| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
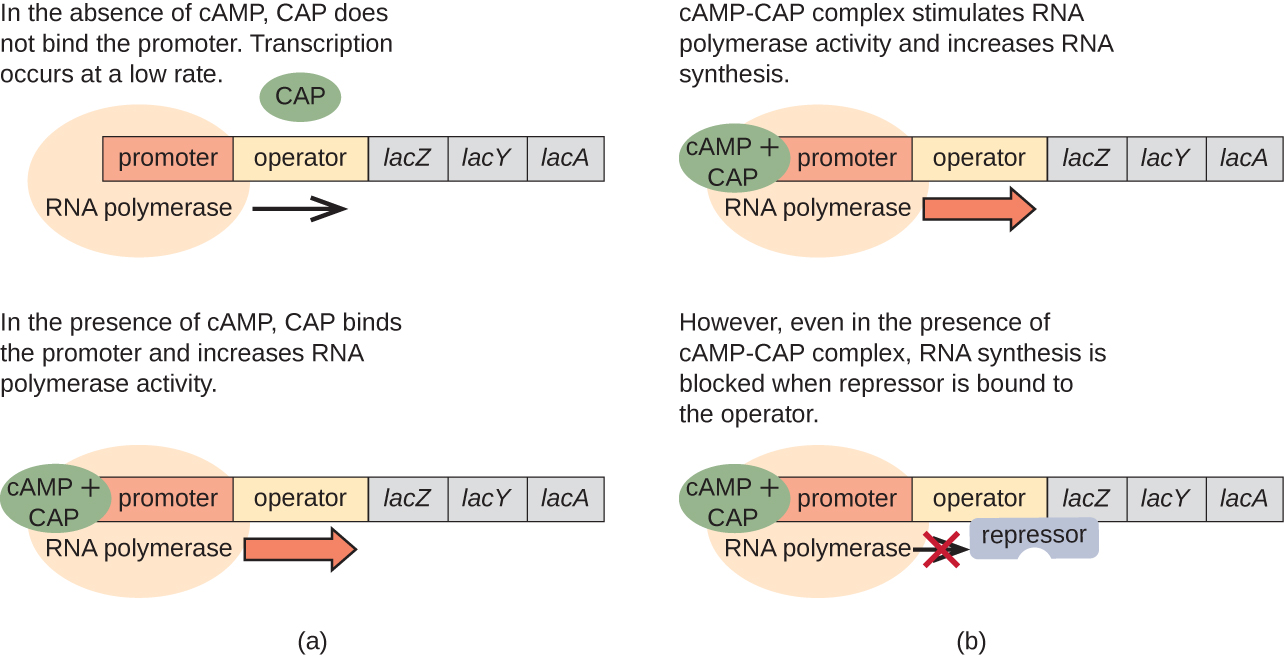
| Conditions Affecting Transcription of the lac Operon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | CAP binds | Lactose | Repressor binds | Transcription |
| + | – | – | + | No |
| + | – | + | – | Some |
| – | + | – | + | No |
| – | + | + | – | Yes |
Watch an animated tutorial about the workings of lac operon here.
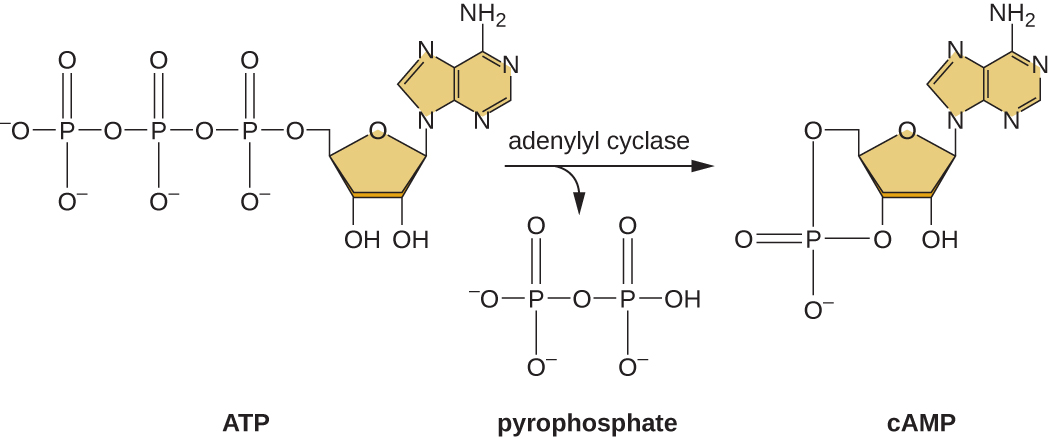
In prokaryotes, there are also several higher levels of gene regulation that have the ability to control the transcription of many related operons simultaneously in response to an environmental signal. A group of operons all controlled simultaneously is called a regulon .
When sensing impending stress, prokaryotes alter the expression of a wide variety of operon s to respond in coordination. They do this through the production of alarmones , which are small intracellular nucleotide derivatives. Alarmones change which genes are expressed and stimulate the expression of specific stress-response genes. The use of alarmones to alter gene expression in response to stress appears to be important in pathogenic bacteria. On encountering host defense mechanisms and other harsh conditions during infection, many operons encoding virulence genes are upregulated in response to alarmone signaling. Knowledge of these responses is key to being able to fully understand the infection process of many pathogens and to the development of therapies to counter this process.
Since the σ subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase confers specificity as to which promoters should be transcribed, altering the σ factor used is another way for bacteria to quickly and globally change what regulons are transcribed at a given time. The σ factor recognizes sequences within a bacterial promoter , so different σ factors will each recognize slightly different promoter sequences. In this way, when the cell senses specific environmental conditions, it may respond by changing which σ factor it expresses, degrading the old one and producing a new one to transcribe the operons encoding genes whose products will be useful under the new environmental condition. For example, in sporulating bacteria of the genera Bacillus and Clostridium (which include many pathogens), a group of σ factors controls the expression of the many genes needed for sporulation in response to sporulation-stimulating signals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?