| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each condition has a particular set point. A set point is the value around which the normal range fluctuates. A normal range is the set of values that is most healthful and stable. For example, the set point for normal human body temperature is approximately 98.6°F. Physiological conditions, such as body temperature and blood pressure, tend to fluctuate within a normal range a few degrees above and below that point. Control centers in the brain play roles in keeping them within the normal range. As the body works to maintain homeostasis, any significant change from the normal range will be resisted and homeostasis will be restored through a process called negative feedback. Negative feedback is a mechanism that prevents a condition from going beyond the normal range by reversing the action once the normal range is exceeded. Negative feedback serves to make the variation smaller, so the imbalance is lessened. The maintenance of homeostasis by negative feedback goes on throughout the body at all times, and an understanding of negative feedback is thus fundamental to an understanding of human physiology.
A negative feedback system has three basic components ( [link] a ). A receptor , is a part of a feedback system that monitors a physiological value (temperature for example). This value is reported to a control center such as the brain. The control center is the part in a feedback system that compares the value to the normal range. If the value deviates too much from the set point, then the control center activates an effector. An effector is the part in a feedback system that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range.
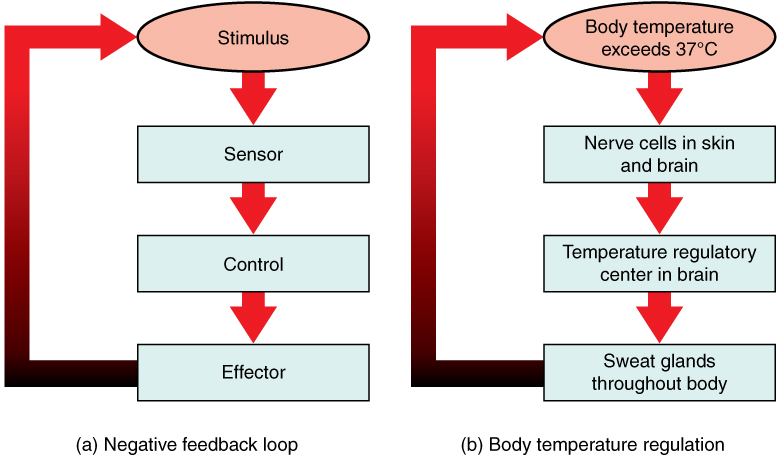
When a stimulus drives a value is outside of the normal range, the system is set in motion. The value must be beyond its normal range (that is, beyond homeostasis). This abnormal value is detected by a specific sensor. For example, in the control of blood glucose, specific cells in the pancreas detect excess glucose (the stimulus) in the bloodstream. These pancreatic cells respond to the increased level of blood glucose by releasing the hormone insulin into the bloodstream. The insulin signals skeletal muscle fibers, fat cells and liver cells to take up the excess glucose, removing it from the bloodstream. As glucose concentration in the bloodstream returns to normal, the decrease in concentration—the actual negative feedback—is detected by pancreatic cells, and insulin release stops. This prevents blood sugar levels from continuing to drop below the normal range.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to anatomy' conversation and receive update notifications?