| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
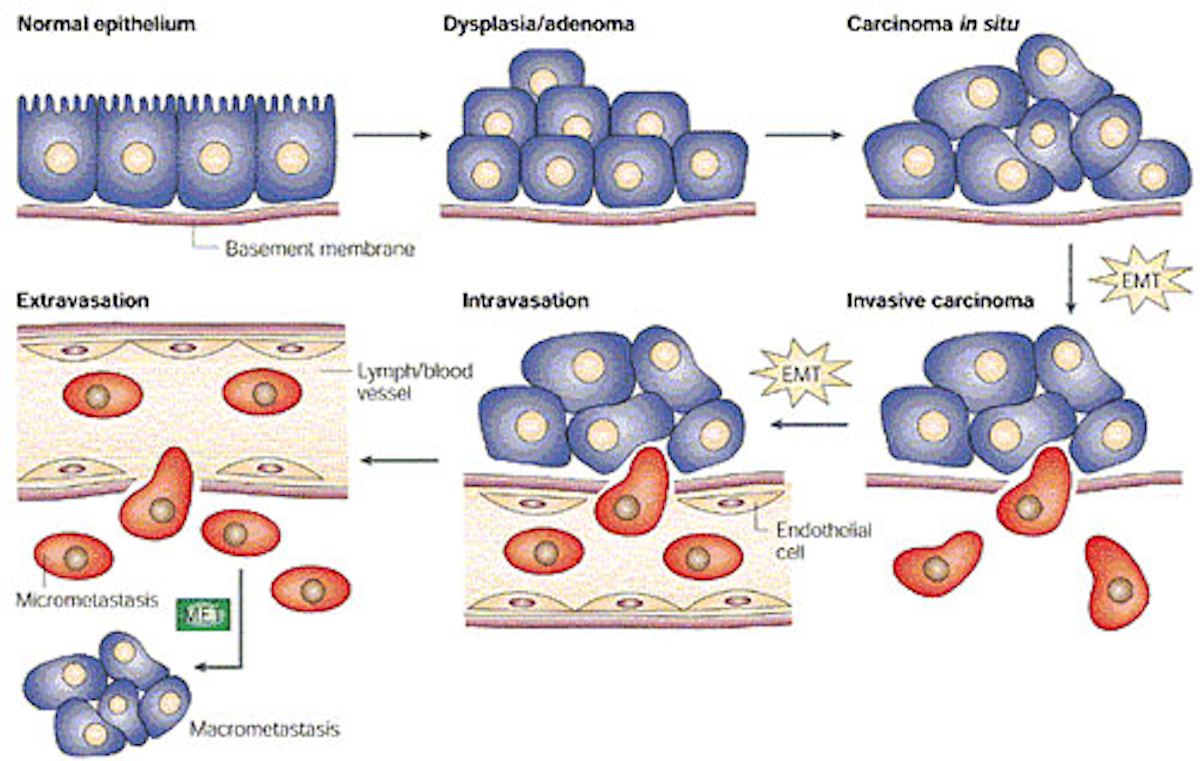
It is known that there are several main causes of cancer and metastasis. Environment and lifestyle habits are among the leadingcauses of cancer in patients. Genetics also plays an important role in the cause of cancer in metastasis. Looking deeper into the genes known to causemetastasis, molecular biologists at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center hope to zero-in on what induces metastasis.
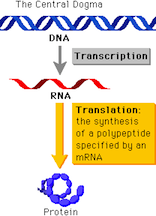
The Central Dogma deals with the transfer of sequences that code genetic information and forms the backbone of molecular biology. TheCentral Dogma is characterized by four main steps: replication, transcription, translation and splicing.
The central dogma of molecular biology begins with transcription, the process in which information in a section of DNA istransferred to a messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA sequence is copied by RNA polymerase to produce a complementary RNA strand. This strand replaces the thymine of DNAwith uracil, a main difference between RNA and DNA. Transcription is usually the first step that leads to the expression of genes. Following transcription istranslation, where the mRNA is translated, following the unique genetic code, into a functional protein. This protein is what regulates genes expression,overall controlling EMT.
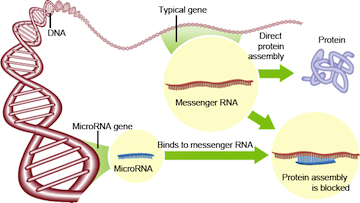
It is believed that microRNA (miRNA) can control EMT ultimately by regulating the proteins that induce or repress the EMT process.These miRNA are short post-transcriptional regulators that bind to target messenger RNA, most commonly resulting in gene-silencing. These miRNA are onaverage 20-24 nucleotides in length, but play an important role in genetic processes. In short, these bind to complementary strands of messengerRNA,preventing the functional protein from being formed, controlling the regulation of EMT.
M.D. Anderson used a database to compile the interactions between different miRNA and mRNA for four particular genes known toinduce EMT. The compiled data gave the specific target mRNA, miRNA, the location of the mRNA-miRNA interactionon the gene, and the interaction energy between the mRNA and miRNA. The interaction energy measures how well an miRNA binds to the mRNA site. For thisstudy, an interaction abs(x) was considered useful information. The constant, x, being a certain cutoff limit. The compiled data can contain multiple mRNA-miRNA interactions. Each gene has a dataset for miRNAs that are up-regulated, implying that the greater amount of miRNA will have more protein inhibition,repressing the gene, and a dataset for down-regulated miRNAs, in which the miRNAs are repressed, implying greater gene expression since the proteininhibition did not occur. We want to determine which miRNA's and mRNA's are significant for further research.
Using the program, R, I sorted each dataset to have each unique miRNA then number of mRNA that interact with each miRNA. From thisnew data, i then sorted the data into unique miRNA and the unique corresponding mRNA. Applying a filter to exclude interaction energies abs(x), the number of unique miRNA- unique mRNA interactions drastically reduced. Our hypothesis that certain miRNA-mRNA interactions appear significant is hard to validate-the datasets themselves lack similar data between them. We also have only one set of data as a whole to compare, and thus cannot have inference to which we cannot prove that some data is statistically significant. Comparing these results to other data from different samples will allow such hypothesis to be confirmed or rejected.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?