| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
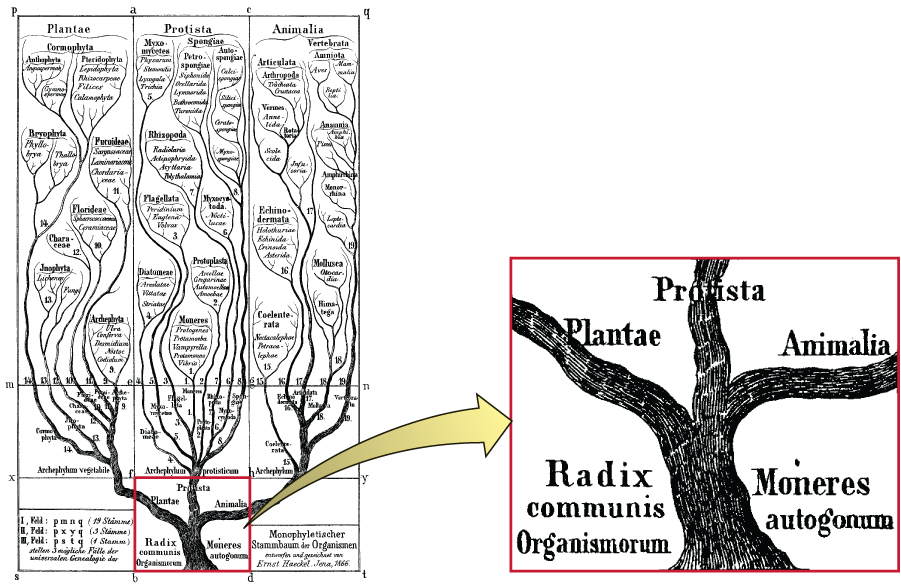
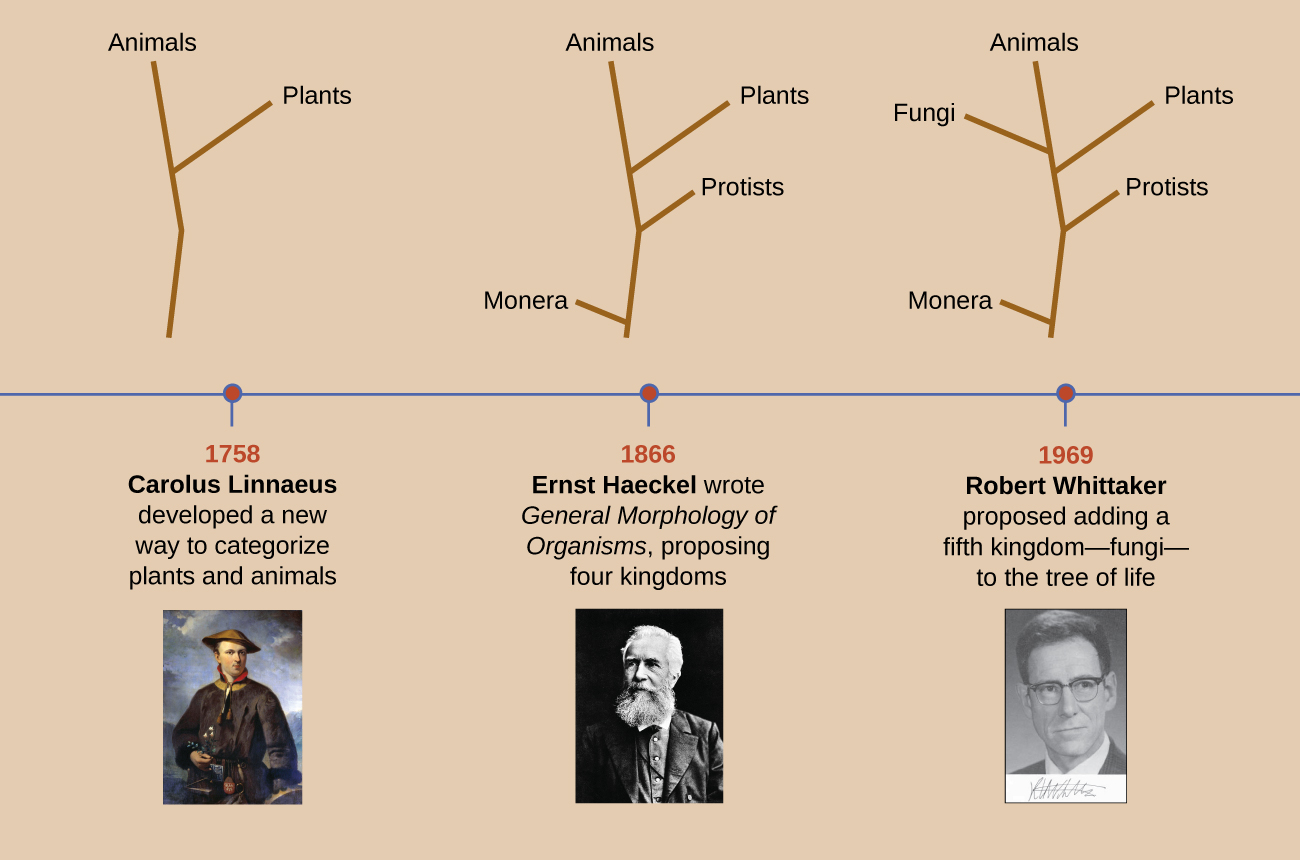
Nearly 100 years later, in 1969, American ecologist Robert Whittaker (1920–1980) proposed adding another kingdom—Fungi—in his tree of life. Whittaker’s tree also contained a level of categorization above the kingdom level—the empire or superkingdom level—to distinguish between organisms that have membrane-bound nuclei in their cells ( eukaryote s ) and those that do not ( prokaryote s ). Empire Prokaryota contained just the Kingdom Monera. The Empire Eukaryota contained the other four kingdoms: Fungi, Protista, Plantae, and Animalia. Whittaker’s five-kingdom tree was considered the standard phylogeny for many years.
[link] shows how the tree of life has changed over time. Note that viruses are not found in any of these trees. That is because they are not made up of cells and thus it is difficult to determine where they would fit into a tree of life.
Antibiotic drugs are specifically designed to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. But after a couple of days on antibiotics, Cora shows no signs of improvement. Also, her CSF cultures came back from the lab negative. Since bacteria or fungi were not isolated from Cora’s CSF sample, her doctor rules out bacterial and fungal meningitis. Viral meningitis is still a possibility.
However, Cora now reports some troubling new symptoms. She is starting to have difficulty walking. Her muscle stiffness has spread from her neck to the rest of her body, and her limbs sometimes jerk involuntarily. In addition, Cora’s cognitive symptoms are worsening. At this point, Cora’s doctor becomes very concerned and orders more tests on the CSF samples.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box. Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
Haeckel’s and Whittaker’s trees presented hypotheses about the phylogeny of different organisms based on readily observable characteristics. But the advent of molecular genetics in the late 20th century revealed other ways to organize phylogenetic trees. Genetic methods allow for a standardized way to compare all living organisms without relying on observable characteristics that can often be subjective. Modern taxonomy relies heavily on comparing the nucleic acids (deoxyribonucleic acid [DNA] or ribonucleic acid [RNA]) or proteins from different organisms. The more similar the nucleic acids and proteins are between two organisms, the more closely related they are considered to be.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?