| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
With the introduction of the concept of signal sampling, which produces a discrete time signal by selecting the values of the continuous time signal at evenly spaced points in time, it is now possible to discuss one of the most important results in signal processing, the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem. Often simply called the sampling theorem, this theorem concerns signals, known as bandlimited signals, with spectra that are zero for all frequencies with absolute value greater than or equal to a certain level. The theorem implies that there is a sufficiently high sampling rate at which a bandlimited signal can be recovered exactly from its samples, which is an important step in the processing of continuous time signals using the tools of discrete time signal processing.
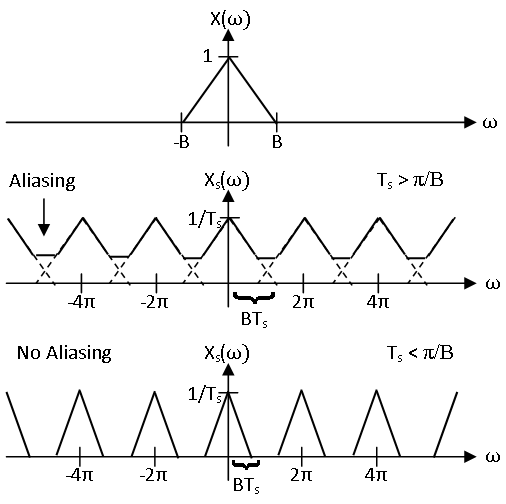
The Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem concerns signals with continuous time Fourier transforms that are only nonzero on the interval for some constant . Such a function is said to be bandlimited to . Essentially, the sampling theorem has already been implicitly introduced in the previous module concerning sampling. Given a continuous time signals with continuous time Fourier transform , recall that the spectrum of sampled signal with sampling period is given by
It had previously been noted that if is bandlimited to , the period of centered about the origin has the same form as scaled in frequency since no aliasing occurs. This is illustrated in [link] . Hence, if any two bandlimited continuous time signals sampled to the same signal, they would have the same continuous time Fourier transform and thus be identical. Thus, for each discrete time signal there is a unique bandlimited continuous time signal that samples to the discrete time signal with sampling period . Therefore, this bandlimited signal can be found from the samples by inverting this bijection.
This is the essence of the sampling theorem. More formally, the sampling theorem states the following. If a signal is bandlimited to , it is completely determined by its samples with sampling rate . That is to say, can be reconstructed exactly from its samples with sampling rate . The angular frequency is often called the angular Nyquist rate. Equivalently, this can be stated in terms of the sampling period . If a signal is bandlimited to , it is completely determined by its samples with sampling period . That is to say, can be reconstructed exactly from its samples with sampling period .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?