| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Chemical digestion in the small intestine relies on the activities of three accessory digestive organs: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder ( [link] ). The digestive role of the liver is to produce bile and export it to the duodenum. The gallbladder primarily stores, concentrates, and releases bile. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes and bicarbonate ions, and delivers it to the duodenum.
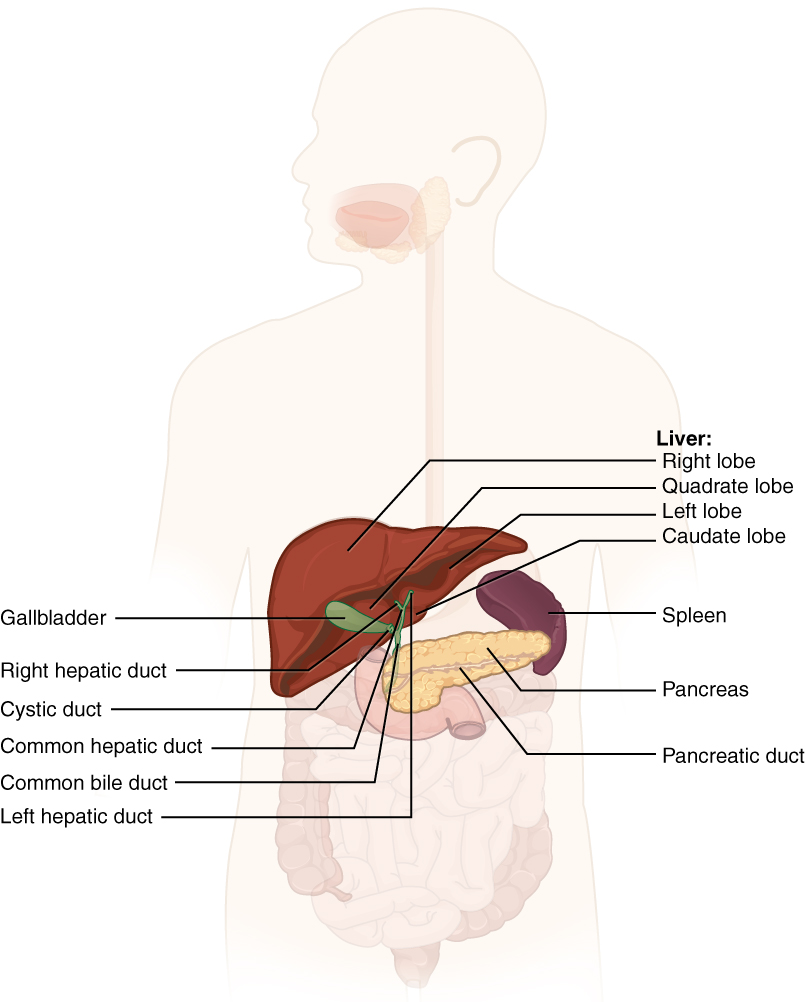
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing about three pounds in an adult. It is also one of the most important organs. In addition to being an accessory digestive organ, it plays a number of roles in metabolism and regulation. The liver lies inferior to the diaphragm in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity and receives protection from the surrounding ribs. The liver is divided into two primary lobes: a large right lobe and a much smaller left lobe. The liver is connected to the abdominal wall and diaphragm by five ligaments. The falciform ligament is visible on the midline of the surface of the liver.
The liver has two blood supplies. The first comes via the hepatic artery and brings fresh oxygenated blood to the liver, in the same way that oxygenated blood is supplied to all the body's organs. The second blood supply is delivered via the hepatic portal vein . This vein is a major component of the hepatic portal system . This system brings blood containing recently absorbed nutrients from the small intestine. The liver monitors the blood coming from the small intestine. The liver will destroy toxins and other undesirable molecules before allowing the blood to return to the heart for distribution to the whole body.
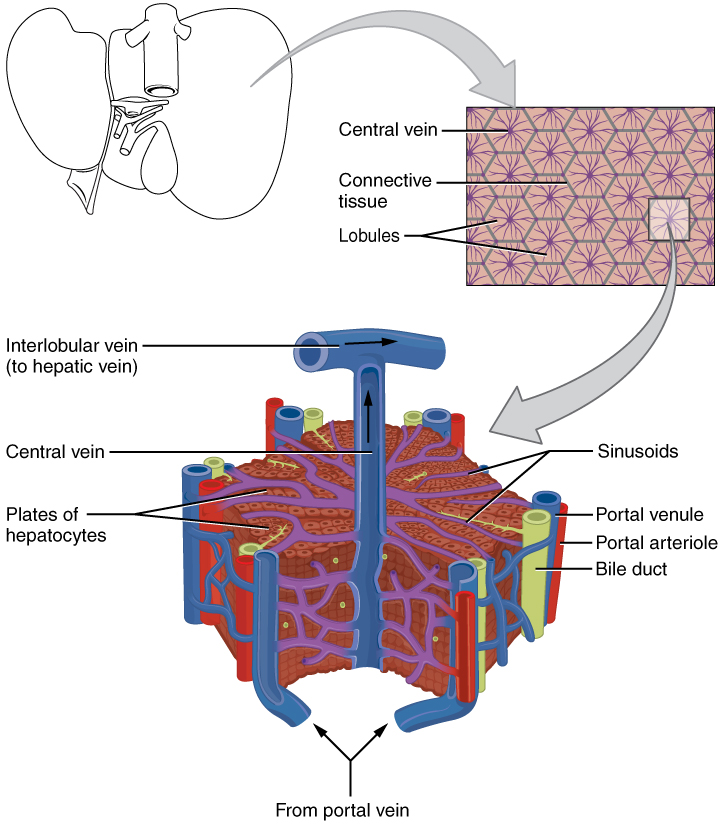
A hepatocyte is the liver’s main cell type, accounting for around 80 percent of the liver's volume. These cells play a role in a wide variety of secretory, metabolic, and endocrine functions. Between adjacent hepatocytes, bile manufactured by the liver accumulates and is directed to the right and left hepatic ducts , which merge to form the common hepatic duct which delivers bile to the gallbladder. This duct then joins with the cystic duct from the gallbladder, forming the common bile duct through which bile flows into the small intestine.
Recall that lipids do not dissolve in water. Thus, before they can be digested in the watery environment of the small intestine, large lipid globules must be broken down into smaller lipid globules, a process called emulsification . Bile is a mixture secreted by the liver to accomplish the emulsification of lipids in the small intestine. Hepatocytes secrete about one liter of bile each day. A yellow-brown or yellow-green solution, bile is a mixture of water, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, and other molecules. The bile salts are most critical to emulsification. Emulsification results in the large lipid globules being pulled apart into many tiny lipid fragments. This change dramatically increases the surface area available for lipid-digesting enzyme activity. This is the same way dish soap works on fats mixed with water.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Digestive system' conversation and receive update notifications?