| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Equations involving radicals abound in the various fields of engineering. Students of engineering must therefore gain confidence and competence in solving equations that include radical expressions. In this module, several different applications that involve the use of radicals to solve engineering problems are presented along with several exercises.
Centripetal force is the inward directed force that is exerted on one body as it moves in a circular path about another body.
Figure 1 illustrates a body that is in circular motion about a center point.
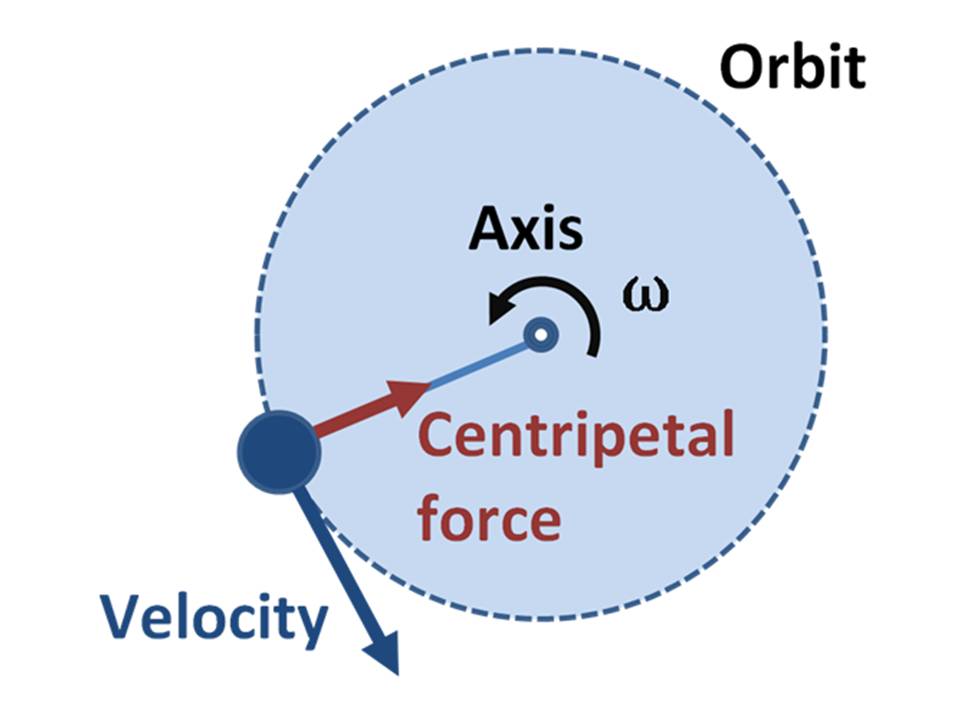
As the object moves about the circle, its angle changes. This time rate of change of the angle is called the angular velocity and is denoted by the symbol ω. The angular velocity has units of radians/sec. As an example, if the object makes 2 revolutions in a second, it would have an angular velocity
Examination of Figure 1 shows the centripetal force being directed inward toward the center of the circular path of the object. The velocity of the object is illustrated as being in the direction of the tangent at the point on the circle occupied by the object. If for any reason the body were released from its orbit about the center point, it would travel in a straight line path indicated in the direction of the velocity.
Quite often, one may measure the amount of time that it takes for the object to complete a complete revolution and denote it as the variable ( T ). This value which is usually expressed in seconds is called the period of revolution. For the example given previously where the object makes 2 revolutions per second, the period of revolution ( T ) is ½ second.
The period of revolution ( T ) measured in seconds can be calculated by means of a relationship that involves the magnitude of the centripetal force ( F ) measured in Newtons, the mass of the object ( m ) measured in kilograms, and the radius ( R ) of the circle measured in meters.
Question: A mass of 2 kg revolves about an axis. The radius of the object about the axis is 0.5 m. It takes 0.25 seconds for the mass to make a single revolution. What is the value of the centripetal force?
Solution: We begin by replacing the variables of equation (2) by their numeric values
Next we take the square of each side of the equation
We can isolate F on the left hand side of the equation as
Which leads to the result
The presence of ice on the wings and fuselage on an aircraft can lead to severe problems during stormy winter weather. Equipment is used to spray aircraft with a de-icing agent prior to take-off in order to remove the ice from the wing surfaces and fuselage of planes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Math 1508 (laboratory) engineering applications of precalculus' conversation and receive update notifications?