| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Structurally speaking, ribonucleic acid (RNA) , is quite similar to DNA. However, whereas DNA molecules are typically long and double stranded, RNA molecules are much shorter and are typically single stranded. RNA molecules perform a variety of roles in the cell but are mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis ( translation ) and its regulation.
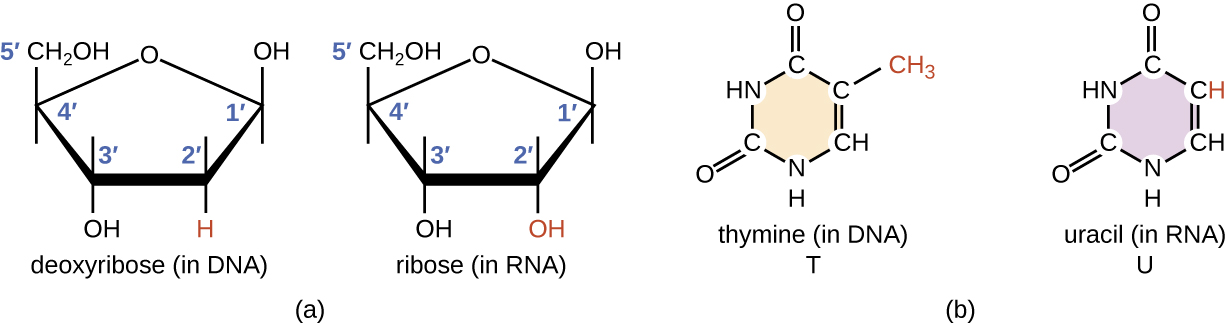
RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds. A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and a phosphate group. The subtle structural difference between the sugars gives DNA added stability, making DNA more suitable for storage of genetic information, whereas the relative instability of RNA makes it more suitable for its more short-term functions. The RNA-specific pyrimidine uracil forms a complementary base pair with adenine and is used instead of the thymine used in DNA. Even though RNA is single stranded, most types of RNA molecules show extensive intramolecular base pairing between complementary sequences within the RNA strand, creating a predictable three-dimensional structure essential for their function ( [link] and [link] ).
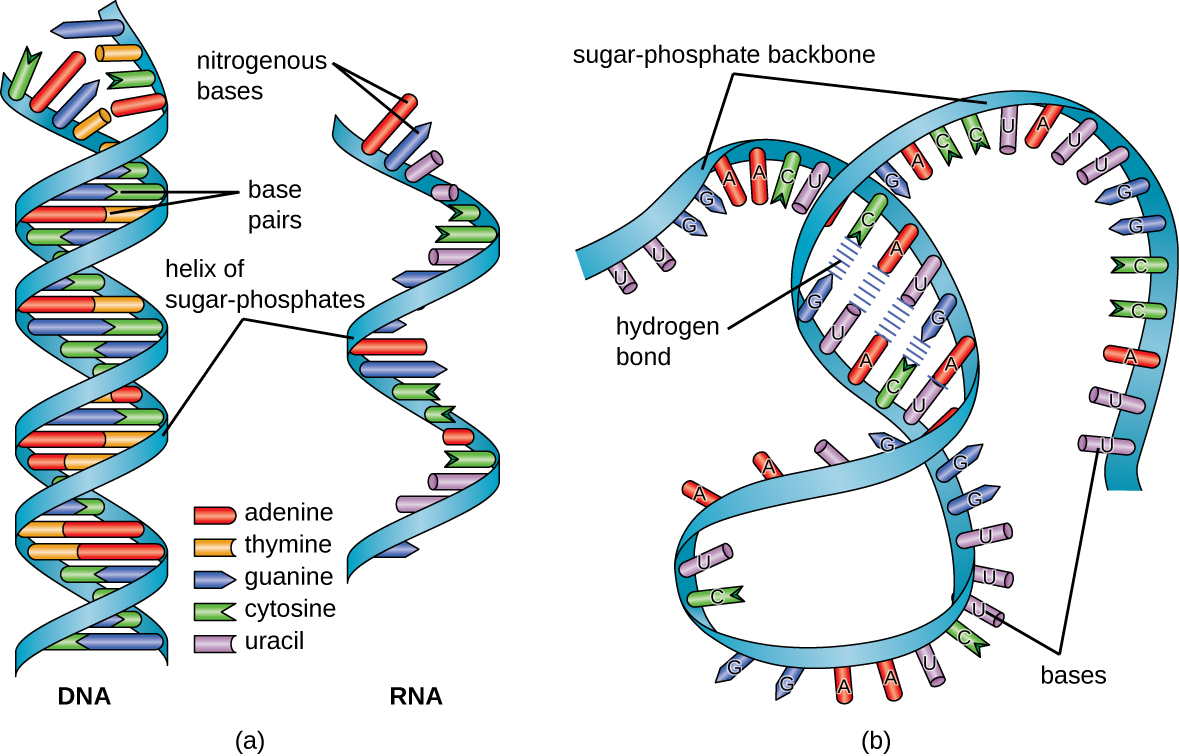
Cells access the information stored in DNA by creating RNA to direct the synthesis of proteins through the process of translation . Proteins within a cell have many functions, including building cellular structures and serving as enzyme catalysts for cellular chemical reactions that give cells their specific characteristics. The three main types of RNA directly involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA) , ribosomal RNA (rRNA) , and transfer RNA (tRNA) .
In 1961, French scientists François Jacob and Jacques Monod hypothesized the existence of an intermediary between DNA and its protein products, which they called messenger RNA. A. Rich. “The Era of RNA Awakening: Structural Biology of RNA in the Early Years.” Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics 42 no. 2 (2009):117–137. Evidence supporting their hypothesis was gathered soon afterwards showing that information from DNA is transmitted to the ribosome for protein synthesis using mRNA. If DNA serves as the complete library of cellular information, mRNA serves as a photocopy of specific information needed at a particular point in time that serves as the instructions to make a protein.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?