| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Momentum is an important quantity because it is conserved. Yet it was not conserved in the examples in Impulse and Linear Momentum and Force , where large changes in momentum were produced by forces acting on the system of interest. Under what circumstances is momentum conserved?
The answer to this question entails considering a sufficiently large system. It is always possible to find a larger system in which total momentum is constant, even if momentum changes for components of the system. If a football player runs into the goalpost in the end zone, there will be a force on him that causes him to bounce backward. However, the Earth also recoils —conserving momentum—because of the force applied to it through the goalpost. Because Earth is many orders of magnitude more massive than the player, its recoil is immeasurably small and can be neglected in any practical sense, but it is real nevertheless.
Consider what happens if the masses of two colliding objects are more similar than the masses of a football player and Earth—for example, one car bumping into another, as shown in [link] . Both cars are coasting in the same direction when the lead car (labeled is bumped by the trailing car (labeled The only unbalanced force on each car is the force of the collision. (Assume that the effects due to friction are negligible.) Car 1 slows down as a result of the collision, losing some momentum, while car 2 speeds up and gains some momentum. We shall now show that the total momentum of the two-car system remains constant.
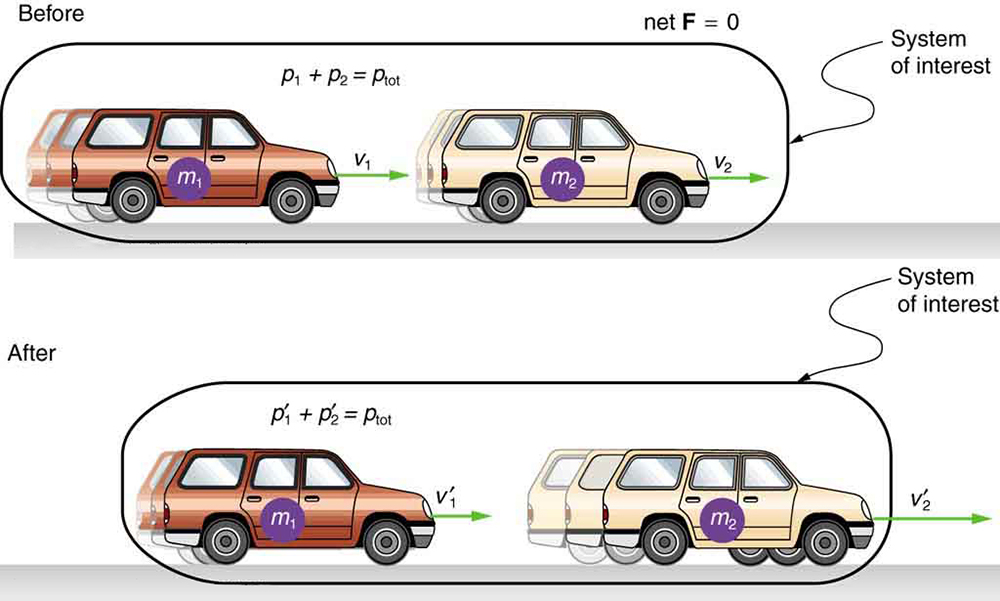
Using the definition of impulse, the change in momentum of car 1 is given by
where is the force on car 1 due to car 2, and is the time the force acts (the duration of the collision). Intuitively, it seems obvious that the collision time is the same for both cars, but it is only true for objects traveling at ordinary speeds. This assumption must be modified for objects travelling near the speed of light, without affecting the result that momentum is conserved.
Similarly, the change in momentum of car 2 is
where is the force on car 2 due to car 1, and we assume the duration of the collision is the same for both cars. We know from Newton’s third law that , and so
Thus, the changes in momentum are equal and opposite, and
Because the changes in momentum add to zero, the total momentum of the two-car system is constant. That is,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Unit 6 - momentum' conversation and receive update notifications?