| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
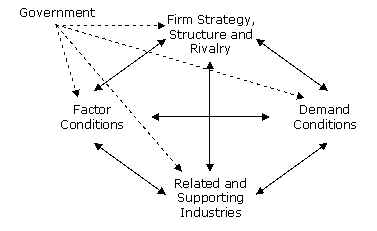
Clusters of businesses related to a specific sector not only draw upon the common innovation infrastructure (or innovation system as discussed later), but also add to it, creating a self-reinforcing virtuous circle (Porter and Stern 1999). This effect is also demonstrated by the work of Varga (2000), who notes, however, that a critical mass of agglomeration within the region is needed for this to occur.
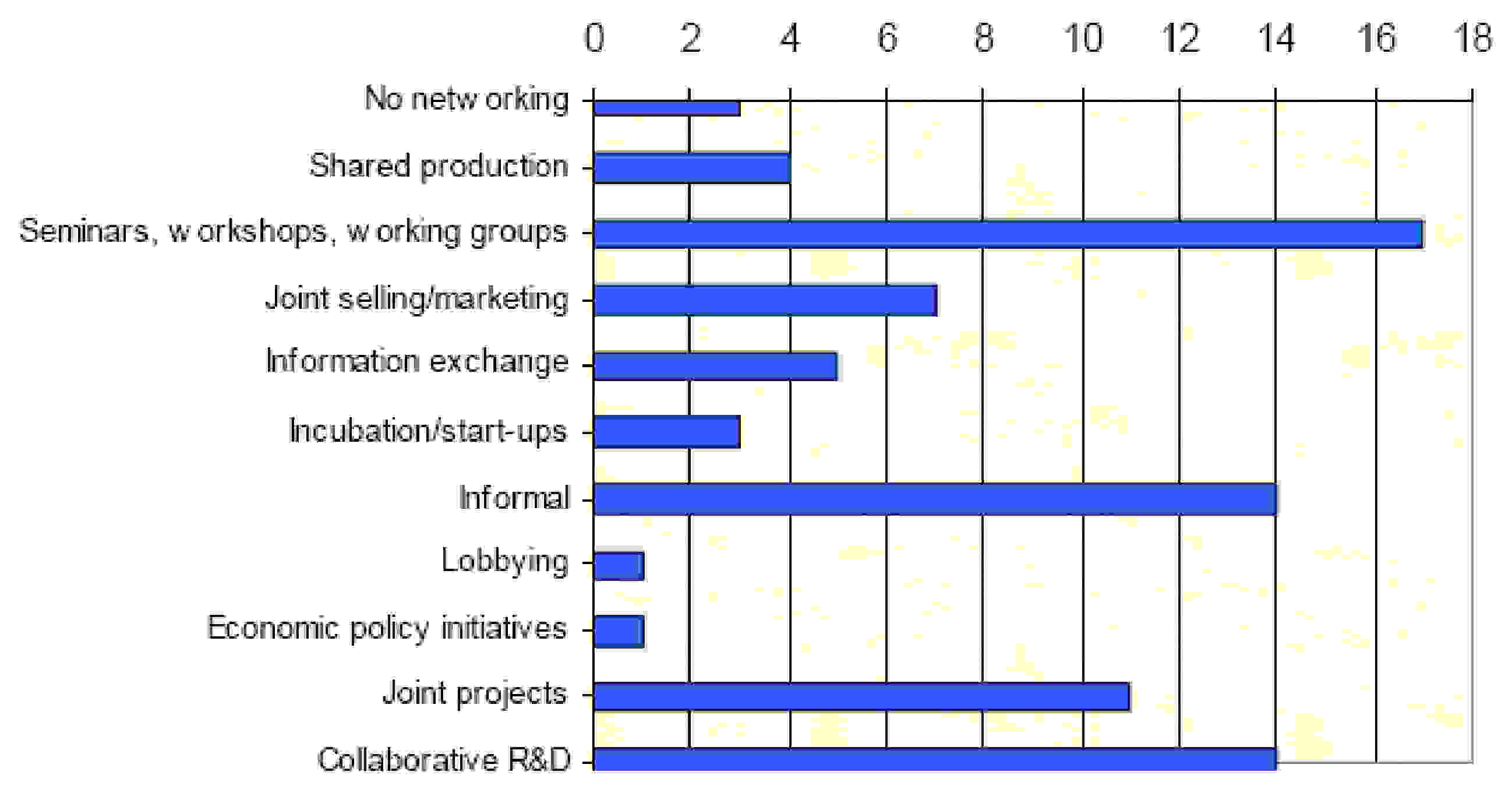
The study conducted by the European Commission also investigated the interaction and types of networking between businesses in the clusters examined. As shown in [link] most of the clusters investigated had extensive informal networking and collaborative R&D activity;
The virtuous circle can lead to growth that is then compounded by the establishment of reputation, further attracting skills, investment and opportunities to the region. Examples of this include ‘Silicon Valley’ (Bresnehan et al. 2001, 2007) and ‘Route 128’ (Dorfman 1983), along with Silicon Glen (Turok 1993) and Cambridge Biotechnology clusters in the UK (Keeble and Tomlinson 1999 and Todtling and Trippl 2005).
As described earlier the effects of clusters do not solely relate to existing firms therein, but also to the formation of new enterprise. The availability of new opportunities within a cluster helps promote entrepreneurship and the presence of support organisations, potential customers and suppliers’ acts to facilitate innovation and entrepreneurship (Rocha 2004). The presence of local networks can also help decrease cost and uncertainty in the development of start-ups, aided by flow of knowledge (Almeida and Kogut 1997).
Clusters also represent a foundation for the formation of formal and informal knowledge distribution networks that support innovation (OECD 1996), which ties in with the concept of knowledge spillovers discussed earlier. The information and knowledge exchange within clusters is the key driver in their development in what Keeble and Wilkinson term an ‘ innovative milieu ’ (Keeble and Tomlinson 1999) as part of ‘ regional collective learning ’. This concept describes the development of a collective regional knowledge base caused through interactions such as networking, research collaborations and the movement of personnel between companies and other organisations.
Proximity is a key component in successful clusters (OECD 1996 and Porter 2000), particularly in regard to facilitating knowledge-spillovers (EU 2003), described as:
“ The proximity of customers, competitors, suppliers, universities and research institutions provided impetus (for) the creation and exchange of information and increases opportunities for innovation. ”
Maskell and Malmberg (1999) outline how the competitiveness of a firm, particularly in the long-term, depends upon its ability to continuously upgrade its knowledge base. To achieve this it must find knowledge sources that provide competitive advantage. As tacit knowledge is the least transferable it requires that businesses place themselves close to its source. Additionally, cost is a factor in developing and maintaining a company’s knowledge base, making proximity to knowledge sources a cost-effective way of closer and more frequent personal contacts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'A study of how a region can lever participation in a global network to accelerate the development of a sustainable technology cluster' conversation and receive update notifications?