| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Humans have a similar temperature regulation feedback system that works by promoting either heat loss or heat gain ( [link] b ). When the brain’s temperature regulation center receives data from the sensors indicating that the body’s temperature exceeds its normal range, it stimulates a cluster of brain cells referred to as the “heat-loss center.” This stimulation has three major effects:
In contrast, when the brain senses the body becoming too cool:
Water concentration in the body is critical for proper functioning. A person’s body retains very tight control on water levels without conscious control by the person. Watch this video to learn more about water concentration in the body. Which organ has primary control over the amount of water in the body?
Positive feedback intensifies a change in the body’s condition rather than reversing it. A deviation from the normal range results in more change, and the system moves farther away from the normal range. Positive feedback in the body is normal only when there is a definite end point. Childbirth, fever, lactation (breast feeding) and the body’s response to blood loss are examples of positive feedback loops that are normal but are activated only when needed.
Childbirth at full term is an example of a situation in which the maintenance of the existing body state is not desired. Enormous changes in the mother’s body are required to expel the baby at the end of pregnancy. And the events of childbirth, once begun, must progress rapidly to a conclusion or the life of the mother and the baby are at risk. The extreme muscular work of labor and delivery are the result of a positive feedback system ( [link] ).
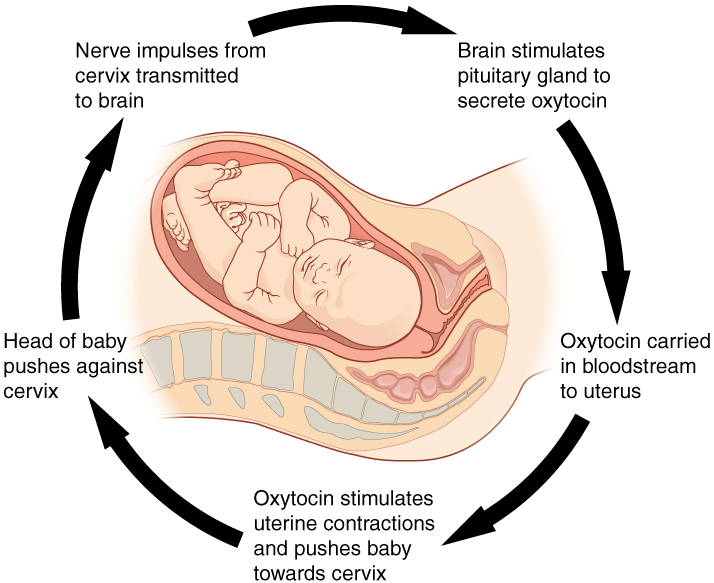
The first contractions of labor push the baby toward the cervix (the lowest part of the uterus). The cervix contains stretch-sensitive nerve cells that monitor stretching. These nerve cells send messages to the brain, which in turn causes the brain to release the hormone oxytocin into the bloodstream. Oxytocin causes stronger contractions of the muscles in of the uterus, pushing the baby further down the birth canal. This causes even greater stretching of the cervix. The cycle of stretching, oxytocin release, and increasingly more forceful contractions stops only when the baby is born. At this point, the stretching of the cervix halts, stopping the release of oxytocin.
Both negative and positive feedback are considered to be homeostatic mechanisms . Homeostatic mechanisms help the body to restore and maintain a homeostatic balance. A negative feedback mechanism serves to make the unwanted change smaller, while a positive feedback mechanism increases the change before the body can return to homeostasis.
Homeostasis is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life. Homeostasis is regulated by negative feedback loops and, much less frequently, by positive feedback loops. Both have the same components of a stimulus, sensor, control center, and effector; however, negative feedback loops work to prevent an excessive response to the stimulus, whereas positive feedback loops intensify the response until an end point is reached.
Water concentration in the body is critical for proper functioning. A person’s body retains very tight control on water levels without conscious control by the person. Watch this video to learn more about water concentration in the body. Which organ has primary control over the amount of water in the body?
The kidneys.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to anatomy' conversation and receive update notifications?