| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A variation of diffusion is the process of filtration. In filtration, material moves according to its concentration gradient through a membrane; sometimes the rate of diffusion is enhanced by pressure, causing the substances to filter more rapidly. This occurs in the kidney, where blood pressure forces large amounts of water and accompanying dissolved substances, or solutes , out of the blood and into the renal tubules. The rate of diffusion in this instance is almost totally dependent on pressure. One of the effects of high blood pressure is the appearance of protein in the urine, which is “squeezed through” by the abnormally high pressure.
In facilitated transport , also called facilitated diffusion, materials diffuse across the plasma membrane with the help of membrane proteins. A concentration gradient exists that would allow these materials to diffuse into the cell without expending cellular energy. However, these materials are ions are polar molecules that are repelled by the hydrophobic parts of the cell membrane. Facilitated transport proteins shield these materials from the repulsive force of the membrane, allowing them to diffuse into the cell.
The material being transported is first attached to protein or glycoprotein receptors on the exterior surface of the plasma membrane. This allows the material that is needed by the cell to be removed from the extracellular fluid. The substances are then passed to specific integral proteins that facilitate their passage. Some of these integral proteins are collections of beta pleated sheets that form a pore or channel through the phospholipid bilayer. Others are carrier proteins which bind with the substance and aid its diffusion through the membrane.
The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins , and they function as either channels for the material or carriers. In both cases, they are transmembrane proteins. Channels are specific for the substance that is being transported. Channel proteins have hydrophilic domains exposed to the intracellular and extracellular fluids; they additionally have a hydrophilic channel through their core that provides a hydrated opening through the membrane layers ( [link] ). Passage through the channel allows polar compounds to avoid the nonpolar central layer of the plasma membrane that would otherwise slow or prevent their entry into the cell. Aquaporins are channel proteins that allow water to pass through the membrane at a very high rate.
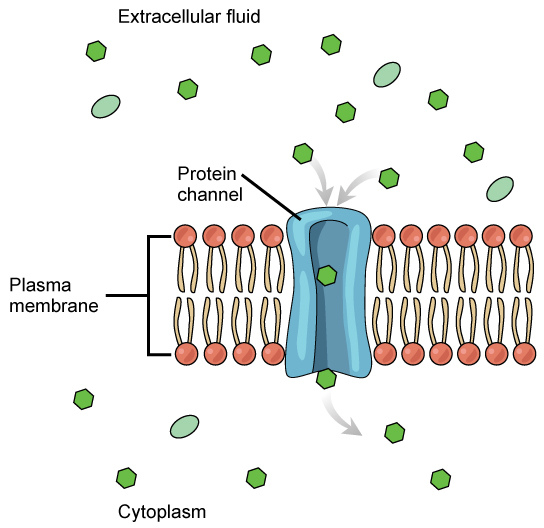
Channel proteins are either open at all times or they are “gated,” which controls the opening of the channel. The attachment of a particular ion to the channel protein may control the opening, or other mechanisms or substances may be involved. In some tissues, sodium and chloride ions pass freely through open channels, whereas in other tissues a gate must be opened to allow passage. An example of this occurs in the kidney, where both forms of channels are found in different parts of the renal tubules. Cells involved in the transmission of electrical impulses, such as nerve and muscle cells, have gated channels for sodium, potassium, and calcium in their membranes. Opening and closing of these channels changes the relative concentrations on opposing sides of the membrane of these ions, resulting in the facilitation of electrical transmission along membranes (in the case of nerve cells) or in muscle contraction (in the case of muscle cells).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ucd bis2a intro to biology v1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?