| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The place theory of pitch perception suggests that different portions of the basilar membrane are sensitive to sounds of different frequencies. More specifically, the base of the basilar membrane responds best to high frequencies and the tip of the basilar membrane responds best to low frequencies. Therefore, hair cells that are in the base portion would be labeled as high-pitch receptors, while those in the tip of basilar membrane would be labeled as low-pitch receptors (Shamma, 2001).
In reality, both theories explain different aspects of pitch perception. At frequencies up to about 4000 Hz, it is clear that both the rate of action potentials and place contribute to our perception of pitch. However, much higher frequency sounds can only be encoded using place cues (Shamma, 2001).
The ability to locate sound in our environments is an important part of hearing . Localizing sound could be considered similar to the way that we perceive depth in our visual fields. Like the monocular and binocular cues that provided information about depth, the auditory system uses both monaural (one-eared) and binaural (two-eared) cues to localize sound.
Each pinna interacts with incoming sound waves differently, depending on the sound’s source relative to our bodies. This interaction provides a monaural cue that is helpful in locating sounds that occur above or below and in front or behind us. The sound waves received by your two ears from sounds that come from directly above, below, in front, or behind you would be identical; therefore, monaural cues are essential (Grothe, Pecka,&McAlpine, 2010).
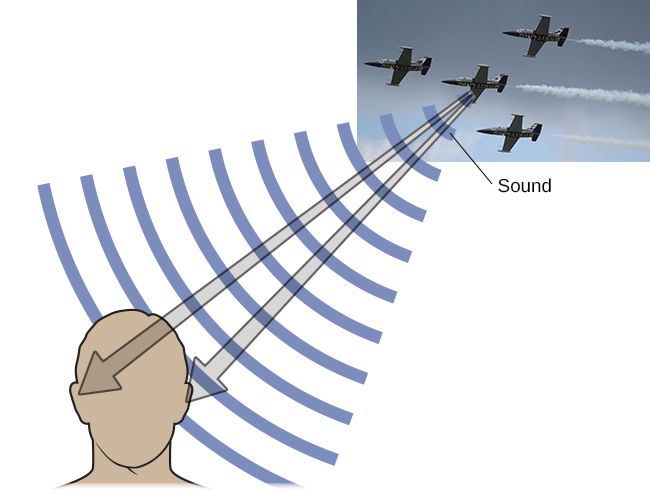
Binaural cues, on the other hand, provide information on the location of a sound along a horizontal axis by relying on differences in patterns of vibration of the eardrum between our two ears. If a sound comes from an off-center location, it creates two types of binaural cues: interaural level differences and interaural timing differences. Interaural level difference refers to the fact that a sound coming from the right side of your body is more intense at your right ear than at your left ear because of the attenuation of the sound wave as it passes through your head. Interaural timing difference refers to the small difference in the time at which a given sound wave arrives at each ear ( [link] ). Certain brain areas monitor these differences to construct where along a horizontal axis a sound originates (Grothe et al., 2010).
Deafness is the partial or complete inability to hear. Some people are born deaf, which is known as congenital deafness . Many others begin to suffer from conductive hearing loss because of age, genetic predisposition, or environmental effects, including exposure to extreme noise (noise-induced hearing loss,certain illnesses (such as measles or mumps), or damage due to toxins (such as those found in certain solvents and metals).
Given the mechanical nature by which the sound wave stimulus is transmitted from the eardrum through the ossicles to the oval window of the cochlea, some degree of hearing loss is inevitable. With conductive hearing loss, hearing problems are associated with a failure in the vibration of the eardrum and/or movement of the ossicles. These problems are often dealt with through devices like hearing aids that amplify incoming sound waves to make vibration of the eardrum and movement of the ossicles more likely to occur.
When the hearing problem is associated with a failure to transmit neural signals from the cochlea to the brain, it is called sensorineural hearing loss . One disease that results in sensorineural hearing loss is Ménière's disease . Although not well understood, Ménière's disease results in a degeneration of inner ear structures that can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus (constant ringing or buzzing), vertigo (a sense of spinning), and an increase in pressure within the inner ear (Semaan&Megerian, 2011). This kind of loss cannot be treated with hearing aids, but some individuals might be candidates for a cochlear implant as a treatment option. Cochlear implants are electronic devices that consist of a microphone, a speech processor, and an electrode array. The device receives incoming sound information and directly stimulates the auditory nerve to transmit information to the brain.
Watch this video describe cochlear implant surgeries and how they work.
Sound waves are funneled into the auditory canal and cause vibrations of the eardrum; these vibrations move the ossicles. As the ossicles move, the stapes presses against the oval window of the cochlea, which causes fluid inside the cochlea to move. As a result, hair cells embedded in the basilar membrane become enlarged, which sends neural impulses to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Pitch perception and sound localization are important aspects of hearing. Our ability to perceive pitch relies on both the firing rate of the hair cells in the basilar membrane as well as their location within the membrane. In terms of sound localization, both monaural and binaural cues are used to locate where sounds originate in our environment.
Individuals can be born deaf, or they can develop deafness as a result of age, genetic predisposition, and/or environmental causes. Hearing loss that results from a failure of the vibration of the eardrum or the resultant movement of the ossicles is called conductive hearing loss. Hearing loss that involves a failure of the transmission of auditory nerve impulses to the brain is called sensorineural hearing loss.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chapter 5: sensation and perception sw' conversation and receive update notifications?