| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Questions or comments concerning this laboratory should be directedto Prof. Charles A. Bouman, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette IN 47907;(765) 494-0340; bouman@ecn.purdue.edu
Speech is an acoustic waveform that conveys information from a speaker to a listener. Given the importance of this form of communication, itis no surprise that many applications of signal processing have been developed to manipulate speech signals. Almost all speechprocessing applications currently fall into three broad categories: speech recognition, speech synthesis, and speech coding.
Speech recognition may be concerned with the identification of certain words, or with the identification of the speaker. Isolated word recognition algorithms attempt to identify individual words, such as in automated telephone services.Automatic speech recognition systems attempt to recognize continuous spoken language, possibly to convert into text within a word processor.These systems often incorporate grammatical cues to increase their accuracy. Speaker identification is mostly used in security applications, as a person'svoice is much like a “fingerprint”.
The objective in speech synthesis is to convert a string of text, or a sequence of words, into natural-sounding speech.One example is the Speech Plus synthesizer used by Stephen Hawking (although it unfortunately gives him an American accent).There are also similar systems which read text for the blind. Speech synthesis has also been used to aid scientists in learning about themechanisms of human speech production, and thereby in the treatment of speech-related disorders.
Speech coding is mainly concerned with exploiting certain redundancies of the speech signal, allowing it to be represented in a compressed form.Much of the research in speech compression has been motivated by the need to conserve bandwidth in communication systems.For example, speech coding is used to reduce the bit rate in digital cellular systems.
In this lab, we will describe some elementary properties of speech signals, introduce a tool known as the short-time discrete-time Fourier Transform , and show how it can be used to form a spectrogram . We will then use the spectrogram to estimate properties of speechwaveforms.
This is the first part of a two-week experiment. During thesecond week ,we will study speech models and linear predictive coding.
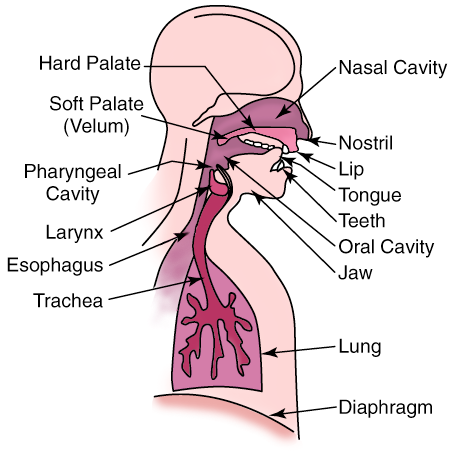
Speech consists of acoustic pressure waves created by the voluntary movements of anatomical structures in the human speech productionsystem, shown in [link] . As the diaphragm forces air through the system,these structures are able to generate and shape a wide variety of waveforms. These waveforms can be broadly categorized into voiced and unvoiced speech .
Voiced sounds, vowels for example, are produced by forcing air through the larynx, with the tension of thevocal cords adjusted so that they vibrate in a relaxed oscillation. This produces quasi-periodic pulses of air which are acousticallyfiltered as they propagate through the vocal tract, and possibly through the nasal cavity.The shape of the cavities that comprise the vocal tract, known as the area function , determines the natural frequencies, or formants , which are emphasized in the speech waveform. The period of the excitation, known as the pitch period , is generally small with respect to the rate at which the vocal tract changes shape.Therefore, a segment of voiced speech covering several pitch periods will appear somewhat periodic . Average values for the pitch period are around 8 ms for male speakers,and 4 ms for female speakers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Purdue digital signal processing labs (ece 438)' conversation and receive update notifications?