| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
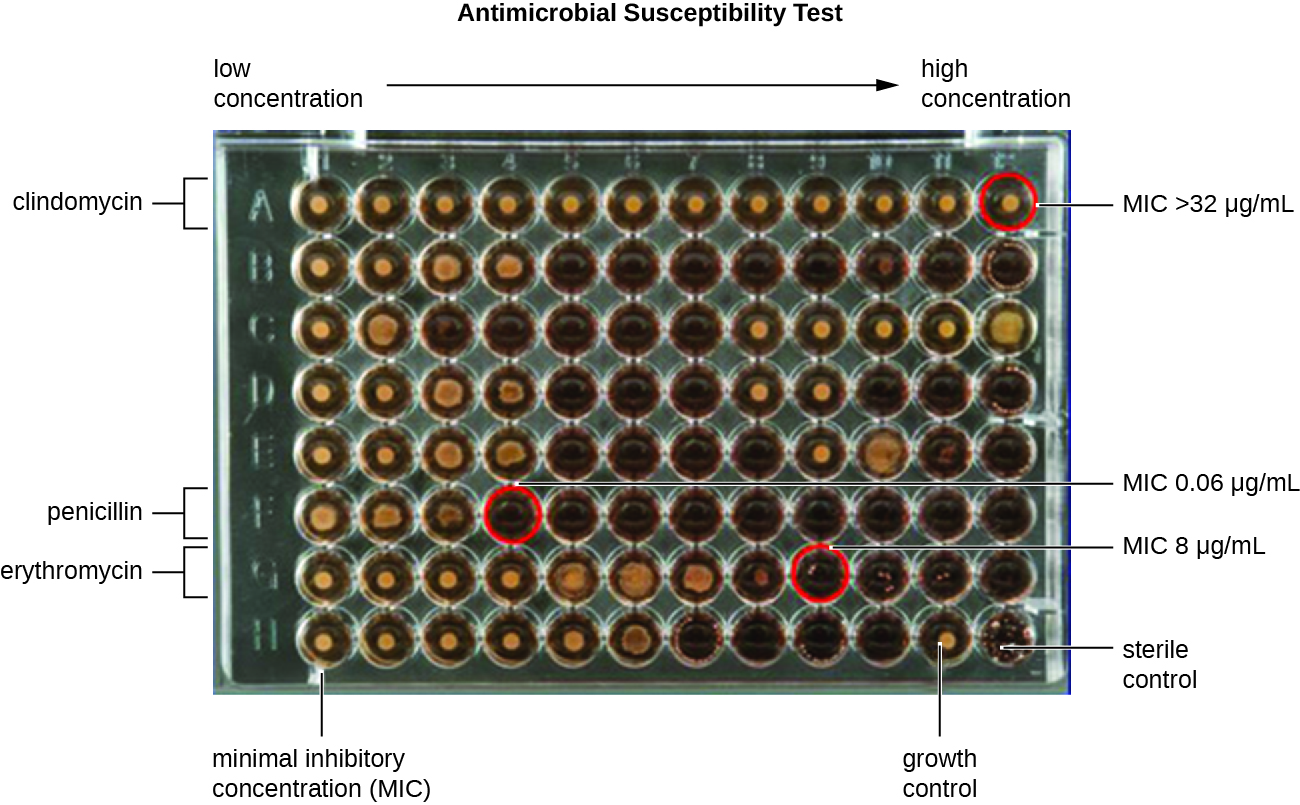


Marisa’s UTI was likely caused by the catheterizations she had in Vietnam. Most bacteria that cause UTIs are members of the normal gut microbiota, but they can cause infections when introduced to the urinary tract, as might have occurred when the catheter was inserted. Alternatively, if the catheter itself was not sterile, bacteria on its surface could have been introduced into Marisa’s body. The antimicrobial therapy Marisa received in Cambodia may also have been a complicating factor because it may have selected for antimicrobial-resistant strains already present in her body. These bacteria would have already contained genes for antimicrobial resistance, either acquired by spontaneous mutation or through horizontal gene transfer, and, therefore, had the best evolutionary advantage for adaptation and growth in the presence of the antimicrobial therapy. As a result, one of these resistant strains may have been subsequently introduced into her urinary tract.
Laboratory testing at the CDC confirmed that the strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Marisa’s urine sample was positive for the presence of NDM, a very active carbapenemase that is beginning to emerge as a new problem in antimicrobial resistance. While NDM-positive strains are resistant to a wide range of antimicrobials, they have shown susceptibility to tigecycline (structurally related to tetracycline ) and the polymyxins B and E ( colistin ).
To prevent her infection from spreading, Marisa was isolated from the other patients in a separate room. All hospital staff interacting with her were advised to follow strict protocols to prevent surface and equipment contamination. This would include especially stringent hand hygiene practices and careful disinfection of all items coming into contact with her.
Marisa’s infection finally responded to tigecycline and eventually cleared. She was discharged a few weeks after admission, and a follow-up stool sample showed her stool to be free of NDM-containing K. pneumoniae , meaning that she was no longer harboring the highly resistant bacterium.
Go back to the previous Clinical Focus box.
The method that can determine the MICs of multiple antimicrobial drugs against a microbial strain using a single agar plate is called the ________.
Etest
If drug A produces a larger zone of inhibition than drug B on the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test, drug A should always be prescribed.
false
How is the information from a Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test used for the recommendation of the clinical use of an antimicrobial drug?
What is the difference between MIC and MBC?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?