| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
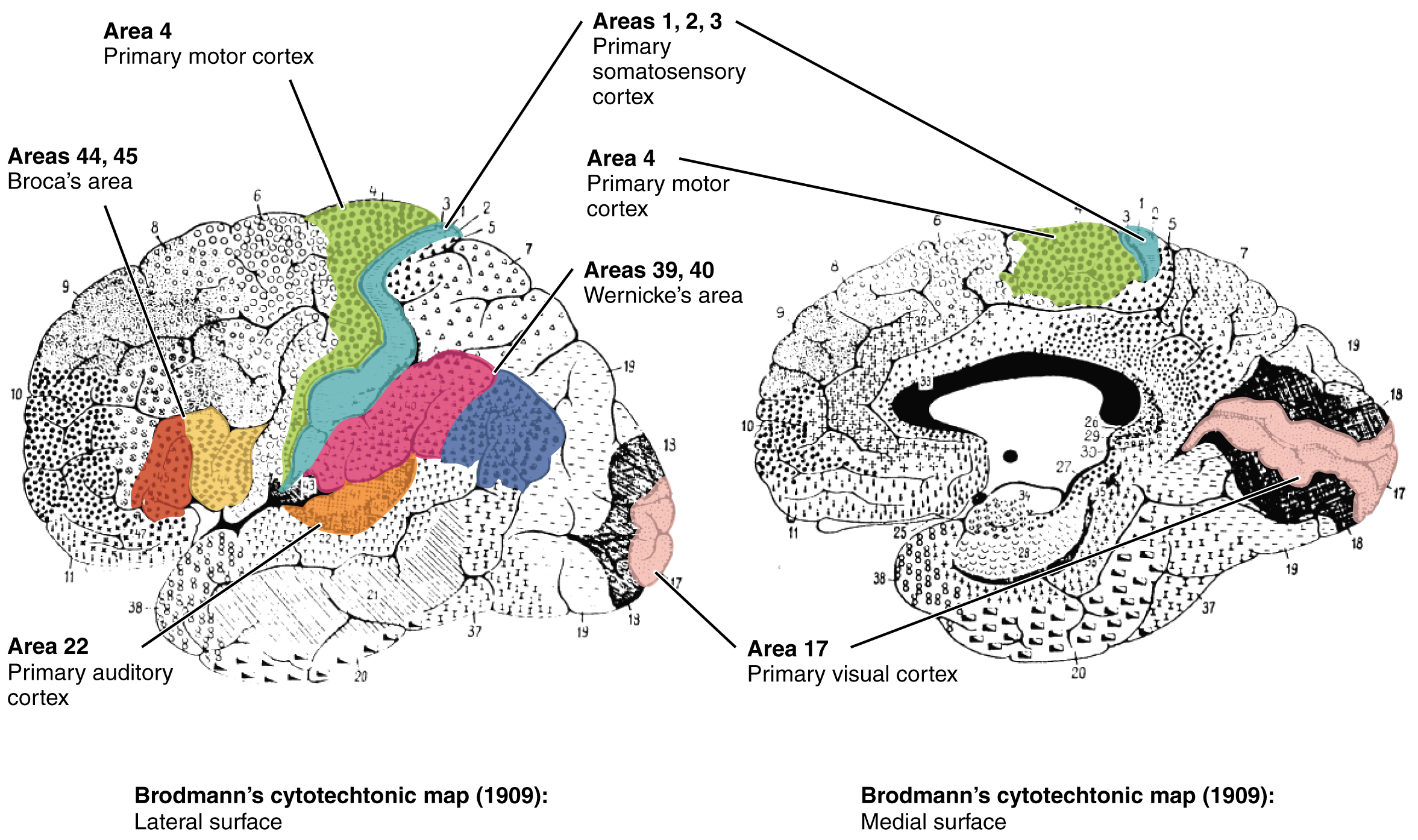
Anterior to the central sulcus is the frontal lobe, which is primarily associated with motor functions. The precentral gyrus is the primary motor cortex. Cells from this region of the cerebral cortex are the upper motor neurons that instruct cells in the spinal cord to move skeletal muscles. Anterior to this region are a few areas that are associated with planned movements. The premotor area is responsible for thinking of a movement to be made. The frontal eye fields are important in eliciting eye movements and in attending to visual stimuli. Broca’s area is responsible for the production of language, or controlling movements responsible for speech; in the vast majority of people, it is located only on the left side. Anterior to these regions is the prefrontal lobe , which serves cognitive functions that can be the basis of personality, short-term memory, and consciousness. The prefrontal lobotomy is an outdated mode of treatment for personality disorders (psychiatric conditions) that profoundly affected the personality of the patient.
Beneath the cerebral cortex are sets of nuclei known as subcortical nuclei that augment cortical processes. The nuclei of the basal forebrain serve as the primary location for acetylcholine production, which modulates the overall activity of the cortex, possibly leading to greater attention to sensory stimuli. Alzheimer’s disease is associated with a loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. The hippocampus and amygdala are medial-lobe structures that, along with the adjacent cortex, are involved in long-term memory formation and emotional responses. The basal nuclei are a set of nuclei in the cerebrum responsible for comparing cortical processing with the general state of activity in the nervous system to influence the likelihood of movement taking place. For example, while a student is sitting in a classroom listening to a lecture, the basal nuclei will keep the urge to jump up and scream from actually happening. (The basal nuclei are also referred to as the basal ganglia, although that is potentially confusing because the term ganglia is typically used for peripheral structures.)
The major structures of the basal nuclei that control movement are the caudate , putamen , and globus pallidus , which are located deep in the cerebrum. The caudate is a long nucleus that follows the basic C-shape of the cerebrum from the frontal lobe, through the parietal and occipital lobes, into the temporal lobe. The putamen is mostly deep in the anterior regions of the frontal and parietal lobes. Together, the caudate and putamen are called the striatum . The globus pallidus is a layered nucleus that lies just medial to the putamen; they are called the lenticular nuclei because they look like curved pieces fitting together like lenses. The globus pallidus has two subdivisions, the external and internal segments, which are lateral and medial, respectively. These nuclei are depicted in a frontal section of the brain in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?