| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Suppose the rate of growth of the fly population is given by and the initial fly population is 100 flies. How many flies are in the population after 15 days?
There are 116 flies.
Evaluate the definite integral using substitution:
This problem requires some rewriting to simplify applying the properties. First, rewrite the exponent on e as a power of x , then bring the x 2 in the denominator up to the numerator using a negative exponent. We have
Let the exponent on e . Then
Bringing the negative sign outside the integral sign, the problem now reads
Next, change the limits of integration:
Notice that now the limits begin with the larger number, meaning we must multiply by −1 and interchange the limits. Thus,
Integrating functions of the form result in the absolute value of the natural log function, as shown in the following rule. Integral formulas for other logarithmic functions, such as and are also included in the rule.
The following formulas can be used to evaluate integrals involving logarithmic functions.
Find the antiderivative of the function
First factor the 3 outside the integral symbol. Then use the u −1 rule. Thus,
See [link] .
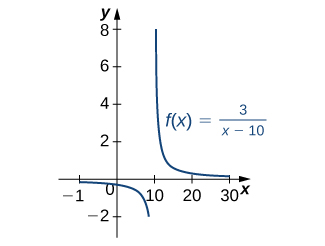
Find the antiderivative of
This can be rewritten as Use substitution. Let then Alter du by factoring out the 2. Thus,
Rewrite the integrand in u :
Then we have
Find the antiderivative of the log function
Follow the format in the formula listed in the rule on integration formulas involving logarithmic functions. Based on this format, we have
[link] is a definite integral of a trigonometric function. With trigonometric functions, we often have to apply a trigonometric property or an identity before we can move forward. Finding the right form of the integrand is usually the key to a smooth integration.
Find the definite integral of
We need substitution to evaluate this problem. Let so Rewrite the integral in terms of u , changing the limits of integration as well. Thus,
Then

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?