| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
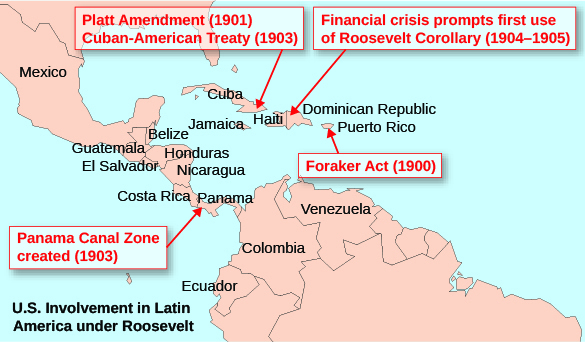
Roosevelt immediately began to put the new corollary to work. He used it to establish protectorates over Cuba and Panama, as well as to direct the United States to manage the Dominican Republic’s custom service revenues. Despite growing resentment from neighboring countries over American intervention in their internal affairs, as well as European concerns from afar, knowledge of Roosevelt’s previous actions in Colombia concerning acquisition of land upon which to build the Panama Canal left many fearful of American reprisals should they resist. Eventually, Presidents Herbert Hoover and Franklin Roosevelt softened American rhetoric regarding U.S. domination of the Western Hemisphere, with the latter proclaiming a new “Good Neighbor Policy” that renounced American intervention in other nations’ affairs. However, subsequent presidents would continue to reference aspects of the Roosevelt Corollary to justify American involvement in Haiti, Nicaragua, and other nations throughout the twentieth century. The map below ( [link] ) shows the widespread effects of Roosevelt’s policies throughout Latin America.
In 1904, Roosevelt put the United States in the role of the “police power” of the Western Hemisphere and set a course for the U.S. relationship with Central and Latin America that played out over the next several decades. He did so with the Roosevelt Corollary, in which he stated:
It is not true that the United States feels any land hunger or entertains any projects as regards the other nations of the Western Hemisphere save as such are for their welfare. All that this country desires is to see the neighboring countries stable, orderly, and prosperous. Any country whose people conduct themselves well can count upon our hearty friendship. . . . Chronic wrongdoing, or an impotence which results in a general loosening of the ties of civilized society, may in America, as elsewhere, require intervention by some civilized nation, and in the Western Hemisphere the adherence of the United States to the Monroe Doctrine may force the United States, however, reluctantly, in flagrant cases of such wrongdoing or impotence, to the exercise of an international police power.”
In the twenty years after he made this statement, the United States would use military force in Latin America over a dozen times. The Roosevelt Corollary was used as a rationale for American involvement in the Dominican Republic, Nicaragua, Haiti, and other Latin American countries, straining relations between Central America and its dominant neighbor to the north throughout the twentieth century.
Although he supported the Open Door notes as an excellent economic policy in China, Roosevelt lamented the fact that the United States had no strong military presence in the region to enforce it. Clearly, without a military presence there, he could not as easily use his “big stick” threat credibly to achieve his foreign policy goals. As a result, when conflicts did arise on the other side of the Pacific, Roosevelt adopted a policy of maintaining a balance of power among the nations there. This was particularly evident when the Russo-Japanese War erupted in 1904.
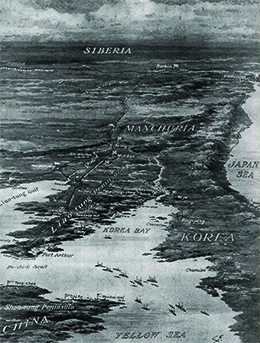
In 1904, angered by the massing of Russian troops along the Manchurian border, and the threat it represented to the region, Japan launched a surprise naval attack upon the Russian fleet. Initially, Roosevelt supported the Japanese position. However, when the Japanese fleet quickly achieved victory after victory, Roosevelt grew concerned over the growth of Japanese influence in the region and the continued threat that it represented to China and American access to those markets ( [link] ). Wishing to maintain the aforementioned balance of power, in 1905, Roosevelt arranged for diplomats from both nations to attend a secret peace conference in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The resultant negotiations secured peace in the region, with Japan gaining control over Korea, several former Russian bases in Manchuria, and the southern half of Sakhalin Island. These negotiations also garnered the Nobel Peace Prize for Roosevelt, the first American to receive the award.
When Japan later exercised its authority over its gains by forcing American business interests out of Manchuria in 1906–1907, Roosevelt felt he needed to invoke his “big stick” foreign policy, even though the distance was great. He did so by sending the U.S. Great White Fleet on maneuvers in the western Pacific Ocean as a show of force from December 1907 through February 1909. Publicly described as a goodwill tour, the message to the Japanese government regarding American interests was equally clear. Subsequent negotiations reinforced the Open Door policy throughout China and the rest of Asia. Roosevelt had, by both the judicious use of the “big stick” and his strategy of maintaining a balance of power, kept U.S. interests in Asia well protected.
Browse the Smithsonian National Portrait Gallery to follow Theodore Roosevelt from Rough Rider to president and beyond.
When Roosevelt succeeded McKinley as president, he implemented a key strategy for building an American empire: the threat, rather than the outright use, of military force. McKinley had engaged the U.S. military in several successful skirmishes and then used the country’s superior industrial power to negotiate beneficial foreign trade agreements. Roosevelt, with his “big stick” policy, was able to keep the United States out of military conflicts by employing the legitimate threat of force. Nonetheless, as negotiations with Japan illustrated, the maintenance of an empire was fraught with complexity. Changing alliances, shifting economic needs, and power politics all meant that the United States would need to tread carefully to maintain its status as a world power.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'U.s. history' conversation and receive update notifications?