| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
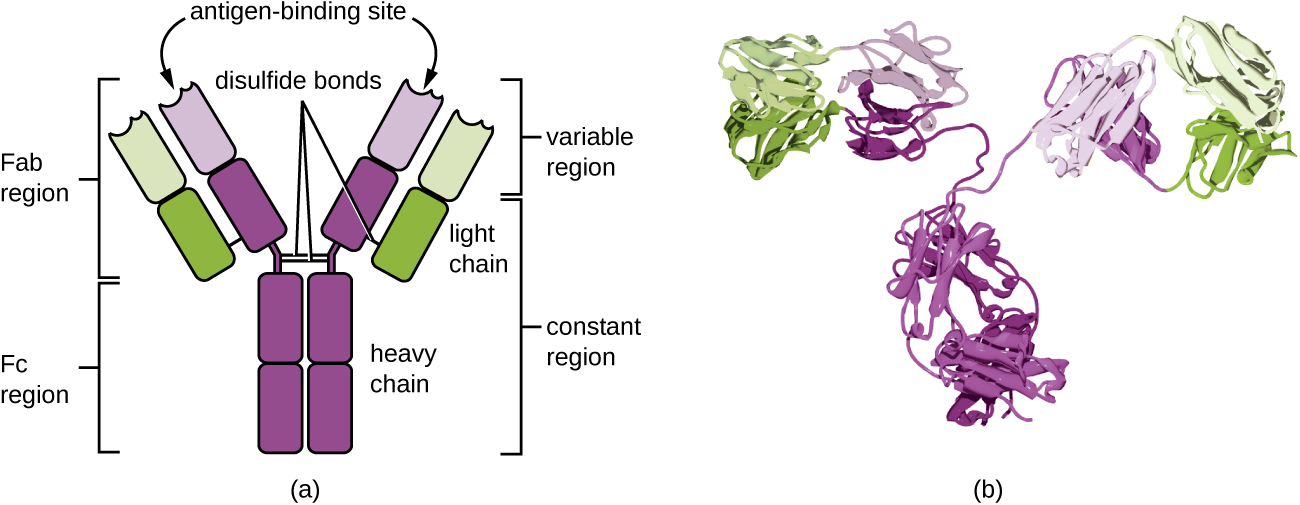
The constant region of an antibody molecule determines its class, or isotype . The five classes of antibodies are IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE. Each class possesses unique heavy chains designated by Greek letters γ, μ, α, δ, and ε, respectively. Antibody classes also exhibit important differences in abundance in serum, arrangement, body sites of action, functional roles, and size ( [link] ).
IgG is a monomer that is by far the most abundant antibody in human blood, accounting for about 80% of total serum antibody. IgG penetrates efficiently into tissue spaces, and is the only antibody class with the ability to cross the placental barrier , providing passive immunity to the developing fetus during pregnancy. IgG is also the most versatile antibody class in terms of its role in the body’s defense against pathogens.
IgM is initially produced in a monomeric membrane-bound form that serves as an antigen-binding receptor on B cells. The secreted form of IgM assembles into a pentamer with five monomers of IgM bound together by a protein structure called the J chain . Although the location of the J chain relative to the Fc regions of the five monomers prevents IgM from performing some of the functions of IgG, the ten available Fab sites associated with a pentameric IgM make it an important antibody in the body’s arsenal of defenses. IgM is the first antibody produced and secreted by B cells during the primary and secondary immune responses, making pathogen-specific IgM a valuable diagnostic marker during active or recent infections.
IgA accounts for about 13% of total serum antibody, and secretory IgA is the most common and abundant antibody class found in the mucus secretions that protect the mucous membranes. IgA can also be found in other secretions such as breast milk , tears , and saliva . Secretory IgA is assembled into a dimeric form with two monomers joined by a protein structure called the secretory component. One of the important functions of secretory IgA is to trap pathogens in mucus so that they can later be eliminated from the body.
Similar to IgM, IgD is a membrane-bound monomer found on the surface of B cells, where it serves as an antigen-binding receptor. However, IgD is not secreted by B cells, and only trace amounts are detected in serum. These trace amounts most likely come from the degradation of old B cells and the release of IgD molecules from their cytoplasmic membranes.
IgE is the least abundant antibody class in serum. Like IgG, it is secreted as a monomer, but its role in adaptive immunity is restricted to anti-parasitic defenses . The Fc region of IgE binds to basophils and mast cells . The Fab region of the bound IgE then interacts with specific antigen epitopes, causing the cells to release potent pro-inflammatory mediators. The inflammatory reaction resulting from the activation of mast cells and basophils aids in the defense against parasites, but this reaction is also central to allergic reactions (see Diseases of the Immune System .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?