| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] compares some of the key mechanisms and examples of some of the EIAs discussed in this section as well as immunoblots, which were discussed in Detecting Antigen-Antibody Complexes .
| Immunoblots&Enzyme Immunoassays | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Assay | Mechanism | Specific Procedures | Examples |
| Immunoblots | Uses enzyme-antibody conjugates to identify specific proteins that have been transferred to an absorbent membrane | Western blot: Detects the presence of a particular protein | Detecting the presence of HIV peptides (or peptides from other infectious agents) in patient sera |
| Immunostaining | Uses enzyme-antibody conjugates to stain specific molecules on or in cells | Immunohistochemistry: Used to stain specific cells in a tissue | Stain for presence of CD8 cells in host tissue |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | Uses enzyme-antibody conjugates to quantify target molecules | Direct ELISA: Uses a single antibody to detect the presence of an antigen | Detection of HIV antigen p24 up to one month after being infected |
| Indirect ELISA: Measures the amount of antibody produced against an antigen | Detection of HIV antibodies in serum | ||
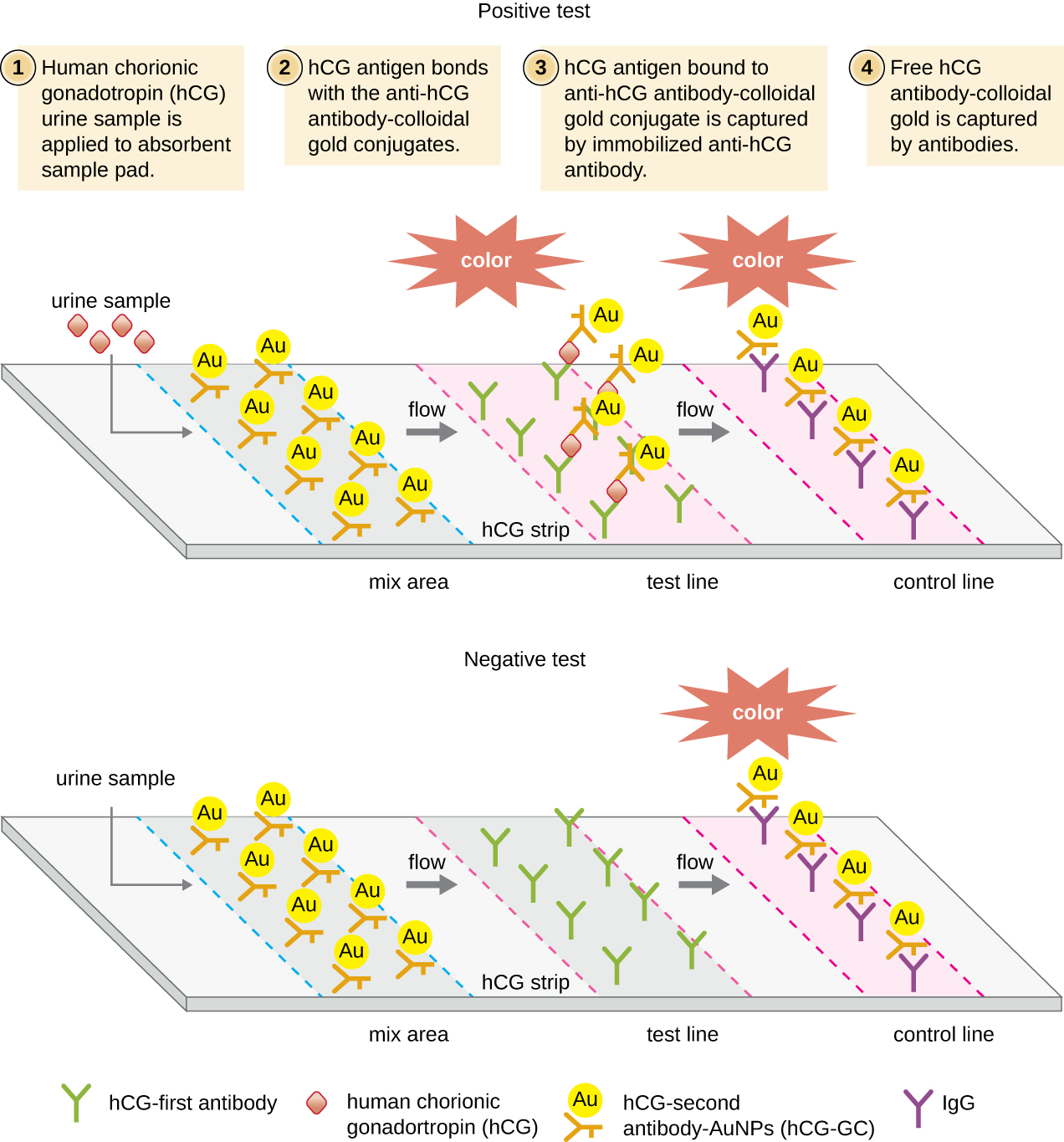
| Immunochromatographic (lateral flow) assays | Techniques use the capture of flowing, color-labeled antigen-antibody complexes by fixed antibody for disease diagnosis | Sandwich ELISA: Measures the amount of antigen bound by the antibody | Detection of antibodies for various pathogens in patient sera (e.g., rapid strep, malaria dipstick) |
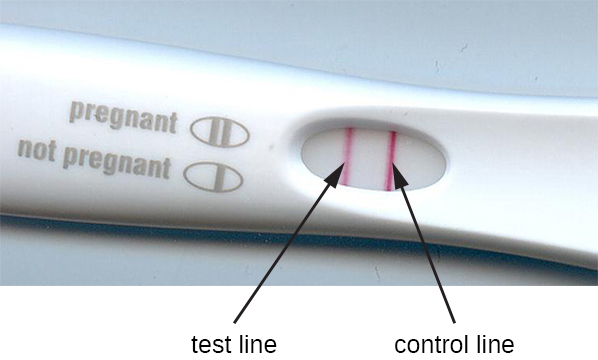
| Pregnancy test detecting human chorionic gonadotrophin in urine |
Although the indirect ELISA for HIV is a sensitive assay, there are several complicating considerations. First, if an infected person is tested too soon after becoming infected, the test can yield false-negative results. The seroconversion window is generally about three weeks, but in some cases, it can be more than two months.
In addition to false negatives, false positives can also occur, usually due to previous infections with other viruses that induce cross-reacting antibodies. The false-positive rate depends on the particular brand of test used, but 0.5% is not unusual. Thomas, Justin G., Victor Jaffe, Judith Shaffer, and Jose Abreu, “HIV Testing: US Recommendations 2014,” Osteopathic Family Physician 6, no. 6 (2014). Because of the possibility of a false positive, all positive tests are followed up with a confirmatory test. This confirmatory test is often an immunoblot (western blot) in which HIV peptides from the patient’s blood are identified using an HIV-specific mAb-enzyme conjugate. A positive western blot would confirm an HIV infection and a negative blot would confirm the absence of HIV despite the positive ELISA.
Unfortunately, western blots for HIV antigens often yield indeterminant results, in which case, they neither confirm nor invalidate the results of the indirect ELISA. In fact, the rate of indeterminants can be 10–49% (which is why, combined with their cost, western blots are not used for screening). Similar to the indirect ELISA, an indeterminant western blot can occur because of cross-reactivity or previous viral infections, vaccinations, or autoimmune diseases.
Jump to the previous Clinical Focus box. Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
To detect antibodies against bacteria in the bloodstream using an EIA, we would run a(n) ________, which we would start by attaching antigen from the bacteria to the wells of a microtiter plate.
indirect ELISA
Why is it important in a sandwich ELISA that the antigen has multiple epitopes? And why might it be advantageous to use polyclonal antisera rather than mAb in this assay?
The pregnancy test strip detects the presence of human chorionic gonadotrophin in urine. This hormone is initially produced by the fetus and later by the placenta. Why is the test strip preferred for this test rather than using either a direct or indirect ELISA with their more quantifiable results?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?