| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have seen that a moving charge experiences force in the presence of magnetic field. Now, current in a wire or a conductor results from the motion of negatively charged “free” or “conduction” electrons. It is, therefore, imperative that these moving electrons will experience “magnetic force” due to the presence of magnetic field.
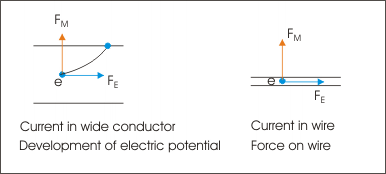
When a straight conductor carrying current is placed in a magnetic field, then conduction electrons in the conductor are under the influence of both electric and magnetic fields. The presence of electric field results in “net drift of charge (electrons)” in the conductor and it is the cause of current in the conductor. The presence of magnetic field, on the other hand, results in side way force on individual electrons (perpendicular to the conductor) resulting in the development of electrical potential across the width of the conductor or a force on the conductor itself depending on whether we are considering current through a wide conductor strip or a thin wire.
The difference in the effect of applications of two field types lies in the difference of nature of force they apply. Electrical force is linear force i.e. in the direction of electric field and is responsible for current in conductor. Magnetic force is non-linear side way force perpendicular to the direction of velocity of moving charge. The magnetic force acts to deflect electrons to the edge of a conductor. If we are considering a wide strip of conductor, then there is scope for electrons to move laterally across the width of the strip. In this case, we observe development of electrical potential difference between the edges of the conductor (known as Hall’s effect). However, if we are considering current through a thin wire, electrons have no scope for transverse motion and they are also not allowed to move out of the body of wire due to electric attractive force. The side way magnetic force, therefore, results in a transverse magnetic force on the wire itself.
Magnetic force and its effect
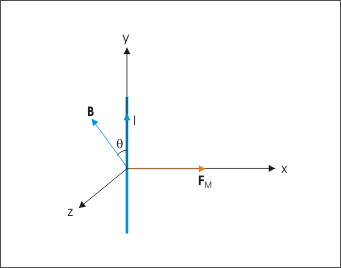
The conductor can have any orientation with respect to magnetic field. Irrespective of the orientations of conductor and magnetic field, the magnetic force is always perpendicular to both conductor length and magnetic field vectors. This fact simplifies our investigation a great deal as we need to consider only transverse magnetic force which is always perpendicular to the direction of current or the conductor length vector. This aspect is illustrated in the figure below in which conductor length vector (in the direction of current) and the magnetic field vector are oriented at an arbitrary angle “θ”, but magnetic force is perpendicular to the conductor.
Direction of magnetic force
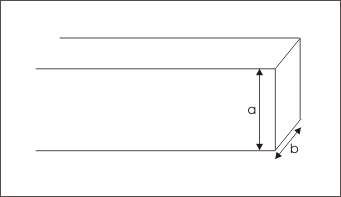
Here, we consider a wide strip of a conductor of width “a” and thickness “b”, which is carrying a current “I”.
Wide strip of a conductor
Let the direction of conventional current be from right to left so that charge carrier electrons are moving from left to right. Also, let magnetic field be directed in to the plane of drawing. The direction of magnetic force is direction of vector expression “ ”. Applying Right hand thumb rule, the direction of vector cross product “ ” is upward direction. Hence, the direction of magnetic force i.e. direction of vector “ ” is downward as shown in the figure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Electricity and magnetism' conversation and receive update notifications?