| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many reactions in chemistry and all biological reactions (reactions in living systems) take place in water. We say that these reactions take place in aqueous solution. Water has many unique properties and is plentiful on Earth. For these reasons reactions in aqueous solutions occur frequently. In this chapter we will look at some of these reactions in detail. Almost all the reactions that occur in aqueous solutions involve ions. We will look at three main types of reactions that occur in aqueous solutions, namely precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions and redox reactions. Before we can learn about the types of reactions, we need to first look at ions in aqueous solutions and electrical conductivity.
Water is seldom pure. Because of the structure of the water molecule, substances can dissolve easily in it. This is very important because if water wasn't able to do this, life would not be able to survive. In rivers and the oceans for example, dissolved oxygen means that organisms (such as fish) are still able to respire (breathe). For plants, dissolved nutrients are also available. In the human body, water is able to carry dissolved substances from one part of the body to another.
Many of the substances that dissolve are ionic and when they dissolve they form ions in solution. We are going to look at how water is able to dissolve ionic compounds, how these ions maintain a balance in the human body, how they affect water hardness and how they cause acid rain.
Water is a polar molecule ( [link] ). This means that one part of the molecule has a slightly positive charge (positive pole) and the other part has a slightly negative charge (negative pole).
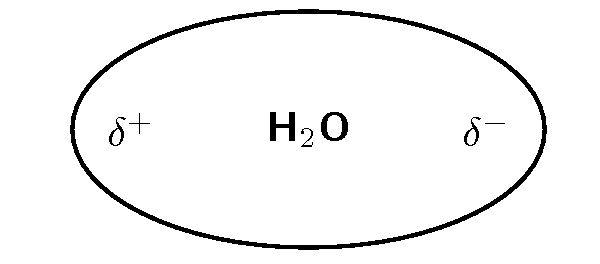
It is the polar nature of water that allows ionic compounds to dissolve in it. In the case of sodium chloride ( ) for example, the positive sodium ions ( ) will be attracted to the negative pole of the water molecule, while the negative chloride ions ( ) will be attracted to the positive pole of the water molecule. In the process, the ionic bonds between the sodium and chloride ions are weakened and the water molecules are able to work their way between the individual ions, surrounding them and slowly dissolving the compound. This process is called dissociation . A simplified representation of this is shown in [link] . We say that dissolution of a substance has occurred when a substance dissociates or dissolves.
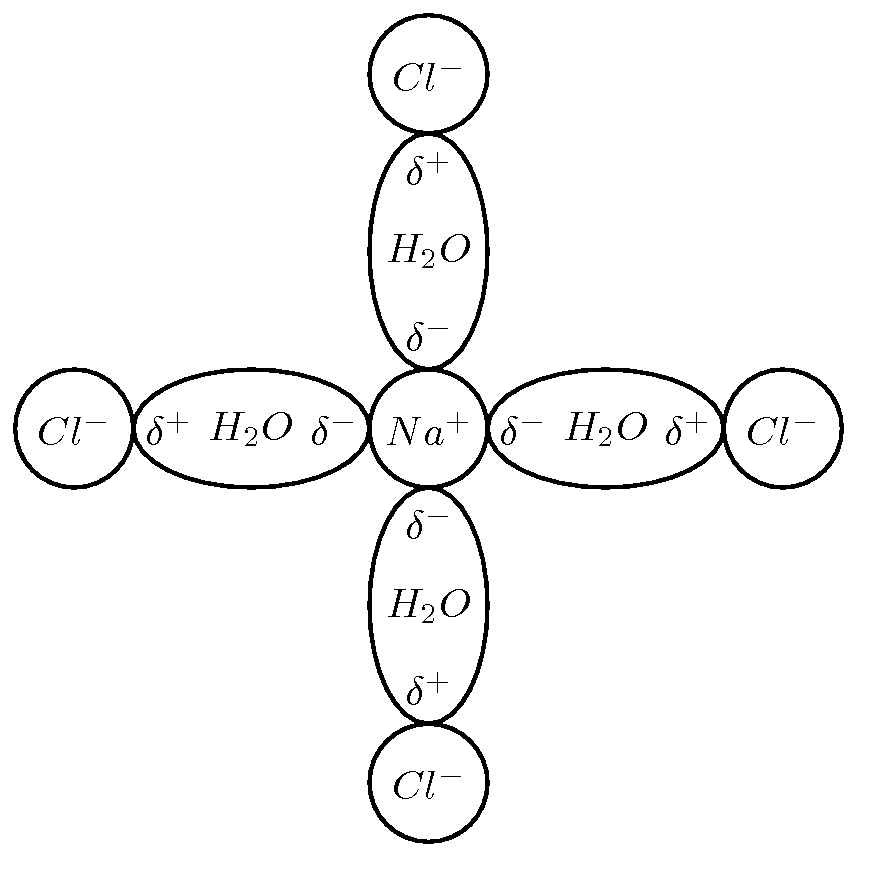
The dissolution of sodium chloride can be represented by the following equation:
The symbols s (solid), l (liquid), g (gas) and aq (material is dissolved in water) are written after the chemical formula to show the state or phase of the material. The dissolution of potassium sulphate into potassium and sulphate ions is shown below as another example:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry grade 10 [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?