| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The mRNA carries the message from the DNA, which controls all of the cellular activities in a cell. If a cell requires a certain protein to be synthesized, the gene for this product is “turned on” and the mRNA is synthesized through the process of transcription (see RNA Transcription ). The mRNA then interacts with ribosomes and other cellular machinery ( [link] ) to direct the synthesis of the protein it encodes during the process of translation (see Protein Synthesis ). mRNA is relatively unstable and short-lived in the cell, especially in prokaryotic cells, ensuring that proteins are only made when needed.
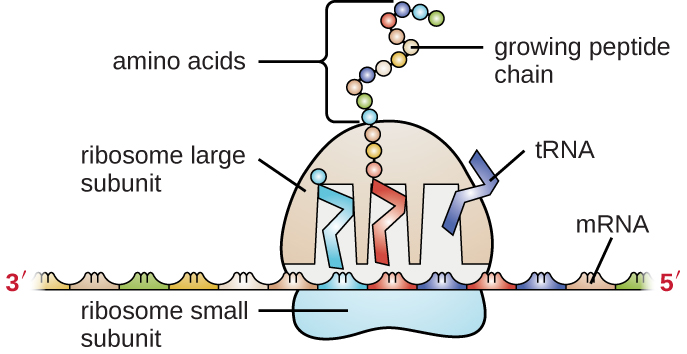
rRNA and tRNA are stable types of RNA. In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, tRNA and rRNA are encoded in the DNA, then copied into long RNA molecules that are cut to release smaller fragments containing the individual mature RNA species. In eukaryotes, synthesis, cutting, and assembly of rRNA into ribosomes takes place in the nucleolus region of the nucleus, but these activities occur in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Neither of these types of RNA carries instructions to direct the synthesis of a polypeptide, but they play other important roles in protein synthesis.
Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein. As its name suggests, rRNA is a major constituent of ribosomes , composing up to about 60% of the ribosome by mass and providing the location where the mRNA binds. The rRNA ensures the proper alignment of the mRNA, tRNA, and the ribosomes; the rRNA of the ribosome also has an enzymatic activity ( peptidyl transferase ) and catalyzes the formation of the peptide bonds between two aligned amino acids during protein synthesis. Although rRNA had long been thought to serve primarily a structural role, its catalytic role within the ribosome was proven in 2000. P. Nissen et al. “The Structural Basis of Ribosome Activity in Peptide Bond Synthesis.” Science 289 no. 5481 (2000):920–930. Scientists in the laboratories of Thomas Steitz (1940–) and Peter Moore (1939–) at Yale University were able to crystallize the ribosome structure from Haloarcula marismortui , a halophilic archaeon isolated from the Dead Sea. Because of the importance of this work, Steitz shared the 2009 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with other scientists who made significant contributions to the understanding of ribosome structure.
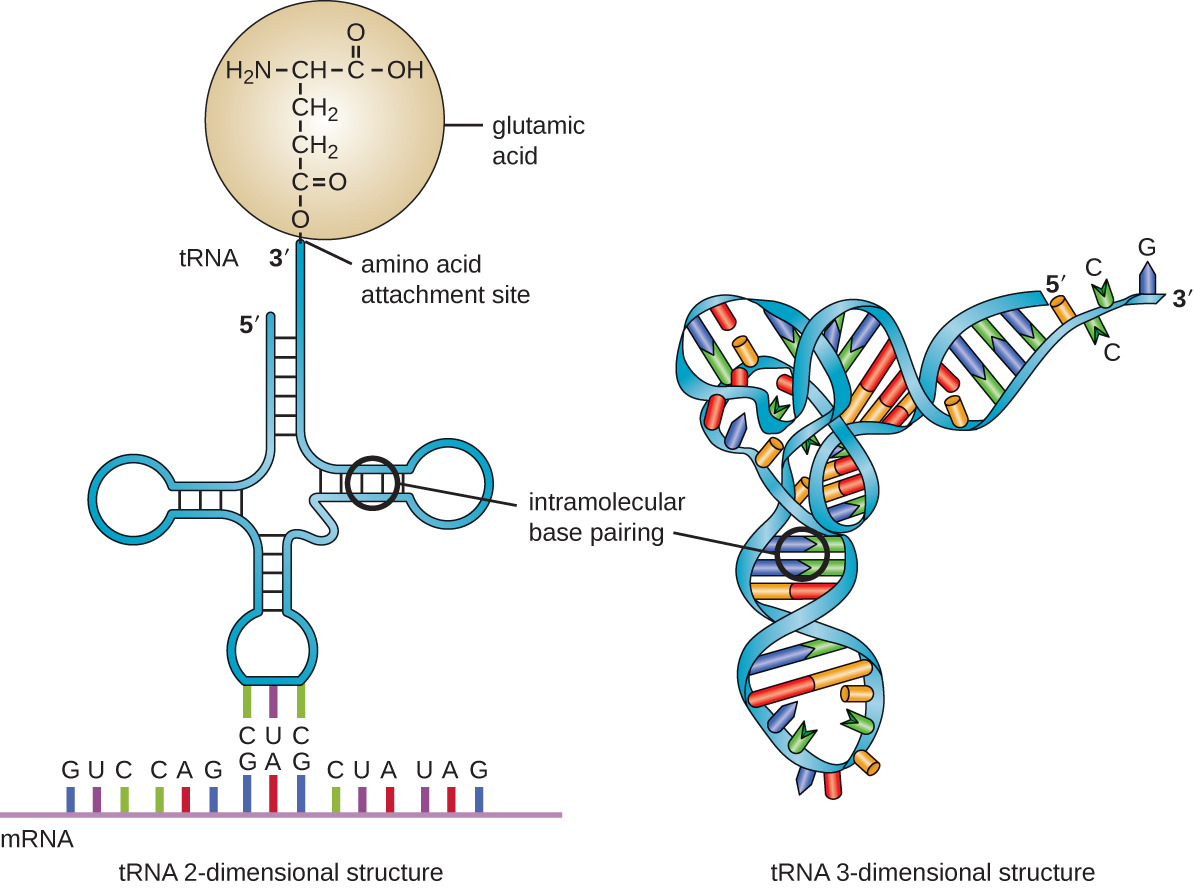
Transfer RNA is the third main type of RNA and one of the smallest, usually only 70–90 nucleotides long. It carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ribosome. It is the base pairing between the tRNA and mRNA that allows for the correct amino acid to be inserted in the polypeptide chain being synthesized ( [link] ). Any mutations in the tRNA or rRNA can result in global problems for the cell because both are necessary for proper protein synthesis ( [link] ).
| Structure and Function of RNA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | rRNA | tRNA | |
| Structure | Short, unstable, single-stranded RNA corresponding to a gene encoded within DNA | Longer, stable RNA molecules composing 60% of ribosome’s mass | Short (70-90 nucleotides), stable RNA with extensive intramolecular base pairing; contains an amino acid binding site and an mRNA binding site |
| Function | Serves as intermediary between DNA and protein; used by ribosome to direct synthesis of protein it encodes | Ensures the proper alignment of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosome during protein synthesis; catalyzes peptide bond formation between amino acids | Carries the correct amino acid to the site of protein synthesis in the ribosome |
Although RNA does not serve as the hereditary information in most cells, RNA does hold this function for many viruses that do not contain DNA . Thus, RNA clearly does have the additional capacity to serve as genetic information. Although RNA is typically single stranded within cells, there is significant diversity in viruses. Rhinoviruses, which cause the common cold; influenza viruses; and the Ebola virus are single-stranded RNA viruses. Rotaviruses, which cause severe gastroenteritis in children and other immunocompromised individuals, are examples of double-stranded RNA viruses. Because double-stranded RNA is uncommon in eukaryotic cells, its presence serves as an indicator of viral infection. The implications for a virus having an RNA genome instead of a DNA genome are discussed in more detail in Viruses .
Match the correct molecule with its description:
| ___tRNA
___rRNA ___mRNA |
A. is a major component of ribosome
B. is a copy of the information in a gene C. carries an amino acid to the ribosome |
C, A, B
What are the differences between DNA nucleotides and RNA nucleotides?
How is the information stored within the base sequence of DNA used to determine a cell’s properties?
How do complementary base pairs contribute to intramolecular base pairing within an RNA molecule?
If an antisense RNA has the sequence 5ʹAUUCGAAUGC3ʹ, what is the sequence of the mRNA to which it will bind? Be sure to label the 5ʹ and 3ʹ ends of the molecule you draw.
Why does double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) stimulate RNA interference?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?