| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
M. genitalium is a more common cause of urethritis in most settings than N. gonorrhoeae , although it is less common than C. trachomatis . It is responsible for approximately 30% of recurrent or persistent infections, 20–25% of nonchlamydial NGU cases, and 15%–20% of NGU cases. M. genitalium attaches to epithelial cells and has substantial antigenic variation that helps it evade host immune responses. It has lipid-associated membrane proteins that are involved in causing inflammation.
Several possible virulence factors have been implicated in the pathogenesis of U. urealyticum ( [link] ). These include the ureaplasma proteins phospholipase A , phospholipase C , multiple banded antigen (MBA), urease , and immunoglobulin α protease . The phospholipases are virulence factors that damage the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells. The immunoglobulin α protease is an important defense against antibodies. It can generate hydrogen peroxide, which may adversely affect host cell membranes through the production of reactive oxygen species.
Treatments differ for gonorrheal and nongonococcal urethritis. However, N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis are often simultaneously present, which is an important consideration for treatment. NGU is most commonly treated using tetracyclines (such as doxycycline ) and azithromycin ; erythromycin is an alternative option. Tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones are most commonly used to treat U. urealyticum , but resistance to tetracyclines is becoming an increasing problem. Ken B Waites. “Ureaplasma Infection Medication.” Medscape , 2015. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/231470-medication. While tetracyclines have been the treatment of choice for M. hominis , increasing resistance means that other options must be used. Clindamycin and fluoroquinolones are alternatives. M. genitalium is generally susceptible to doxycycline, azithromycin, and moxifloxacin . Like other mycoplasma, M. genitalium does not have a cell wall and therefore β-lactams (including penicillins and cephalosporins) are not effective treatments.
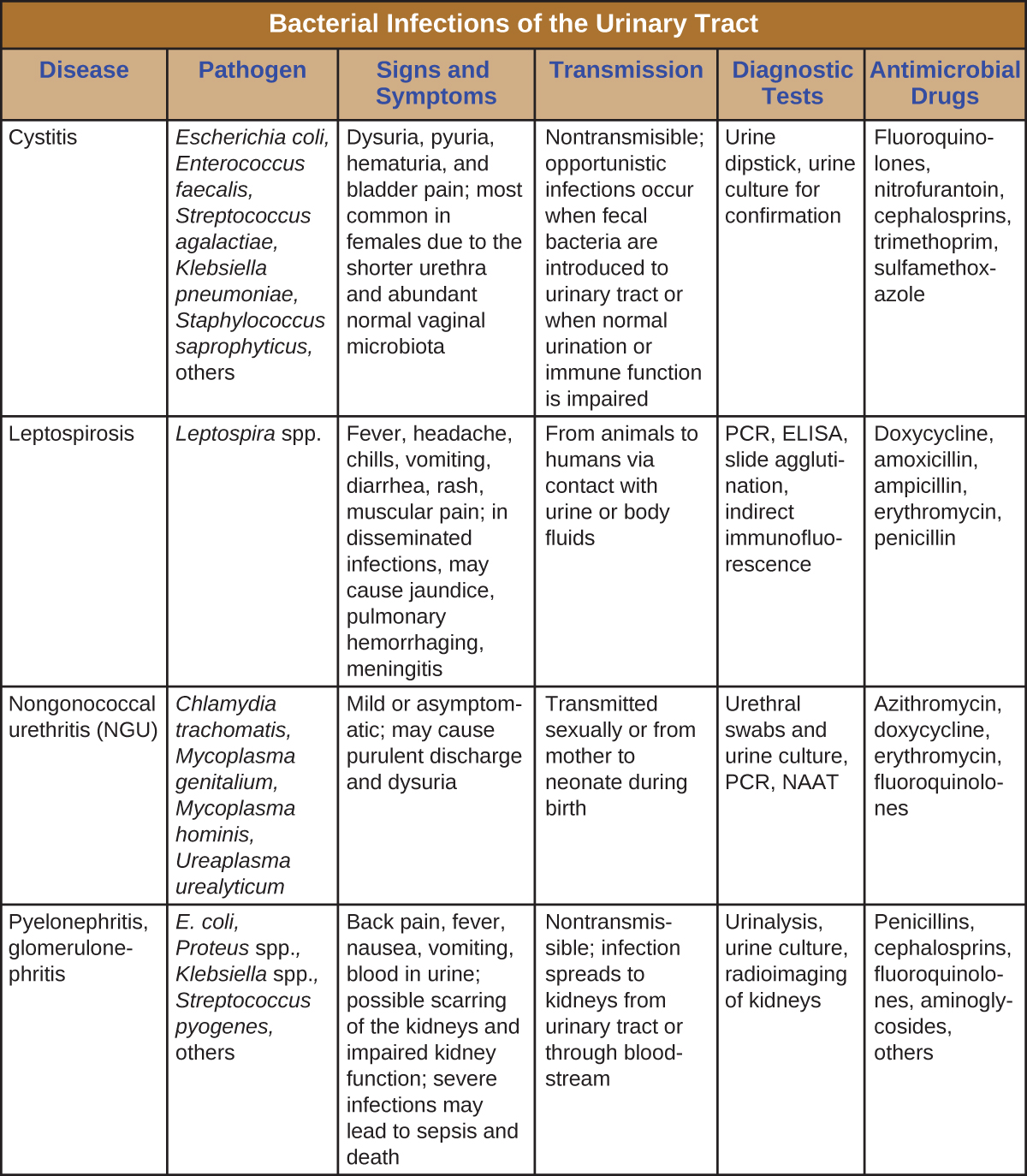
Urinary tract infections can cause inflammation of the urethra (urethritis), bladder (cystitis), and kidneys (pyelonephritis), and can sometimes spread to other body systems through the bloodstream. [link] captures the most important features of various types of UTIs.
Pyelonephritis is a potentially severe infection of the _____.
kidneys
What is pyuria?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?