| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The respiratory tract can be infected by a variety of bacteria, both gram positive and gram negative. Although the diseases that they cause may range from mild to severe, in most cases, the microbes remain localized within the respiratory system. Fortunately, most of these infections also respond well to antibiotic therapy.
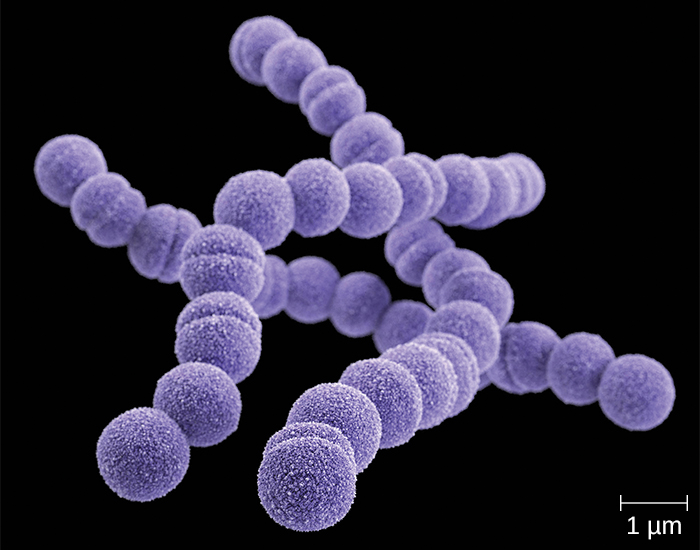
A common upper respiratory infection, streptococcal pharyngitis ( strep throat ) is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes . This gram-positive bacterium appears as chains of cocci, as seen in [link] . Rebecca Lancefield serologically classified streptococci in the 1930s using carbohydrate antigens from the bacterial cell walls. S. pyogenes is the sole member of the Lancefield group A streptococci and is often referred to as GAS, or group A strep.
Similar to streptococcal infections of the skin, the mucosal membranes of the pharynx are damaged by the release of a variety of exoenzymes and exotoxins by this extracellular pathogen. Many strains of S. pyogenes can degrade connective tissues by using hyaluronidase , collagenase and streptokinase . Streptokinase activates plasmin, which leads to degradation of fibrin and, in turn, dissolution of blood clots, which assists in the spread of the pathogen. Released toxins include streptolysin s that can destroy red and white blood cells. The classic signs of streptococcal pharyngitis are a fever higher than 38 °C (100.4 °F); intense pharyngeal pain; erythema associated with pharyngeal inflammation; and swollen, dark-red palatine tonsils, often dotted with patches of pus; and petechiae (microcapillary hemorrhages) on the soft or hard palate (roof of the mouth) ( [link] ). The submandibular lymph nodes beneath the angle of the jaw are also often swollen during strep throat.
Some strains of group A streptococci produce erythrogenic toxin . This exotoxin is encoded by a temperate bacteriophage (bacterial virus) and is an example of phage conversion (see The Viral Life Cycle ). The toxin attacks the plasma membranes of capillary endothelial cells and leads to scarlet fever (or scarlatina), a disseminated fine red rash on the skin, and strawberry tongue , a red rash on the tongue ( [link] ). Severe cases may even lead to streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS) , which results from massive superantigen production that leads to septic shock and death.
S. pyogenes can be easily spread by direct contact or droplet transmission through coughing and sneezing. The disease can be diagnosed quickly using a rapid enzyme immunoassay for the group A antigen. However, due to a significant rate of false-negative results (up to 30% WL Lean et al. “Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: A Meta-Analysis.” Pediatrics 134, no. 4 (2014):771–781. ), culture identification is still the gold standard to confirm pharyngitis due to S. pyogenes . S. pyogenes can be identified as a catalase-negative, beta hemolytic bacterium that is susceptible to 0.04 units of bacitracin. Antibiotic resistance is limited for this bacterium, so most β-lactams remain effective; oral amoxicillin and intramuscular penicillin G are those most commonly prescribed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?