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe sends a command down to the spinal cord to initiate walking, a copy of that instruction is sent to the cerebellum. Sensory feedback from the muscles and joints, proprioceptive information about the movements of walking, and sensations of balance are sent to the cerebellum through the inferior olive and the cerebellum compares them. If walking is not coordinated, perhaps because the ground is uneven or a strong wind is blowing, then the cerebellum sends out a corrective command to compensate for the difference between the original cortical command and the sensory feedback. The output of the cerebellum is into the midbrain, which then sends a descending input to the spinal cord to correct the messages going to skeletal muscles.
The description of the CNS is concentrated on the structures of the brain, but the spinal cord is another major organ of the system. Whereas the brain develops out of expansions of the neural tube into primary and then secondary vesicles, the spinal cord maintains the tube structure and is only specialized into certain regions. As the spinal cord continues to develop in the newborn, anatomical features mark its surface. The anterior midline is marked by the anterior median fissure , and the posterior midline is marked by the posterior median sulcus . Axons enter the posterior side through the dorsal (posterior) nerve root , which marks the posterolateral sulcus on either side. The axons emerging from the anterior side do so through the ventral (anterior) nerve root . Note that it is common to see the terms dorsal (dorsal = “back”) and ventral (ventral = “belly”) used interchangeably with posterior and anterior, particularly in reference to nerves and the structures of the spinal cord. You should learn to be comfortable with both.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bmcc 103 - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?